Robotaxi Era Arrives: Can Chinese Firms Seize the Lead?
![]() 06/27 2025
06/27 2025
![]() 670
670
"Self-driving taxis represent one of the most promising applications of AI technology."
Author | Wei Qiang
Editor | Lu Xucheng
On June 22, 2025, Tesla officially launched its Robotaxi service, transforming 10 Model Y vehicles into autonomous taxis for use within a designated area in South Austin, USA. This testing zone spans a small section, taking approximately 30 minutes to drive from one end to the other, with geofencing measures in place.

Currently, the service is exclusively available to invited users, offering a fixed fare of $4.2 per trip and operating from 6 AM to midnight. For safety reasons, a safety officer is stationed in the front passenger seat of each Robotaxi, and the vehicles are equipped with a remote monitoring system. Users can communicate with remote service personnel by pressing the Support button on the rear screen to ask questions.
After experiencing the service, some bloggers and local users found it operates similarly to a conventional taxi service. Users must log into the Robotaxi App within the operating area, confirm their destination, place an order, wait for the car, verify the vehicle number upon arrival, and press "Start" on the APP once aboard to commence the trip. Users can view the real-time route map in the car and enjoy entertainment options such as watching movies, listening to music, or playing games.
Tesla founder Elon Musk tweeted, "This marks the culmination of a decade of hard work by everyone." Musk noted that Tesla's AI chip and software team was built from scratch within the company. The successful launch of Robotaxi signifies its commercial operation, "representing the full realization of Tesla's vision and end-to-end model technology route for autonomous driving."
Previously, Musk had announced that Tesla's self-driving taxis would be introduced in the US in June, with a fleet size exceeding 100,000 vehicles by 2026. In addition to selling smart electric vehicles, self-driving taxis and humanoid robots contribute to Tesla's market valuation exceeding $1 trillion.
However, upon reviewing the Robotaxi's actual test phase, Blue Shark Finance believes it is still in its infancy, with a limited operating range (not expanding beyond Austin until the end of 2025).
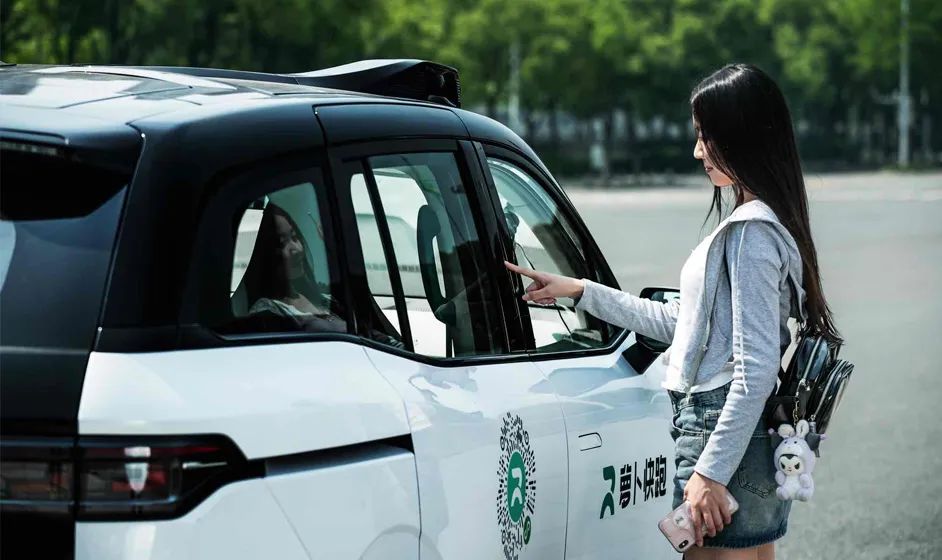
In August 2022, Baidu's Luobo Kuaipao achieved driverless autonomous driving services in Chongqing and Wuhan (with a remote operation team). As of May 2025, Luobo Kuaipao's order volume had surpassed 11 million, covering 15 cities globally, outpacing Google's Waymo's 10 million orders.
Market Turmoil
From the current number of operating cities, scope, total order volume, and even the cost per vehicle (less than $30,000 per vehicle), Luobo Kuaipao undoubtedly stands as the world's leading self-driving taxi company.
Just as Tesla revolutionized the smart electric vehicle sector (launching the Model 3 in 2016 with over 400,000 global orders and establishing the Tesla Shanghai Gigafactory in 2019, igniting the global new energy vehicle market and fostering the rapid evolution of Chinese smart vehicle enterprises), its official launch of self-driving taxis signifies explosive growth in this market (with an estimated fleet size of 100,000 vehicles by 2026, compared to just over 1,000 vehicles for Luobo Kuaipao and others in 2025). Can Chinese self-driving taxi enterprises seize the lead?

1. Both Baidu's Luobo Kuaipao and Google's Waymo adopt a multi-sensor fusion (lidar, millimeter-wave radar, etc.) + high-precision map technology route, leveraging their respective mapping advantages and prioritizing safety. This approach is safer than Tesla's pure vision route but comes at a higher cost (Waymo costs several hundred thousand dollars per vehicle).
Tesla and XPeng Motors opt for a pure vision route for autonomous driving primarily due to cost considerations (lower costs) and their belief that autonomous driving, akin to human driving, can achieve safe operation through vision alone. With the proliferation of large AI model algorithms and a significant reduction in inference costs, their algorithms and computing power have the potential to yield excellent autonomous driving results. China boasts the world's largest smart vehicle industry chain (encompassing batteries, sensors, complete vehicles, etc.), enabling Luobo Kuaipao to further reduce the cost per self-driving taxi, even with more expensive lidar sensors. Here, Baidu holds a distinct advantage.
2. Collaborating for Data Aggregation. Although Tesla's Robotaxi project is in its nascent stages with a small number of orders, its autonomous driving system utilizes FSD (Full Self-Driving), pre-installed in all Tesla models. By 2024, Tesla had sold 8 million electric vehicles, which are constantly on the road, accumulating driving data (standard and real-time) from various countries and regions worldwide. Data is the cornerstone of accelerating large model evolution, giving Tesla a unique competitive edge.
To enhance data for better training of autonomous driving solutions, Waymo, in addition to operating its own fleet in cities like San Francisco and Los Angeles, collaborates with companies like Uber to leverage their platform's massive order volume for testing.
Previously, Baidu Group founder Robin Li revealed that Luobo Kuaipao seeks partnerships with mobile operators, local taxi companies, and third-party fleet operators (to expand its user base and collect more data). Recently, Luobo Kuaipao reached a strategic cooperation with China Auto Rental to launch the world's first self-driving car rental service. This year, Luobo Kuaipao initiated open-road validation tests in Dubai (Middle East), and the testing area in Hong Kong has been further expanded. On June 20, Bloomberg reported that Luobo Kuaipao is accelerating its expansion into the Southeast Asian market. Earlier, media reported that Luobo Kuaipao was also exploring entry into European markets such as Switzerland and Turkey.
Other Chinese autonomous driving technology providers, such as WeRide, announced on June 16 a tripartite agreement with Uber and the Dubai Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) to launch commercial Robotaxi services in Dubai.
3. Who Will Reach Profitability Faster? NVIDIA founder Jen-Hsun Huang views the direction of autonomous driving (taxis) as one of the most important in the next decade, alongside robots. Goldman Sachs predicts that the global Robotaxi market will experience explosive growth in 2025, with a market size anticipated to reach $40 billion to $45.7 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 60%. Since Google began exploring autonomous driving in 2009, Baidu has been an early and significant player in domestic autonomous driving, with Luobo Kuaipao commencing large-scale operations in 2024. In the first quarter of 2025, Luobo Kuaipao provided over 1.4 million travel services globally, a year-on-year increase of 75%. Based on Luobo Kuaipao's cost advantage per vehicle, technological maturity, and operating scale, Robin Li stated that a "clear path to profitability" has been identified. In contrast, Waymo, with a parent company (Google) valued at over $2 trillion, has a cost per vehicle of several hundred thousand dollars and remains far from profitability (able to absorb losses).
Tesla's Robotaxi operation is too small and still in the testing phase, so profitability discussions are premature. Autonomous driving technology providers such as WeRide, TuSimple, and Pony.ai earn revenue through 2B services but incurred heavy losses as of 2024.
Unmanned Frenzy
From Tesla to Luobo Kuaipao, they all paint a promising picture for the future of self-driving taxis – cars will cease to be a depreciating asset (cost). Owners of self-driving taxis can have them pick them up on their way to or from work, allowing them to focus on other tasks, watch movies, listen to music, etc., without having to control the car or worry about traffic jams. When not in use for personal transportation, the self-driving taxis can take to the streets to pick up passengers and generate income for their owners.
However, from Tesla to Luobo Kuaipao to Waymo, the most pressing need currently is to continuously secure licenses (permits) for testing and operating self-driving taxis in various countries and cities.
Although Luobo Kuaipao's data over the past two years indicates that under China's complex road conditions, the actual accident rate of Luobo Kuaipao vehicles is only 1/14 that of human drivers, no national or local government dares to fully liberalize this emerging field of autonomous (driverless) driving.
The Chinese government is acutely aware that China possesses leading AI large models (DS), a comprehensive and large-scale new energy vehicle upstream and downstream chain, high intelligence levels in new energy vehicles, relatively standardized data (traffic rules and people), and easy data collection (simply by driving). These factors provide China with both internal and external conditions to take the lead globally in autonomous driving, one of the most important application scenarios for AI.
On April 1, 2025, China's first local regulation on autonomous driving, the "Regulations on Autonomous Driving Vehicles in Beijing," officially took effect – allowing L3-level vehicles to be piloted on main roads within the Fifth Ring Road, airport highways, and other scenarios. For the first time, the responsibility entity was clearly transferred to the automaker – if the system fails to issue timely warnings or malfunctions in autonomous driving mode, the automaker shall bear compensation liability, and the driver is only responsible if they fail to respond to the takeover request.

Earlier, on March 1, Wuhan implemented the "Wuhan Regulations on Promoting the Development of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles," allowing L3-level vehicles to be piloted in areas such as the Yangtze River Axis Smart Corridor.
China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology plans to release certification standards for L3-level autonomous driving vehicles in 2025, encompassing hardware configurations like lidar, high-precision maps, and computing power (exceeding 1000 TOPS), as well as testing processes such as extreme weather simulation validation.
The rollout of policies from Wuhan to Beijing to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology clearly benefits self-driving taxi enterprises like Luobo Kuaipao.
In May 2024, Luobo Kuaipao released Apollo ADFM, the world's first large model supporting L4-level autonomous driving. It ensures vehicle stability and reliability through a 10-level safety redundancy scheme and a 6-level MRC safety strategy, making it 10 times safer than human driving. Luobo Kuaipao has previously implemented self-driving taxis in ultra-first-tier cities with complex traffic environments such as Beijing, Shenzhen, and Wuhan, adeptly handling diverse participants like pedestrians, cars, and bicycles, as well as environments like bus lanes, narrow and complex road sections, construction sites, and narrow roads at night. This enables rapid coverage of complex urban-level scenarios. This domestic experience allows Luobo Kuaipao to gain trust and swiftly implement its services in overseas markets such as Dubai and Hong Kong.
However, Luobo Kuaipao is not the only player targeting the autonomous driving (self-driving taxi) market. There are also autonomous driving technology providers such as WeRide and Pony.ai, as well as mobile travel giants like Didi Chuxing and automotive giants like BYD and Geely (which owns Caocao Mobility). If Luobo Kuaipao aims to maintain its leading position, it must continue to invest heavily in technological research and development, secure more testing licenses (permits) from governments in more countries and regions, and collaborate with more partners, including local taxi companies, T3 Mobility, and other travel platforms, ride-hailing companies providing operational support to Didi, Gaode, and others, as well as travel platforms like Ctrip and Qunar. This requires robust ground promotion and operational execution capabilities.