Can Robotaxi Fortify Tesla's Competitive Edge?
![]() 06/25 2025
06/25 2025
![]() 743
743
Musk's grandest ambition proves challenging to achieve.
Robotaxi is viewed as Musk's most transformative venture for Tesla, met with controversy upon its debut a year ago. Nonetheless, investors chose to continue trusting it, driven by Tesla's impressive FSD (Full Self-Driving) performance.
However, just a day after its launch, Tesla's Robotaxi faced the threat of being shelved by regulators. Tesla once again found itself in a strategic tug-of-war with regulators. Without the status of a special advisor, it remains unclear how much leeway the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) will grant to Musk.

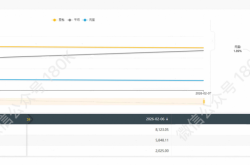
The silver lining is that the operation of Robotaxi did indeed prop up Tesla's share price to some extent. Just one day of operation led to an 8.23% surge in Tesla's share price, showcasing a significant promotional effect.
However, amidst the applause for Tesla's Robotaxi, there are also louder voices of skepticism and opposition. Can this venture truly sustain Tesla's future?
A Late Entrant
Unlike its previous strides in the new energy vehicle sector, Tesla is not a pioneer in the Robotaxi field but rather a late entrant.
Especially in the US market, Tesla lags significantly behind its competitors. As early as 2015, Google began testing its autonomous taxi project and commenced commercial operations in 2018, sparking an investment boom in Robotaxi across Silicon Valley.
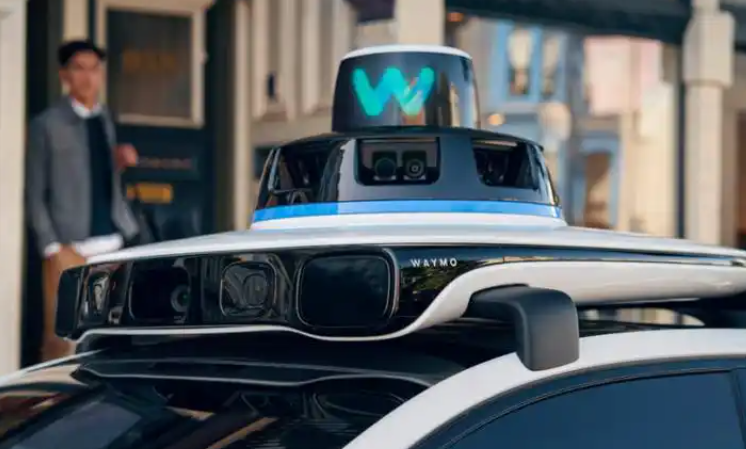
After the retreat of investment in autonomous driving in 2023, Waymo, a subsidiary of Google, emerged as the sole technology company still operating in the US.
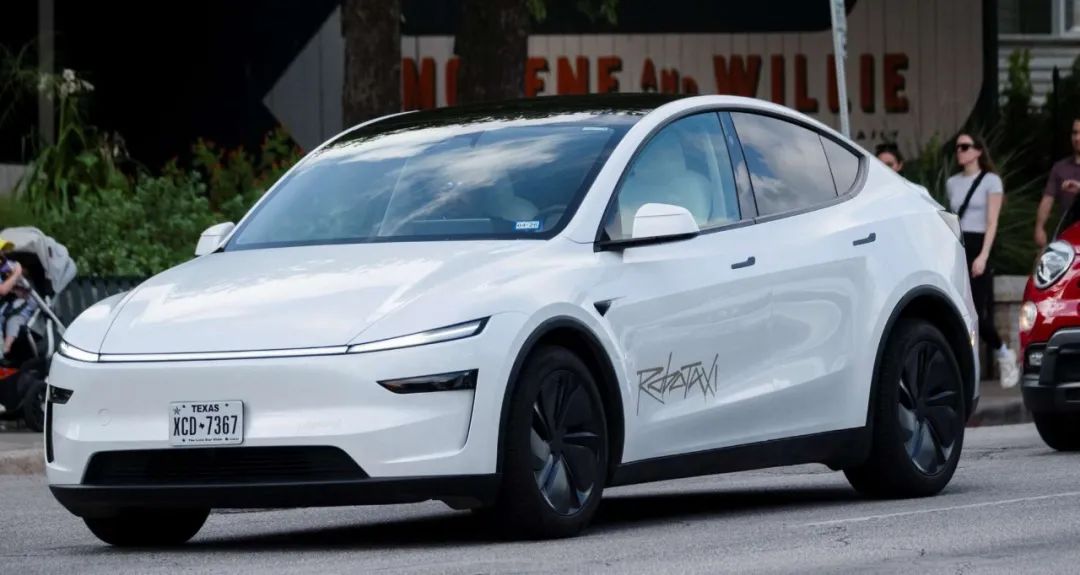

With breakthroughs in intelligent assisted driving technology, Tesla announced in 2024 that it would launch a steering wheel-free version of the Cybercab Robotaxi and planned to operate "fully unsupervised" Robotaxi services in Austin, Texas.
2024 was also a period of intense interest in domestic Robotaxi. Baidu's Luobo Kuaipao became a hot topic of discussion among the public in Wuhan. With the continuous buzz around autonomous driving for all and end-to-end solutions, Robotaxi emerged as a symbol of the advent of future technology.
However, in this nascent market, Tesla is indeed a late entrant. While Tesla has always aimed to achieve autonomous driving with its FSD and has been making consistent progress, the reality is that Tesla cannot attain this goal solely through direct car sales.
Especially amidst declining sales of Tesla vehicles, Musk can only heavily bet on Robotaxi technology to stabilize the share price.

With FSD failing to boost Tesla's sales, Musk urgently needed to find ways to share research and development costs. The cost of running the computing center per minute needed to be recouped through car sales. However, Tesla's sales declined by 13% in the first quarter, and FSD subscriptions did not meet expected levels.
Musk chose to make a bold move by linking FSD with Robotaxi. Since the general public has a low acceptance of autonomous driving, the first step is to enhance consumer awareness.
Proficient in cost control, Musk discovered new opportunities in Robotaxi. Waymo, the largest Robotaxi company in the US, has over 1,500 test vehicles covering multiple major cities. However, due to the high cost per vehicle, it still struggles to achieve profitability.
Tesla's Robotaxi is currently being developed based on mass-produced models. With a mature manufacturing system, it can be produced at a lower cost and holds a price advantage. It is reported that the operating cost of Tesla's Robotaxi is $0.20 per mile, one-fifth of the average cost in the Waymo industry.

Lower costs are most evident in lower fares. According to a post by Tesla CEO Musk on his social platform X, the fare for each ride is $4.20, significantly lower than that of taxis and competitors.
Just like the ongoing food delivery wars in China, late entrants can only expand the market through price wars. The underlying logic of business competition remains the same in both the East and the West.
Debate on Technology and Safety
Behind Tesla's low-cost operation of Robotaxi lies a debate on the technical route of autonomous driving. Unlike traditional Robotaxi companies, Tesla adopted a pure vision approach from the outset, relying solely on cameras to collect data for decision-making.
Traditional Robotaxi companies adopt a multi-sensor fusion solution. To ensure operational safety, they usually add redundancy to guarantee absolute safety.
However, Tesla's autonomous driving team, led by Musk, is more confident in the capabilities of the pure vision approach and AI large models.
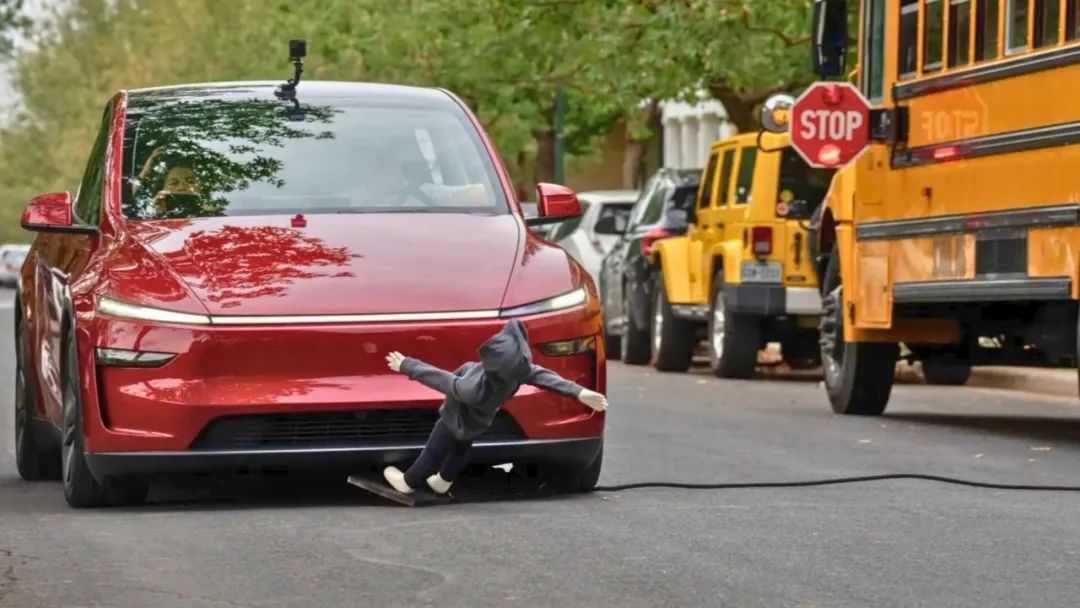
During the trial operation of Tesla's Robotaxi, numerous experience videos have been released, showing that these Robotaxi seem to have violated multiple traffic rules in Austin.
Concerns about the safety performance of Tesla's Robotaxi are not only continuously monitored by onlookers but also questioned by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). NHTSA sent Tesla a 12-page emergency inquiry letter, requiring it to provide details on the safety guarantee plan for the Robotaxi fleet in extreme weather by June 19, 2025, or face a fine of nearly $28,000 per day.

In response to NHTSA's inquiry, Tesla requested that the regulatory agency not disclose Robotaxi safety information, claiming it to be commercial secrets that should not be made public. Tesla's Senior Counsel for Regulatory Affairs, Kathy Bryan, emphasized that the technical details submitted to NHTSA have "irreplaceable commercial value." Competitors could optimize their own autonomous driving systems by analyzing core parameters such as their algorithms for responding to inclement weather and sensor fusion strategies.
This stance is starkly contrary to Tesla's usually open approach towards new energy vehicle technology. Tesla has always been transparent about it, including previously publishing multiple related patents. Simultaneously, disclosing Robotaxi technology is also a necessary step to ensure regulation. Waymo has already disclosed 127 safety indicators of its fifth-generation autonomous driving system to NHTSA.
Behind this competition lies the regulatory department's measurement standards for autonomous driving capabilities. Currently, there is no clear and quantifiable specific standard for autonomous driving capabilities, including the most crucial aspect of safety. NHTSA's inquiry mentioned several points, including extreme weather adaptability, safety redundancy, operational design domain, and data reliability.
Particularly, extreme weather adaptability, which is evidently targeted at those using a pure vision approach or a vision-based approach like Tesla, requires autonomous driving to meet test scenarios such as dense fog with visibility less than 50 meters, rainstorm simulations with rainfall greater than 100mm/h, and dust storm simulations with instantaneous wind speeds greater than 25m/s.

This testing standard is gradually being accepted by regulatory authorities in other countries and may become a crucial standard influencing the global autonomous driving industry.
Furthermore, a clear definition of the operational design domain constrains automakers' disorderly technological expansion. Tesla's approach of continuously expanding the use of FSD through software updates has been viewed by regulators as a significant risk vulnerability. This restriction necessitates a clear definition of the operating boundaries of the autonomous driving system to prevent automakers from indefinitely expanding driving capabilities.
What seems to be a technical debate about autonomous driving Robotaxi is, in essence, about the regulation of traffic safety. Ensuring system safety is the paramount priority for Robotaxi, not merely low costs or other advantages.
It can be said that the investigation into Tesla's Robotaxi marks the entry of the autonomous driving industry into a period of safety benchmark reconstruction. On the surface, regulatory scrutiny is aimed at Tesla's technological questions, but in reality, it is a redefinition of safety standards for the entire industry.
Especially with the rapid advancement of assisted driving technology, regulatory authorities need to shoulder significant responsibilities. While ensuring technological progress, they must also prevent unscrupulous enterprises from deploying unsafe systems on the road.
In the short term, Tesla's regulatory dilemma will delay the commercialization process of Robotaxi, forcing enterprises to enhance safety redundancy design and increase compliance costs. However, in the long run, this incident will drive the industry to establish a more transparent safety assessment system.
According to a McKinsey report, the global autonomous taxi market size will reach $45 billion by 2025. Musk's market expectations are not unrealistic, but the core issue is whether Tesla can provide a safe system to forge a second technological moat and maintain Tesla's leadership in the electric vehicle industry.
Note: Some images are sourced from the internet. Please contact us for removal if there is any infringement.