Lou Tiancheng: Commercialization Prospects of Robotaxi Hinge on Large-scale Deployment, with Waymo, Pony.ai, and Baidu Leading the "L4 Table"
![]() 06/30 2025
06/30 2025
![]() 634
634
Author | Duoke
Source | Beiduo Finance

The operational deployment of Robotaxi is accelerating.
Beiduo Finance has learned that on June 22, local time, Tesla officially launched its Robotaxi service in Austin, Texas, with around 10 Model Y vehicles serving as the first batch of driverless taxis. However, the service is currently limited to an electronic fence in south-central Austin, and each vehicle is equipped with a safety officer in the passenger seat.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk congratulated the launch on social media, emphasizing that the Robotaxi represents a decade of hard work by Tesla's AI chip and software teams. He hopes to expand the service to more cities by the end of the year and have millions of Tesla vehicles autonomously accepting rides by 2026.
Nevertheless, industry voices remain divided on the future prospects of Tesla's Robotaxi. Lou Tiancheng, co-founder and CTO of Pony.ai, recently told Tencent Auto that globally, only Waymo, Baidu, and Pony.ai occupy the "L4 table," with Tesla and WeRide not among them.
Lou Tiancheng's assertion has sparked controversy but also highlights the core issues for the commercialization and deployment of L4 autonomous driving globally: achieving true "driverlessness" and "large-scale deployment" under the principle of "gradual testing and deployment".
Clearly, Robotaxi development is far from its final stage, and innovative practices by major players will drive the overall commercialization process, supporting the global autonomous driving technology to advance in a safer, smarter, and more inclusive direction and fostering steady improvement in the industry system.
I. Driverless Operation and Large-scale Deployment Define the "L4 Table"
With recent technological advancements, differentiation within the intelligent driving field has become increasingly evident. L2, specializing in assisted driving, is the mainstream configuration in the current market, entering a stage of rapid popularization. According to a Canalys report, it is estimated that the penetration rate of L2 and above functions in the Chinese market will reach 62% by 2025, marking a significant increase.
In contrast, L4 autonomous driving technology, exemplified by Robotaxi, due to its high technical threshold and long return period, is still in the stage of rushing towards large-scale commercialization. Some companies have even downgraded from L4 to L2. Lou Tiancheng and Pony.ai, under his leadership, have consistently adhered to the L4 technology path.
Lou Tiancheng, known as the "First Chinese Programmer," was once a doctoral student at the Tsinghua Theoretical Computer Science Center under Turing Award winner Andrew Yao. After graduation, he joined Google X to develop self-driving cars (now Waymo) and later served as the chair of Baidu's Autonomous Driving Business Unit's technical committee, becoming the youngest T10-level engineer.
In late 2016, Lou Tiancheng co-founded Pony.ai with Peng Jun, the chief architect of Baidu's self-driving car project, as co-founder and CTO. Pony.ai focuses on L4 autonomous driving and is committed to the full deployment of autonomous driving technology that can independently complete driving tasks in a limited area without human intervention.
Lou Tiancheng's over ten years of experience in the L4 field has endowed him with substantial industry expertise and discourse power. In his view, L4 autonomous driving has two key thresholds: driverlessness and large-scale deployment. Driverlessness implies no driver in the vehicle; large-scale deployment means users can hail a car anytime by opening an app within a relatively large area, rather than a single ride experience. "It's not about arranging a ride for you; it's about being able to hail a ride hundreds, thousands, or tens of thousands of times."
Based on these two core criteria, Lou Tiancheng believes that currently, only Waymo, Pony.ai, and Baidu globally meet the requirements to "sit at the L4 table," while other companies, including Tesla and domestic L4 enterprise WeRide, have not reached the state of these three companies two and a half years ago.
"There's a vast difference between taking a ride once and being able to hail a ride consistently, which may require six or seven years of effort," Lou Tiancheng revealed the true state of industry development in the interview.
Taking WeRide, which Lou Tiancheng believes does not "sit at the table," as an example, the company adopts a global and full-matrix strategy of "full-scenario coverage" and currently operates over 1,200 autonomous vehicles worldwide. However, according to Guohai Securities analysis, the number of Robotaxis among its autonomous vehicles is about 500, indicating limited large-scale deployment.
According to WeRide's financial report, the company's operating revenue has declined for two consecutive years, with a 10.1% drop in 2024, and its net loss for the same period expanded to 2.517 billion yuan. As of June 27's close, WeRide's total market value was less than $2.3 billion, down nearly 80% from its peak market value of $11.1 billion.
Today, the autonomous driving industry has entered the next phase of competition. As of May 2025, Waymo's fleet size exceeded 1,500 vehicles, completing over 250,000 paid rides per week; Pony.ai also expects to start mass production of Robotaxis in the second quarter of 2025 and plans to expand its fleet size to 1,000 by the end of the year.
Lou Tiancheng noted that the process of driverless Robotaxi places high demands on technology. Before L4 enterprises can deliver full results, they will go through a "vacuum period" of significant internal progress but apparent stagnation to the outside world, leading to misconceptions about technological bottlenecks. This is also why there are not many players at the "L4 table" currently.
Regarding the industry's future, Lou Tiancheng added that the "L4 table" pattern is not static. The current high-level intelligent driving industry is essentially verifying AI driving ability, but what truly generates value is the existence of vehicles that do not require human driving and have their interior space optimized for the riding experience.
Therefore, changing vehicle forms is the first step and the lowest threshold for the industry to enter the final stage of high-level intelligent driving. High-level intelligent driving bets on the future transformation of travel and vehicle forms, and the technical strength and operational experience in the L4 field are the core driving forces for realizing this transformation.
II. Technology and Cost Reduction Drive the Commercialization Process
From a macro perspective, the broad market prospects of Robotaxi are a consensus in the industry. Goldman Sachs' research report indicates that the Chinese Robotaxi market will grow from $54 million in 2025 to $47 billion in 2035; by 2035, the Robotaxi fleet size is expected to reach 1.9 million vehicles, accounting for 25% of shared mobility vehicles.
With increasing consumer acceptance in first-tier cities, tightening supply of human drivers, and support from governments and the insurance industry, Goldman Sachs expects that by 2030, 500,000 Robotaxis will operate in over 10 Chinese cities. This field will shift from discussing technical feasibility to achieving commercialization.
Lou Tiancheng reminded that as early as two to two and a half years ago, many L4 players were already capable of achieving "driverlessness." This means the autonomous driving field has already solved the technical threshold issue and is now exploring the "hard technology + strong scenarios" development paradigm for driverless vehicles from a high-dimensional perspective of technological maturity.
Taking Pony.ai as an example, its seventh-generation driverless Robotaxi, the Toyota BZ4X, was recently unveiled at the Hong Kong Auto Show, showcasing the latest autonomous driving software and hardware systems and technological highlights. Similarly, the GAC Aion Tyrannosaurus autonomous vehicle equipped with Pony.ai's seventh-generation autonomous driving system has obtained a license for road testing of intelligent and connected vehicles and has started public road testing in Guangzhou and Shenzhen.
Meanwhile, news about Robotaxi mass production continues to emerge. Baidu's Robotaxi service, Luobo Kuaipao, plans to deploy over 1,000 fully driverless vehicles in downtown Dubai; Waymo, under Google, has also announced a partnership with Magna to build an autonomous driving factory and expand its Robotaxi service, with the industry steadily moving towards the "mass production era".
The core of large-scale Robotaxi deployment lies in cost optimization. Goldman Sachs' research report points out that the current hardware cost of a single Robotaxi is approximately $40,000 (including lidar, domain controllers, etc.). As commercialization dawns, Robotaxi's "self-financing" ability has become an important indicator for measuring enterprises' core competitiveness.
Therefore, various enterprises have initiated commercial engines for cost reduction and efficiency enhancement. Pony.ai's seventh-generation autonomous driving system reduces hardware costs by 70% compared to the previous generation through 100% automotive-grade component design, with an 80% reduction in the cost of the on-board computing unit and a 68% reduction in lidar costs.
Looking at the performance end, Pony.ai's revenue in 2024 increased by 4.3% year-on-year to 548 million yuan ($75.025 million), achieving revenue growth for three consecutive years; Robotaxi business revenue increased by 200% year-on-year, with registered users growing by over 20% month-on-month, showing the beginnings of a scale effect.

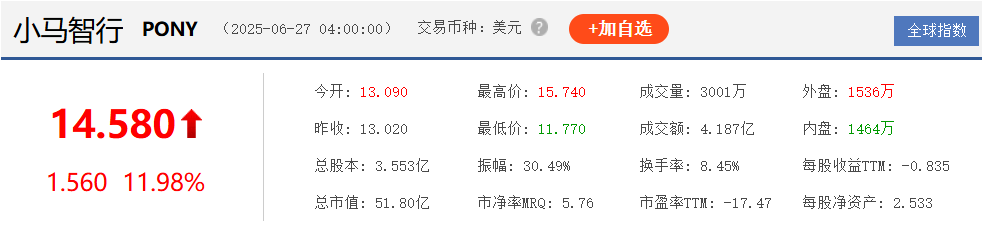
As of June 27's close, Pony.ai was trading at $14.58 per share, with a market value of over $5.18 billion. The company was also recently included in the Nasdaq China Golden Dragon Index, becoming the first and only L4 autonomous driving company to be included, alongside popular Chinese ADRs such as Alibaba, JD.com, and NetEase.
Baidu has also revealed that the sixth-generation model of Luobo Kuaipao reduces the overall vehicle cost by 60% and operating costs by 30% compared to the previous generation, with an 80% reduction in service costs; it is expected to achieve a break-even point in Wuhan by the end of 2024 and enter a period of full profitability in 2025.
Cost reduction and mass production capabilities will undoubtedly be directly related to the profitability inflection point of Robotaxis. How leading enterprises seize the opportunity in the "mass production era" and establish a benchmark for achieving a dynamic balance between operating costs and revenue within the industry is worth looking forward to.
III. Conclusion
Robotaxi is at a critical juncture in industry development and will experience a three-stage transition of "cost optimization - regional penetration - ecological integration" in the next decade, with the industry's final outcome still unknown.
However, according to Lou Tiancheng's theory, Waymo, Pony.ai, and Luobo Kuaipao are significantly ahead in terms of technological maturity and the scale of commercial deployment, while Tesla and WeRide remain in the "challenger" tier.
Nevertheless, compared to internal competition in technology and scale, the starting point and endpoint of Robotaxi enterprises always lie in exploring the practical deployment and safe application of autonomous driving technology, thereby promoting fundamental changes in the urban travel ecosystem and jointly realizing commercial and social value creation.