Is Computing Power Rental a Promising Business Venture?
![]() 06/23 2025
06/23 2025
![]() 608
608

Amidst the burgeoning digital economy, computing power has emerged as a pivotal strategic resource. From everyday intelligent applications to profound enterprise digital transformations and efficient government governance, every facet relies heavily on robust computing power support. In recent years, the exponential growth in AI technology demand has spurred a quiet revolution centered around computing power.
01
The Sudden Rise of the Computing Power Internet Concept
On May 17, during the "2025 World Telecommunications and Information Society Day Commemoration Event," the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), in collaboration with China Telecom, China Mobile, and China Unicom, jointly launched the "Computing Power Internet Testbed" and unveiled the "Computing Power Internet Architecture 1.0," sparking widespread online discussions. Just two weeks later, on May 30, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the "Computing Power Interconnection Action Plan," clearly outlining the establishment of comprehensive standards, identification, and rule systems for computing power interconnection by 2026, emphasizing the promotion of the Computing Power Internet and the cultivation of a unified national market for computing power services centered around interconnectivity. Since then, the Computing Power Internet concept has frequently graced major media headlines, becoming a hot topic in the tech world.
So, what exactly is the Computing Power Internet, and how does it differ from the traditional internet we know? Essentially, it's not a new physical network but a significant upgrade to the existing internet. By leveraging standardized computing power identifications and protocol interfaces, it seamlessly connects scattered computing power resources nationwide, creating a cross-domain resource interconnection network that enables intelligent perception, real-time discovery, and on-demand acquisition of heterogeneous computing power across the entire network. Simply put, the Computing Power Internet is akin to a "highway network" tailored for the flow of computing power. Its core function is to transcend geographical limitations, achieve interconnectivity and interoperability, revitalize idle computing power, drastically improve utilization efficiency, reduce costs, and provide users with a more convenient and efficient computing power service experience.
China has achieved remarkable strides in computing power infrastructure, with various regions actively deploying computing power centers. However, the issue of uneven computing power distribution is increasingly evident. Some regions suffer from excess resources and high equipment idleness, while others grapple with shortages, making it challenging to meet development needs. This imbalance not only results in significant resource waste but also severely hinders the improvement of computing power utilization efficiency. The Computing Power Internet aims to tackle this challenge. In the future, users will be able to flexibly purchase computing power resources based on their needs, akin to purchasing electricity by "kilowatt-hours," truly achieving "on-demand use, immediate access," and making computing power services accessible to all.
Compared to the national "East Data and West Computing" strategy and operator-proposed computing power networks, the Computing Power Internet's ambition is even grander. While "East Data and West Computing" focuses on cross-regional data transmission and processing, and computing power networks concentrate on localized integration, the Computing Power Internet aims for network-wide interconnectivity and interoperability, connecting disparate computing power infrastructures (akin to "computing power islands") into a cohesive whole, enabling free-flowing and efficient nationwide allocation of computing power resources, much like the human body's meridians and collaterals, ensuring unimpeded flow.
02
Operator-led Construction: The Core Driver of Industrial Development
With the accelerated AI-real economy integration and the vigorous development of new-quality productivity, accelerating the intelligent evolution of digital information infrastructure and building a solid digital foundation have become pivotal for fostering new-quality productivity. Only by possessing large-scale computing power and massive data storage capabilities can we provide robust support for industrial innovation and development. As the national team and mainstay in computing power network construction and operation, the three major telecom operators have actively responded to national strategies, continually expanding their involvement in Computing Power Internet construction amidst the ongoing "East Data and West Computing" project, emerging as the core driver of Computing Power Internet development.
Currently, based on the Computing Power Internet architecture, the three major telecom operators have proposed testbed schemes and actively undertaken verification practices.
China Telecom is constructing a smart computing internet testbed, leveraging the "Xirang" integrated smart computing service platform to build an intelligent cloud system integrating computing power, platforms, data, models, and applications. By accessing various cross-domain heterogeneous resources, it aims to establish a unified national computing power network, empowering the digital and intelligent transformation of myriad industries. In terms of computing power scheduling, Tianyi Cloud Xirang facilitates intelligent and efficient cross-domain, cross-service provider computing power scheduling through orchestration, business, and job scheduling schemes, promoting the formation of a Computing Power Internet characterized by intelligent perception, real-time discovery, and on-demand acquisition, realizing "one-point access and full computing penetration" services. Regarding computing power access, Tianyi Cloud has formulated standardized specifications for computing power access management, enabling grid-connected access of various forms and types of computing power, such as public clouds, private clouds, third-party computing power, and bare computing power, accelerating computing power grid connection progress, promoting the use of unified invocation interfaces and communication protocols among different computing power service entities, facilitating flexible migration and scheduling of computing power applications and data, and enhancing the callable capability of computing power resources. In terms of arithmetic and computing collaboration, Tianyi Cloud Xirang facilitates coordinated scheduling of computing power and data elements, offering multiple data collaboration modes to meet different business scenarios, thereby improving global computing power utilization rates.
China Mobile is constructing an innovative testbed for the computing power network, validating technologies such as wide-area high throughput and computing power routing on the "Four-in-One" computing network brain platform, achieving resource-wide perception, integrated orchestration, and intelligent scheduling, innovating services like in-training edge inference and data express delivery, and building an inclusive computing power system. China Mobile has comprehensively upgraded its integrated intelligent computing power network resource system, innovatively proposing a new "134" integrated intelligent computing power network resource system. "1" signifies adhering to the development goal of integrated and symbiotic intelligent computing networks. "3" involves upgrading three types of core resources: computing, networks, and data centers, to create smarter computing, forming a three-dimensional smart computing layout with full cloud, edge, and end coverage; to build more intelligent networks, enabling east-central-west region computing power interconnectivity and interoperability; and to establish a greener and smarter base, constructing new data centers with high density, efficiency, and energy savings. "4" denotes adhering to the development principles of intellectualization, networking, greening, and autonomy.
China Unicom is developing a computing power interconnection plan and testbed, constructing a "four-in-one" architecture based on the "Xingluo" computing power scheduling platform, all-optical base, and intelligent industrial internet, reinforcing resource-wide coordination, and empowering a new digital economy ecosystem through a unified identification system and cross-domain scheduling capabilities.
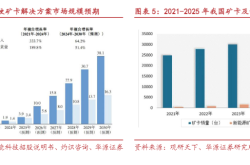
China's Computing Power Internet construction has yielded initial results. At the resource interconnection and scheduling level, it has completed the resource identification of 499 computing power resource pools from 131 enterprises, amassing 111.3 EFlops of intelligent computing resources. These resources are widely utilized across various fields, playing a crucial role in the digital and intelligent transformation of numerous industries. However, it's undeniable that China's Computing Power Internet is still in its nascent stages and faces numerous challenges. Computing power resources are scattered and lack unified standards, complicating coordinated deployment. Nonetheless, experts generally believe that the prospects for Computing Power Internet construction are promising, as it can not only integrate dispersed computing power, promote computing power popularization, enhance computing power utilization efficiency, accelerate AI application deployment and industry digital and intelligent transformation but also support key technology research, facilitate innovation achievement transformation, and realize computing power grid-connected access in various forms and cloud-based multi-tenancy reuse.
03
The Ascendance of the Computing Power Rental Industry: A New Frontier in the Digital Economy
Computing power serves as the cornerstone of AI large models, currently the heart of the AI technological revolution. Amidst the global AI boom, computing power demand has skyrocketed. However, the current international environment is complex and volatile, with Chinese enterprises and institutions facing numerous restrictions on importing high-end computing power chips (primarily GPUs and TPUs). Domestic computing power chips cannot meet market demand in the short term, exacerbating the computing power supply-demand contradiction. The advent of the Computing Power Internet offers a novel solution by networking computing power, effectively improving domestic computing power utilization rates and alleviating computing power shortages. Simultaneously, the computing power rental industry has emerged as a new frontier in the digital economy.
Essentially, computing power rental is a business model grounded in AI computing power cloud services. It allows users to flexibly rent computing resources like CPUs, GPUs, memory, and storage space based on their needs, fulfilling computing demands without the necessity of purchasing expensive computing equipment. For enterprises and institutions requiring large-scale computing capabilities but unwilling to bear high upfront costs, computing power rental is undoubtedly an ideal choice. By renting computing resources, users can swiftly launch projects, leverage stable and efficient computing resources, significantly shorten R&D cycles, and reduce R&D costs.
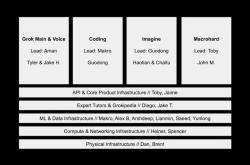
In fact, the computing power rental industry has a lengthy history abroad. Taking the American company CoreWeave as an example, founded in 2017 as the cryptocurrency mining enterprise Atlantic, it amassed a substantial amount of NVIDIA GPU resources through Ethereum mining and decisively shifted its business focus in 2019 to concentrate on AI cloud and infrastructure construction. As of late 2024, CoreWeave operated 32 data centers, primarily situated in low-electricity-cost regions of the United States, with nodes in European technology hubs like London and Stockholm to meet customers' demands for geographically proximate AI computing power. The company has deployed over 250,000 GPUs, mostly using NVIDIA Hopper architecture products, making it a significant infrastructure cloud service provider for high-performance chips like NVIDIA H100, H200, and GH200, and the first cloud vendor to fully offer NVIDIA GB200 NVL72.
In terms of business models, CoreWeave primarily offers three services. First, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), specifically bare metal GPU rentals, enables users to directly access H100 and A100 chips, thus eliminating performance losses associated with virtualization. Its clusters leverage the NVIDIA InfiniBand architecture, ideally suited for high-intensity tasks like AI training and rendering. Unlike traditional cloud providers, this offers a higher computing density but demands heightened technical proficiency from users. Second, Management Software as a Service (MSaaS), through CoreWeave's Cloud Net Service, provides a pre-configured GPU driver-managed environment, simplifying virtual private cloud deployment, achieving network isolation and acceleration with the aid of the NVIDIA BlueField 3 DPU, and reducing management complexity. However, its exclusive features restrict its applicability to non-AI users. Lastly, Application Services, encompassing SUNK services, Tensor-accelerated inference, real-time monitoring, etc., are designed to boost customer efficiency, lower technical barriers, and continually enhance application service capabilities through collaboration with AI enterprises. Among these, IaaS, specifically GPU bare metal rentals, stands as CoreWeave's core business.
The domestic computing power rental industry is witnessing rapid growth, particularly notable in the first quarter of this year. Reports from companies like Hongjing Technology, Xiechuang Data, Youfang Technology, Hainan Huatie, and Runjian Shares have all highlighted advancements in computing power-related ventures, with some even experiencing revenue growth through computing power rentals. Amid surging internet capital expenditures and Sino-US supply chain constraints, the domestic computing power rental industry holds unique competitive advantages over its overseas counterparts. With the ever-increasing domestic demand for computing power, the industry boasts promising long-term prospects. Its strong customization capabilities for AI scenarios and substantial customer needs are gradually reshaping the traditional competitive landscape of cloud vendors.
However, despite its rapid development, the computing power rental industry confronts numerous challenges. Heavy reliance on suppliers like NVIDIA could lead to supply instability. Limited electricity resources and high data center operating costs escalate corporate operational pressures. High customer concentration makes the industry less resilient to risks. Rapid technological advancements mean that enterprises that fail to keep pace may face elimination. The uncertainty surrounding the AI industry's growth also introduces variables into the computing power rental industry. Additionally, significant capital expenditures and high financing capacity requirements pose challenges that enterprises must navigate during their development.
CoreWeave's development trajectory and business model underscore the vast potential and growth trajectory of the computing power rental industry. With continuous technological advancements, market expansion, and deepening applications, the computing power rental industry will undoubtedly assume an increasingly pivotal role in the digital economy. Nevertheless, industry participants must closely monitor the various challenges and risks during their development, proactively explore countermeasures, and foster the healthy and sustainable growth of the computing power rental industry.