Who Can Become the 'Ultimate Streamer' of Humanoid Robots?
![]() 02/07 2025
02/07 2025
![]() 607
607

On December 2, during this year's Spring Festival Gala, Unitree Robotics' robot yangko dance captivated audiences, solidifying its status as a viral sensation and reigniting public interest in humanoid robots.
It's undeniable that the field of robotics is becoming increasingly competitive.
In March 2023, Samsung invested over 300 million yuan in Rainbow Robotics, a local robot manufacturer whose HUBO robot represents South Korea's first bipedal walking robot.
From Boston Dynamics and Honda to Tesla, OpenAI, and Microsoft, the advent of the generative AI era has sparked a fresh wave of competition in robotics.
Humanoid robots are not a new concept. In 1973, Kazuo Kato from Waseda University in Japan led his team in developing the world's first full-sized humanoid robot, WABOT-1. However, half a century later, commercialization remains elusive, primarily hindered by performance and cost challenges.
Robots consist of three core technical modules: motion, sensors, and artificial intelligence. For traditional robots, often just one of these technologies is sufficient for practical use. For instance, industrial robots prioritize motion control, while cleaning robots emphasize navigation sensors.
Humanoid robots differ significantly. They must be versatile across various scenarios rather than limited to a single task. This complexity demands higher technological integration, larger datasets, and advanced language and instruction understanding. However, until recently, AI data and models developed in isolation, leading to slow iteration speeds and high, unyielding costs.
The rise of large models has drastically altered this landscape.
From Transformer in 2017 to GPT-1, BERT, GPT-2, GPT-3, and GPT-4, model parameters have soared from billions to trillions in just a few years. Large models are now evolving from single-modal (text, speech, vision) to multi-modal fusion, paving the way for seamless integration of voice, vision, decision-making, control, and other technologies into humanoid robots, significantly enhancing their capabilities.
In April 2023, AI company Levatas collaborated with Boston Dynamics to integrate ChatGPT and Google's speech synthesis technology into the Spot robot dog, enabling human interaction.
Rapid advancements in underlying technologies have illuminated the path to large-scale humanoid robot commercialization, with major tech companies worldwide actively preparing for this shift. Nevertheless, humanoid robots still face a long journey before becoming a household staple.
Firstly, current humanoid robots offer limited capabilities and lack substitution benefits.
For example, household service robots cannot fully replace human services, and commercial guidance and reception robots can only answer basic questions, failing to address all customer inquiries.
As a result, humanoid robots lacking robust substitution value remain unappealing to consumers.
The product positioning of industry players underscores a focus on B-end scenarios. For instance, Tesla Bot's initial mass-produced robots will likely be deployed in super factories, while UBTECH collaborates with enterprises to explore humanoid robot applications in new energy vehicles and 3C electronics.
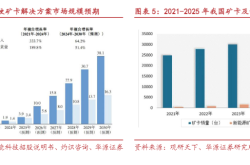
Secondly, fundamental technological shortcomings persist. For instance, robot batteries need to support up to 20 hours of continuous operation, but most humanoid robots currently run for less than 2 hours. Additionally, costs easily exceed tens of thousands of dollars, making large-scale adoption unfeasible. Future annual manufacturing cost reductions of 15%-20% are imperative.
In the short term, humanoid robots may not present a lucrative business opportunity, but over the next 30 years, they will undoubtedly become an irresistible industry. Fundamentally, humanoid robots' value lies in replacing high-cost labor, a certainty in the making.
Current technical and cost challenges will diminish over time.
Cost reduction is inevitable with continuous commercialization, as seen with computers, smartphones, and electric vehicles. Initially, Honda's ASIMO and Boston Dynamics' Atlas cost up to $3 million and $1.9 million, respectively. Now, Tesla aims for a $20,000 cost, with further reductions anticipated.
Technology will also continue to iterate and improve. Due to immature lithium-ion battery technology, Boston Dynamics' first-generation Atlas was cable-powered in 2013 but switched to an independent battery in the 2016 second-generation model.
Musk predicts a long-term human demand for 10 billion humanoid robots. Even if just one-tenth of this demand is met, the industrial potential will be staggering.
With the world's largest population and manufacturing industry, China is already the largest robot consumer market, with robust B-end and C-end demand. Moreover, China's robot software and hardware technologies are catching up, positioning the country well to nurture globally competitive robot companies.
Currently, domestic leaders in humanoid robots include UBTECH (founded in 2012) and CloudMinds (founded in 2015). However, given their early starts and modest market shares, future standouts are likely to be major companies like Xiaomi and ByteDance, which boast advantages in talent, capital, market reach, and brand strength.
The upstream sector offers stronger visibility and profitability. Analyzing robot material costs, reducers, servos, and controllers account for 35%, 20%, and 15% of industrial robot costs, respectively, totaling 70%. Given humanoid robots' increased joints and degrees of freedom, these component proportions may be even higher.
The reducer market includes players like Han's Motor, Leadshine Technology, Tongchuan Technology, Zhongdalide, and Guomao, all with production capacity. However, Green Harmonic Drive stands out, having established a virtuous cycle of "R&D - production expansion - profitability - further R&D and production expansion." By 2022, Green Harmonic Drive's annual production capacity reached 400,000 units, potentially rising to 590,000 in 2023. In comparison, Tongchuan Technology, Han's Motor, and Guomao produced only 100,000, 60,000, and 30,000 units annually in 2021. As a manufacturer, Green Harmonic Drive's net profit margin exceeding 30% is impressive.
The servo motor market shows clear differentiation. High-end production is dominated by foreign companies like Mitsubishi, Yaskawa, Fanuc, and Siemens. Domestic players like Inovenc Technology, Jiangte Electric, Jiangsu Leili, Leadshine Technology, and Haozhi Electromechanical focus on mid-to-low-end markets, with Inovenc Technology leading the pack. In 2022, Inovenc Technology's domestic servo market share reached 21.5%, up 5 percentage points from 2021. With domestic substitution trends and increasing robot volumes, Inovenc Technology's potential is high.
The domestic controller market is fragmented, with companies like Canoop, Wanxun Automatic Control, Googol Tech, Invt Electric, and Haide Control yet to form significant market competitiveness. Current domestic production rates are below 20%, and future success remains uncertain.
In the long run, humanoid robots are a promising venture poised for growth. Short-term hype is inconsequential; what matters is long-term tracking and identifying key players.
Disclaimer:
This article discusses content related to listed companies based on publicly available information from legal disclosures (including but not limited to temporary announcements, periodic reports, and official interactive platforms). The information or opinions presented do not constitute investment or other business advice, and Market Value Observation assumes no responsibility for actions taken based on this article.
--END--