Unveiling the World's Largest Robotics Unicorn: Seven Major Robotics Bubbles Exposed
![]() 06/06 2025
06/06 2025
![]() 676
676
For over half a year, robots have been a hot topic, with discussions buzzing around their dancing, running, and boxing abilities. However, there has been scant talk about how these robots actually make money.
Today, the Hong Kong stock market welcomes the IPO of a super unicorn with a focus on robotics. Through its prospectus, we can finally delve into the question: which robotics ventures are mere illusions floating in the sky, and which have firmly rooted themselves in the market's soil? Which are mere fluff and which are genuinely sought after by consumers?
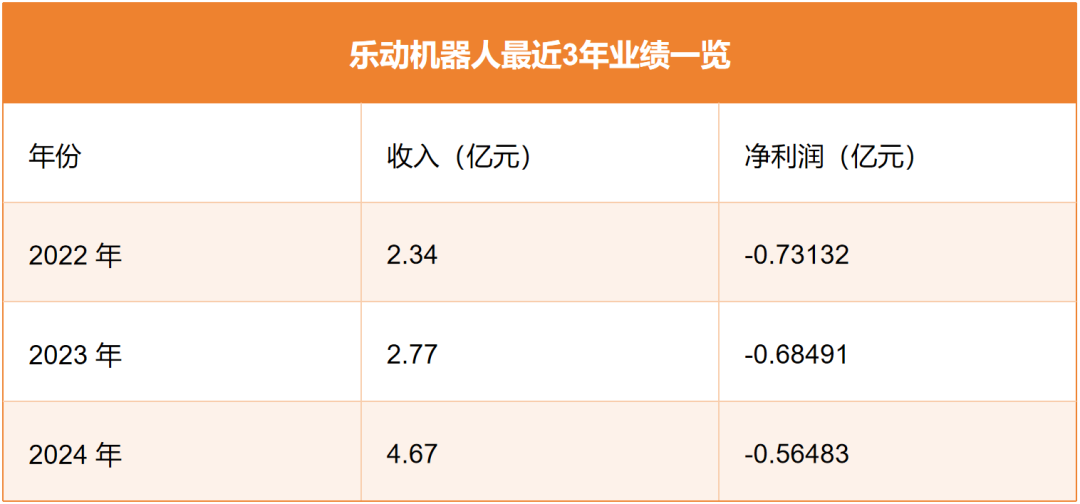
On May 30, Ludin Robotics, headquartered in Nanshan, Shenzhen, is rushing to go public. Its main direction is robot vision perception sensors, accounting for 72.9% of its total revenue in 2024.
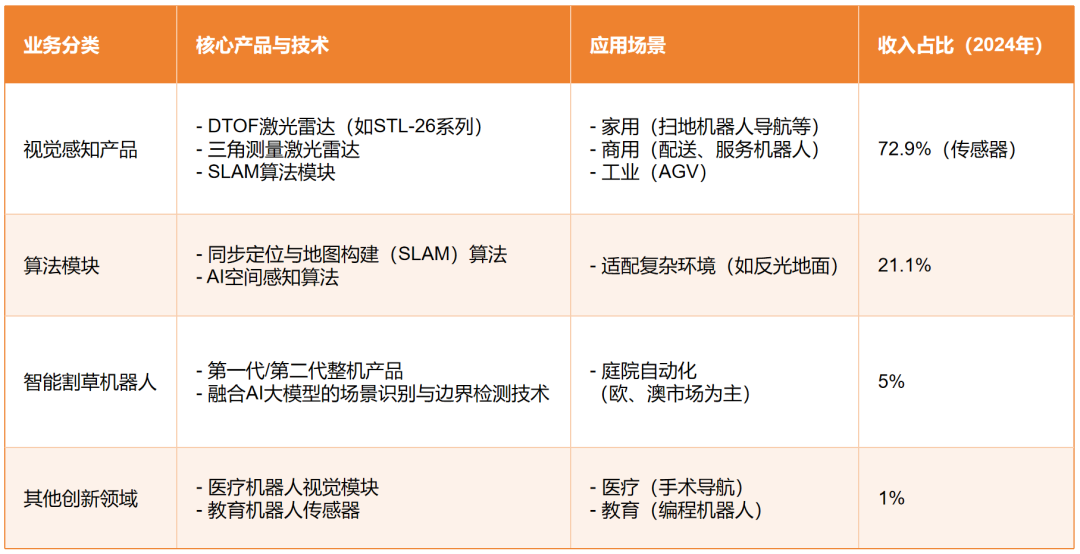 Caption: Ludin Robotics' core business
Caption: Ludin Robotics' core business
In terms of revenue, Ludin Robotics stands as the world's largest robotics company specializing in visual perception technology. In other words, its revenue from "intelligent eyes" technology surpasses that of any other similar company globally.
From this perspective, we can dissect which robots are in genuine market demand and which are mere superficial novelties.
The conclusions of this article may defy your expectations, so read on carefully.
- 01 -
Sweeping Robots
Sweeping robots are in genuine demand for certain demographics.
Among Ludin Robotics' customers, the core segment is household service robots, with sweeping robots being the heart of this category.
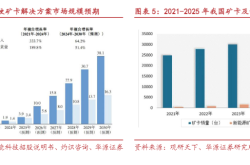
According to CIC's report, the global smart robot market size has surged from 158.3 billion yuan in 2020 to 369 billion yuan in 2024, with a compound annual growth rate of 23.6%. Household service robots occupy a significant share of this market.
Within this category, sweeping robots are the most technologically mature and have the highest market penetration.
China is the world's largest market for household service robots.
In recent years, functional enhancements have gradually transformed sweeping robots into a genuine demand for some households.
For instance, they now have "sharper eyes" with semi-solid-state lidar combined with AI algorithms capable of recognizing hundreds of obstacles. They are "more efficient" with suction power exceeding 20,000 Pa, and mopping upgraded to "professional housekeeping standards." They "understand you better" by connecting with smart speakers and comprehending instructions. They can even "take care of themselves" with base stations offering functions like automatic mop washing, hot air drying, and dust collection.
Thus, sweeping robots have become a genuine demand for users with high cleaning standards, those pursuing a high quality of life, those with fast-paced lifestyles, and those who lack time for housework.
Take pet-owning families as an example; the anti-entanglement roller brush solves the problem of hair cleaning and can mark restricted areas for pets. These features make sweeping robots a must-have for pet owners.
Despite the growing market, the current penetration rate of sweeping robots remains relatively low. For instance, it is expected to reach only 12% in 2025. For many, sweeping robots are not a necessity; they may believe that traditional cleaning methods suffice or find them expensive and inconvenient.
- 02 -
Lawn Mowing Robots
Lawn mowing robots are not in demand for most people and are still in the nascent stages.
They are primarily used in private yards and small lawns. Typically small in size, easy to operate, and low in noise, they meet basic lawn trimming needs for households.
According to CIC data cited in the document, global sales of smart lawn mowing robots in 2024 were approximately 383,500 units, with a market size of 6.1 billion yuan and a penetration rate of less than 2.0% in the global lawn mowing machinery market.
This indicates that most households still rely on traditional push/ride-on lawn mowers or manual trimming, with lawn mowing robots yet to become a mainstream choice.
The two core reasons for this are:
1. Cost advantage of traditional methods: Push lawn mowers can be as cheap as tens of dollars and are easy to operate, which is not enticing enough for small lawn users.
2. Limited market awareness: Consumers have limited knowledge about smart lawn mowing robots, especially in non-European and American markets where product promotion needs more time.
However, in high-end European and American markets, local rigid demand is emerging. For instance, in regions with high labor costs like Europe, North America, and Australia, the demand for lawn mowing robots is significant.
Germany, one of Europe's largest smart lawn mowing robot markets, has become a key base for Ludin Robotics' European expansion. After mass production of Ludin's first-generation smart lawn mowing robot in 2024, sales exceeded 10,000 units and surpassed 15,000 units in the first half of 2025. The majority of these orders came from overseas markets, confirming the urgent need for automated lawn care in high labor cost areas.
- 03 -
Industrial and Logistics Robots
Industrial and logistics robots have become a genuine demand in certain scenarios.
The automotive industry is highly dependent on them. In 2019, the proportion of industrial robots applied in the foreign automotive industry was 45%, and 50% in the domestic industry.
The high demand for robots in automobile production stems from the extreme accuracy, efficiency, and stability required in various processes like welding, painting, and assembly, making them indispensable.
Moreover, the demand in the logistics industry is growing rapidly.
In 2023, China's logistics robot market reached 16.8 billion yuan, with picking robots accounting for over 40%. By 2025, the market size is expected to exceed 20 billion yuan, with a compound annual growth rate of 28%.
For example, STO Express's Tianjin transfer center in Jinghai District adopted a double-decked, three-dimensional cross-matrix sorting line in 2025, capable of processing up to 18,000 express packages per hour, a 40% increase in efficiency. Each sorter can monitor 20 gates.
Reducing labor costs is a key factor driving this rigid demand.
Globally, population aging has led to a decline in the workforce and rising labor costs. In China, from 2003 to 2016, labor cost growth far outpaced productivity growth, putting immense pressure on the manufacturing sector.
The application of industrial and logistics robots effectively alleviates this issue. Robot costs are usually one-fourth of labor costs and can improve work quality, efficiency, and operate 24/7.
From a global perspective, there is still a gap between China's industrial robot density and that of developed countries. In 2019, China ranked 15th in industrial robot density, compared to the United States (1,287 units/10,000 people), Germany (1,311 units/10,000 people), and Japan (1,248 units/10,000 people), indicating significant room for improvement.
- 04 -
Service Robots
Service robots are not an absolute rigid demand, but their development trend suggests a gradual increase in potential demand.
They function as "smart assistants" for household chores and tasks.
Based on their functions, they can be broadly categorized into:
1. Family life: For elderly individuals with mobility issues, robots can chat, play music, control appliances, and assist with cleaning and cooking.
2. Catering industry: Robots deliver meals and beverages, enhancing restaurant efficiency.
3. Commercial services: Robots serve as customer service, shopping guides, waiters, etc.
4. Healthcare: Robots assist in surgeries and patient rehabilitation training.
According to CIC data, global shipments of commercial service robots reached about 1 million units in 2024, with large-scale deployments in catering, retail, hotels, and other fields.
The reasons why service robots are not an absolute rigid demand are multifaceted:
1. Price factor: Current service robot prices are relatively high (ranging from a few thousand to tens of thousands), making purchase costs a significant consideration for ordinary families.
2. Technical limitations: Service robot technology is still developing, with imperfections in functions like speech recognition accuracy and autonomous navigation reliability, potentially affecting user experience.
3. User habits: Traditional family lifestyles are deeply ingrained, and user acceptance needs improvement.
However, in specific scenarios, service robots may become a rigid demand, such as elderly care robots.
As disclosed in a pilot project by the Beijing Health Commission, the Unitree robot dog connected to the emergency system of the 301 Hospital can detect an elderly fall within 23 seconds and automatically call an ambulance, three times faster than traditional wearable devices. It also monitors respiratory rates through millimeter-wave radar penetrating bathroom glass, avoiding privacy concerns and playing a crucial role in ensuring elderly safety.
- 05 -
Children's Companion Robots
Children's companion robots are not an absolute rigid demand but have enormous development potential and may become one in the future.
In the long run, children's growth faces multiple needs:
1. Emotional companionship: With shrinking family sizes, many children lack peer play opportunities, and parents are too busy to spend time with them. Children's companion robots provide emotional companionship and interaction.
2. Educational assistance: These robots offer various educational resources like storytelling, singing songs, and learning knowledge, aiding children's learning and intellectual development.
3. Entertainment interaction: They engage children in various games like dancing, singing, and playing, providing entertainment and enriching their after-school lives.
The reasons they are not an absolute rigid demand now are:
1. Cost factor: The price is relatively high.
2. Children's short attention span: They easily lose interest in new things.
3. Importance of parent-child relationship: While robots provide some companionship, they cannot replace parental care. Parents may worry that children will become overly dependent on these robots, affecting their socialization and communication skills.
QYResearch's survey shows that the global children's companion robot market size was approximately 147 million USD in 2024 and is expected to reach 232 million USD by 2031, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.9% from 2025 to 2031. The relatively small market size and slow growth rate reflect its low penetration rate, especially in non-first-tier cities and rural areas where potential demand remains untapped.
- 06 -
Pet Robots
Pet robots are currently not an absolute rigid demand, and their demand is minimal.
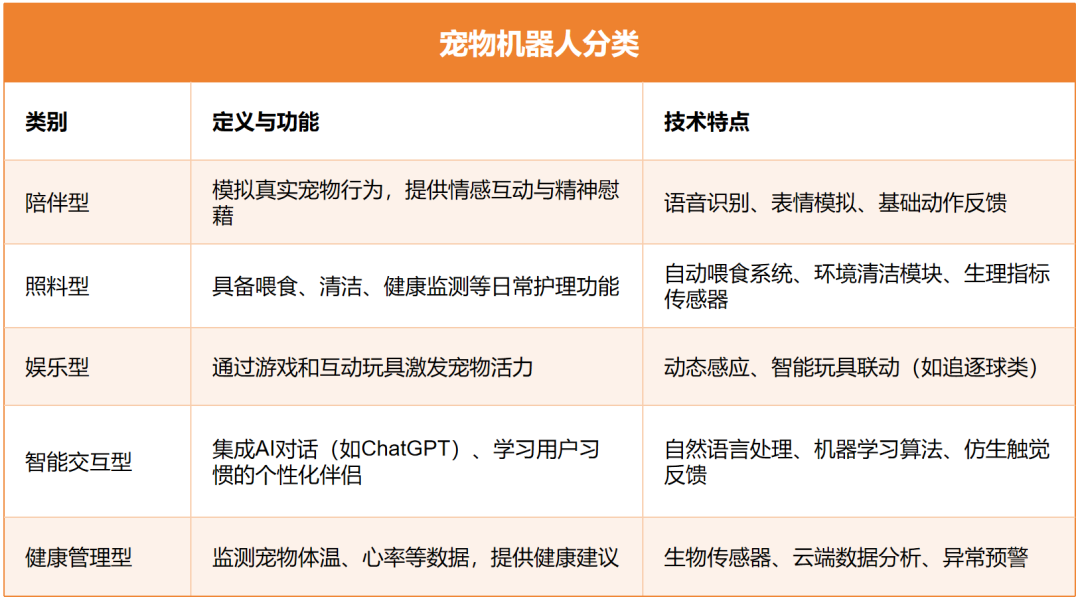
According to US-based "Verified Market Reports," the global pet robot market size was only 1.3 billion USD in 2024, accounting for a small proportion of the entire robot market, indicating limited rigid demand.
Consumer feedback reveals that people of all ages buy pet robots, but their motivations are diverse and not all represent rigid demand.
Some buy out of curiosity, like Ms. Wang, a post-70s math major who bought a pet robot for research. Others choose them as substitutes because they cannot own real pets, like pet allergy sufferers. However, this type of demand is uncommon.
- 07 -
Drones
Drones have become a rigid demand in certain fields but not others.
The two main scenarios for rigid demand are:
1. Logistics: JD.com Express, for instance, deeply collaborated with Renmin University of China in early 2025. The smart express service center on the Tongzhou Campus uses unmanned delivery vehicles and indoor delivery robots for automated package delivery.
2. Industrial: In power inspection, drones carry various detection equipment to efficiently inspect power lines, promptly identifying faults and potential hazards, reducing the risks and costs of manual inspections.
In the consumer market, most people have no demand for drones. For photography enthusiasts and professional filmmakers, drones are invaluable tools for capturing unique perspectives and high-quality footage.
Currently, consumer drone prices range widely, from the 4drc V26 at 139-199 yuan to the DJI Mini 3 at 2689-5776 yuan. However, even for lower-priced products, the necessity of purchase is low for most consumers.
This article does not constitute investment advice.