Tesla's Robotaxi Launches: Modest Start Amidst Future Expansion Challenges
![]() 06/23 2025
06/23 2025
![]() 606
606


Source: Smart Auto Tech
On Sunday, June 22, Eastern Standard Time (EST), Tesla’s highly anticipated autonomous Robotaxi service officially launched a pilot program in Austin, Texas. However, the rollout was relatively subdued, with operations appearing more cautious than the ambitious vision previously outlined by Tesla CEO Elon Musk.
The service is currently limited to invited users, with the Robotaxi fleet actively avoiding complex intersections in Austin and prioritizing routes with simpler traffic conditions. Tesla plans to gradually expand the invitation range based on initial data, aiming to open the service to the public by the end of 2025.

Robotaxi Day One Operations:
Limited Scale, Invited Experience
On Sunday, Musk announced the official launch of the Robotaxi on his social media platform X. Some social media celebrities posted videos of their first rides in the Robotaxi. According to information shared on social media, about 10 Model Y vehicles were operating on the first day, with no one in the driver’s seat and only a "safety supervisor" in the passenger seat. This setup reflects Tesla’s balance between public safety and technology demonstration.
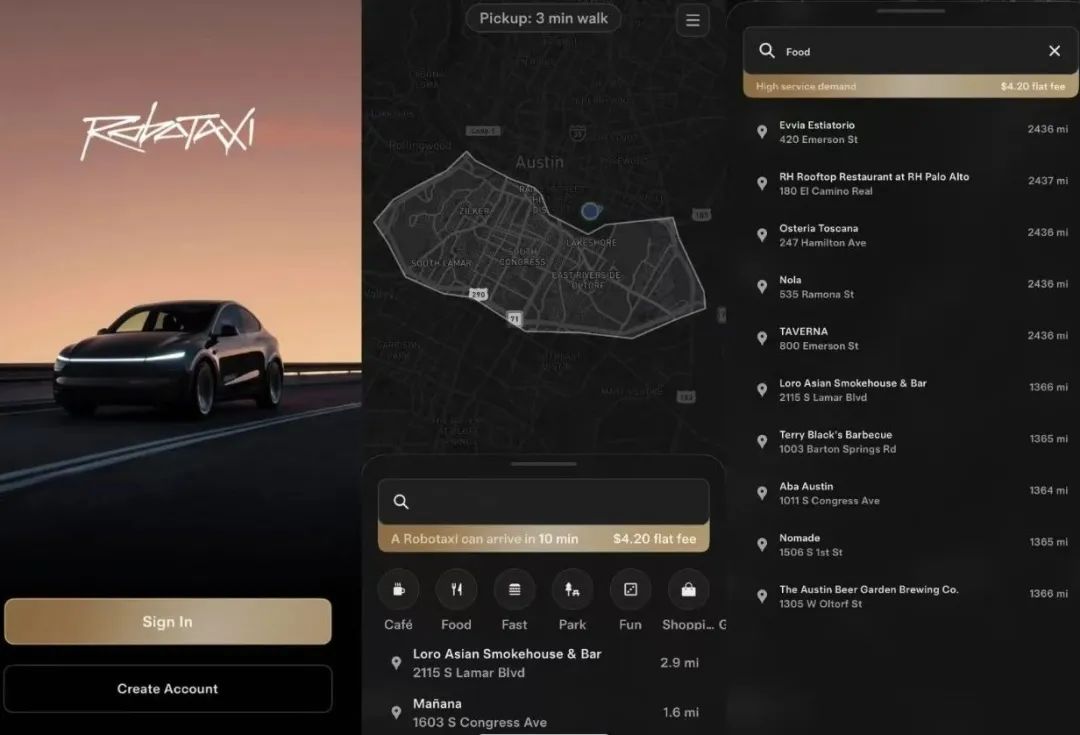
Operations are strictly confined to a 50-square-kilometer area designated by the government, with service hours from 6 AM to midnight.
Notably, Robotaxi passengers are not the general public but rather carefully selected individuals invited by Tesla. In recent days, Tesla has invited some social media celebrities to experience the service first. This means that regular consumers may have to wait some time before being able to ride the Robotaxi. On Sunday afternoon, EST, Tesla investor and social media celebrity Sawyer Merritt posted a video on X showing him using Tesla’s autonomous taxi app to hail a ride to nearby bars and restaurants.


Industry Expansion:
Facing Multiple Challenges in Technology and Regulations
Despite Tesla’s successful small-scale deployment of the Robotaxi, industry experts point out that Tesla will still face significant challenges if it aims to quickly expand its scale in Austin and other cities.
Firstly, regulatory pressure is a primary challenge faced by Tesla. On the eve of the pilot launch, Tesla experienced pressure from regulatory authorities. Seven Austin legislators from both the Texas Senate and House of Representatives jointly wrote a letter requesting that the Robotaxi launch be delayed until new regulations take effect on September 1. However, Tesla stuck to its original plan and chose to advance testing in an environment where the regulatory framework had not yet been fully implemented. Notably, Texas Governor Greg Abbott, a Republican, signed a bill on Friday requiring state permission to operate autonomous vehicles, which will take effect on September 1.
Meanwhile, the Robotaxi’s operating range is limited to a confined area in Austin. In terms of pricing strategy, Musk stated on X that the fixed fee for rides on the first day of the Robotaxi launch is $4.20. This contrasts sharply with competitors like Waymo and Cruise, who typically charge between $6-12 and often use a mileage-based pricing model. Tesla’s flat rate aims to eliminate uncertainty and enhance the attractiveness of the user experience.
Musk further explained the motivation behind this low-price strategy during the earnings call: "Low prices are a catalyst for popularization, and we pursue scale rather than excessive profits." Pilot data shows that the actual cost of short trips (such as 3-5 kilometers) may be lower than Tesla’s operating expenses, indicating that the company is willing to subsidize losses in the initial stage to capture market share.
According to the new Texas bill that will take effect on September 1, autonomous vehicle operators must obtain approval from the Texas Department of Motor Vehicles to operate on public streets without a driver. The state government has the authority to revoke the licenses of operators deemed to pose a threat to the public. Additionally, the law requires companies to provide information to allow emergency responders to properly handle their autonomous vehicles in case of an emergency.

Technology and Safety:
The Key to Continuous Optimization
Tesla’s autonomous driving technology has always been the focus of industry attention. Relying on cameras, sensors, and artificial intelligence algorithms, it aims to achieve highly automated driving of vehicles. However, in practical applications, this technology still faces questions. For example, the reliability and safety of the autonomous driving system still need further verification in complex road conditions and severe weather scenarios.
The Robotaxi fleet showcased this time is equipped with Tesla’s Hardware HW4.0 and FSD v12 software, continuing its pure vision technology approach and relying on 8 high-definition cameras for 360° environmental perception. Unlike competitors like Waymo, Tesla adheres to a pure vision technology route and abandons additional sensors such as lidar, a choice that remains controversial within the industry.
Tesla publicly demonstrated its command center system for the first time, equipped with large screens and steering wheels in the backend center, enabling real-time monitoring of all vehicles and remote takeover in emergencies.
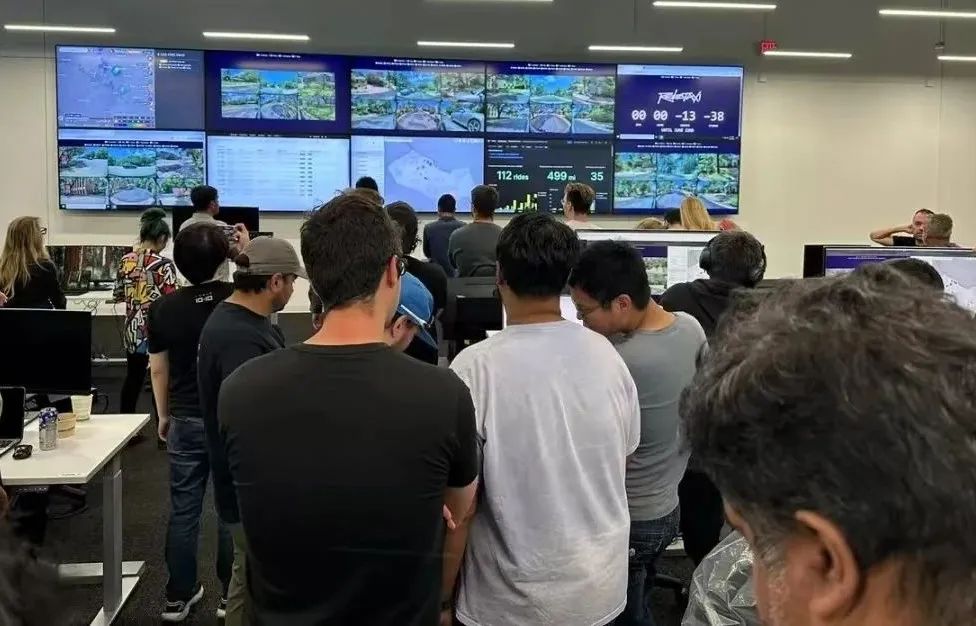

Meanwhile, the presence of "safety supervisors" in this Robotaxi operation reflects Tesla’s cautious attitude towards current technology. While Musk is confident in the company’s autonomous driving technology, markets and regulatory agencies need to see more actual data and long-term safety records before fully recognizing the maturity of its technology.
Therefore, safety verification takes precedence over scale expansion. According to third-party test data, Tesla’s FSD system requires manual intervention every 13 miles on average, with particularly insufficient recognition capabilities in scenarios with smoke and heavy rain. Incidents involving pioneers like Waymo in Phoenix have triggered a crisis of trust in autonomous driving technology among the public, which undoubtedly serves as a warning to the industry.
Tesla has chosen a "gradual automation" route: initial supervisors act as a "safety belt," which will be gradually removed as data proves reliability. Additionally, Tesla’s choice to launch the pilot in Austin, a "friendly environment" with mild weather and well-structured roads, significantly reduces initial technical risks.
While continuously optimizing its technology, Tesla also needs to respond to strict scrutiny from regulatory authorities. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has previously launched an investigation into Tesla’s autonomous driving technology, focusing on its safety performance in various scenarios. For Tesla, how to further improve the safety and stability of its technology while meeting regulatory requirements will be one of the key factors determining the future large-scale promotion of Robotaxi.
Musk previously admitted that this service is "not really autonomous driving," which contrasts with his past optimistic promises of full autonomous driving. After multiple delays in the full autonomous driving timeline, Tesla urgently needs to prove the feasibility of its technology through the actual operation of Robotaxi to respond to external expectations and doubts.

Market Prospects:
Huge Potential but Still Needs Time to Verify
In the long run, the autonomous taxi market is considered to have huge potential. With the acceleration of urbanization and the growing demand for convenient travel, autonomous taxis are expected to change the existing urban transportation landscape, improve travel efficiency, reduce traffic accidents, and alleviate traffic congestion.
However, realizing this vision still requires overcoming many obstacles. Besides technological and regulatory challenges, market acceptance is also an important factor. A public opinion survey shows that only 23% of Americans are willing to ride a Robotaxi without a safety officer, compared to 41% among Tesla owners. How to increase public trust in autonomous taxis and encourage more people to choose this new mode of transportation is a common challenge for Tesla and the entire industry.
Exploring business models and profitability also faces challenges. Although Musk has outlined a blueprint for generating substantial profits through Robotaxi, details such as specific operating costs, sustainable pricing models, and revenue-sharing mechanisms with car owners remain to be clarified.
Taking the currently much-talked-about pricing strategy as an example: the flat fee of $4.20 undoubtedly creates a highly competitive psychological anchor. Analysis suggests that this price may be based on the operating costs of the Model Y (approximately $0.50 per trip for electricity consumption and approximately $2 after maintenance and insurance sharing), with the remaining portion representing marginal profit. However, the additional labor costs incurred by initially equipping safety supervisors make this pricing strategy quite aggressive - Tesla is clearly betting on a significant cost reduction after removing supervisors in the future.
Meanwhile, in terms of competitors, companies like Waymo have already started commercial operations in some regions, and Tesla urgently needs to establish a differentiated advantage in the fierce market competition to secure a place in the future market.
Looking ahead, Tesla plans to expand Robotaxi services to cities such as Houston and Dallas in the United States by the end of 2025, cover major US cities in 2026, and initiate pilots in Europe and Asia. Musk’s ultimate vision is to create a vast "autonomous driving network" where users can summon vehicles through subscription services, ultimately ushering in the era of "mobility as a service."
The official launch of Tesla’s Robotaxi is just the beginning. In the future, Tesla needs to continue efforts in technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and market promotion to turn Musk’s grand vision into reality.
Industry experts generally believe that the operational data and user feedback from the Austin pilot will have a crucial impact on Tesla’s subsequent market expansion strategies.
For the entire autonomous driving industry, Tesla’s move will also serve as a demonstration and driving force, prompting more companies to accelerate their research, development, and deployment efforts to jointly welcome the era of autonomous driving.
Disclaimer:
All works on this public account marked as "Source: XXX (not Smart Auto Tech)" are reproduced from other media. The purpose of reproduction is to deliver and share more information and does not represent the platform’s endorsement of their views or responsibility for their authenticity. The copyright belongs to the original author. Please contact us for deletion if there is any infringement.