AI-Driven Super Cycle for Memory Chips
![]() 02/09 2026
02/09 2026
![]() 453
453

Significant Performance Divergence Among Domestic Concept Stocks
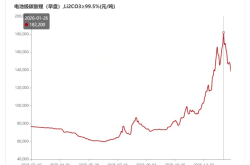
The global memory chip industry is experiencing an unprecedented 'super cycle.' The 'siphon effect' on memory production capacity triggered by the explosion in AI infrastructure demand has driven up prices for core categories such as DRAM, NAND, and HBM (High Bandwidth Memory). Samsung's NAND flash memory supply prices surged by over 100% in the first quarter, far exceeding market expectations.
Shengma Finance noted that amid this industry wave, the performance of domestic memory chip concept stocks has shown a stark divergence. According to corporate earnings preview data for 2025 (as of January 26), among 29 memory chip concept stocks, 20 reported year-on-year net profit growth, while 9 posted losses, highlighting the industry's 'Matthew effect.' Meanwhile, global industry leaders like Synopsys and Micron warned that the memory chip shortage would persist until 2027, with some institutions projecting it could extend to 2028. Domestic manufacturers face a development window of opportunities and challenges amid this supply-demand restructuring.
Domestic Concept Stocks Show Performance Divergence: Leaders and Dark Horses Lead the Way
From the 2025 earnings preview data of memory chip concept stocks, the industry's profit landscape exhibits a 'three-tiered divergence,' with the scale advantages of leading firms contrasting sharply with the explosive growth of niche market dark horses, while losses at some companies expose competitive weaknesses in the industry.
Leading firms have solidified profit barriers, excelling in both scale and growth. Data shows that three companies have net profit forecasts exceeding RMB 1.5 billion, forming the first tier. Dahua Technology tops the list with a net profit forecast of up to RMB 3.854 billion, representing a year-on-year growth rate of up to 32.65%. As a leader in the memory module sector, it benefits from dual drivers of AI server and data center storage demand.
Montage Technology follows closely, with a net profit forecast ranging from RMB 2.15 billion to RMB 2.35 billion and a year-on-year growth rate of 52.29%-66.46%. Its technological edge in DDR5 memory interface chips positions it as a key player in the high-end memory supply chain. GigaDevice's net profit forecast tops out at RMB 1.61 billion, up 46% year-on-year, with 2025 revenue expected to reach RMB 9.203 billion, a 25% increase. The synchronized growth in revenue and profit underscores the effectiveness of its synergistic development in NOR Flash and MCU businesses.
The performance of these three companies underscores the competitive barriers of leading manufacturers in technology R&D, customer resources, and capacity deployment, making them more likely to secure orders and profit advantages during industry shortage cycles.
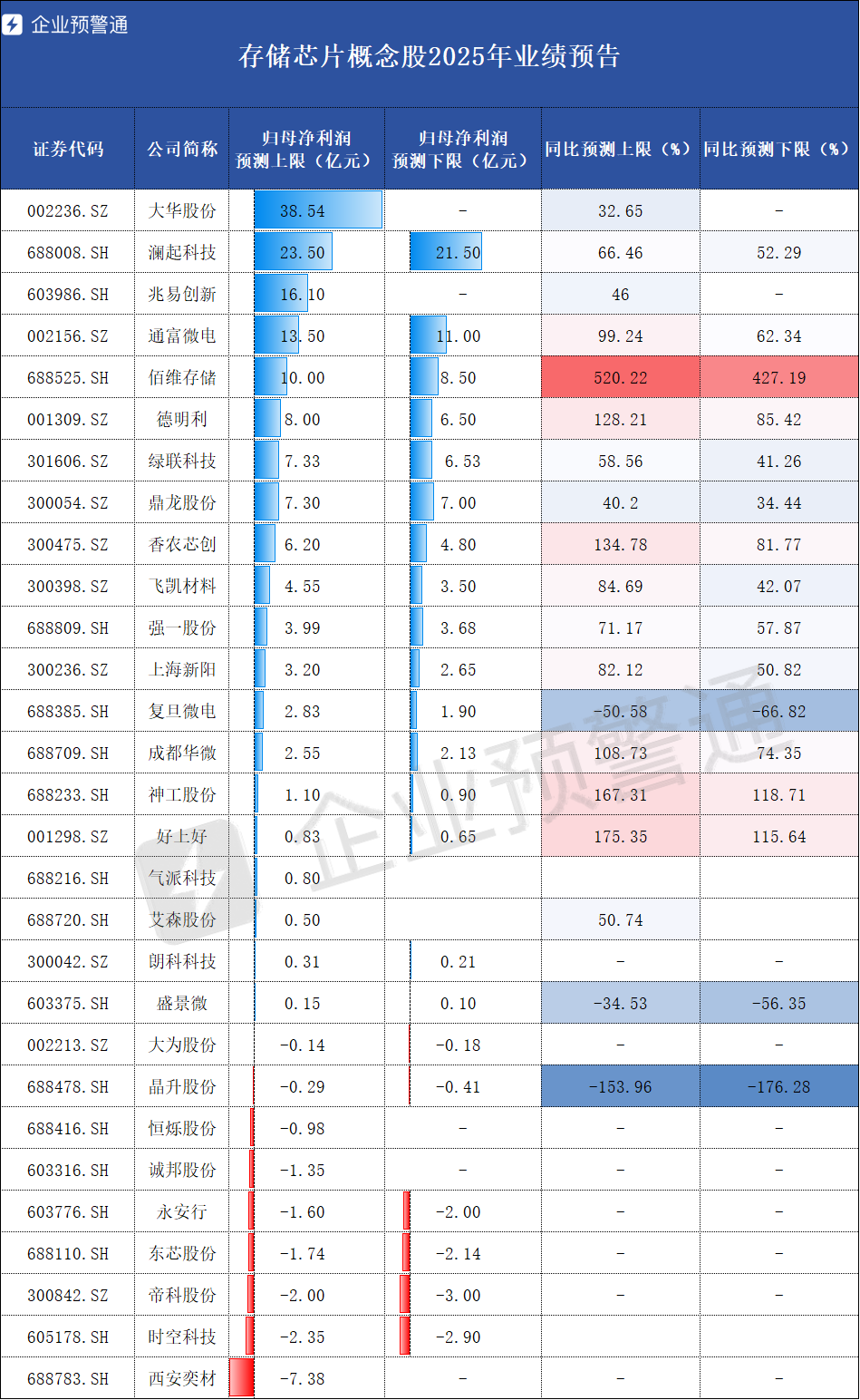
In the earnings previews, several small-to-mid-cap companies demonstrated remarkable growth potential, representing the industry's 'second growth curve.' Biwin Storage (688525.SH) emerged as the fastest-growing firm, with a year-on-year growth rate ranging from 427.19% to 520.22% and a net profit forecast of RMB 850 million to RMB 1 billion. Its layout (strategic layout ) in memory modules and advanced packaging aligns precisely with AI servers' demand for high-performance storage. The company also confirmed in investor research that storage product prices are expected to rise continuously in the first and second quarters of 2026.
Haoshanghao and SG Microelectronics followed closely, with year-on-year growth rates of up to 175.35% and 167.31%, respectively. The former benefits from consumer electronics storage upgrades in memory distribution and solution design, while the latter leverages technological breakthroughs in semiconductor silicon materials to gain an edge in the upstream materials segment of memory chips.
Shannon Systems reported a year-on-year growth rate of up to 134.78%, with a net profit forecast of RMB 480 million to RMB 620 million. Its synergy between memory chip agency and self-developed module businesses enables rapid profit realization during industry price hikes. The explosive growth of these companies validates the opportunities in niche segments of the memory industry—whether in HBM support, memory materials, or distribution. Precise entry into high-demand areas allows small-to-mid-sized manufacturers to achieve leapfrog development.
While some rejoice, others face challenges. During the industry's boom, some companies have not escaped losses, exposing accelerated risks. In contrast to the high-performance firms, nine companies reported losses in their 2025 previews, reflecting the industry's cutthroat competition. Xi'an Yicai emerged as the biggest loser, with a net profit forecast of a RMB 738 million loss. Dongxin Semiconductor and Jingsheng Technology also expect losses for the previous year.
Fudan Microelectronics and Shengjing Micro, while not incurring losses, saw significant year-on-year profit declines. Fudan Microelectronics forecasts a net profit of RMB 190 million to RMB 283 million, down 50.58%-66.82% year-on-year. Shengjing Micro expects a net profit of RMB 10 million to RMB 15 million, a 34.53%-56.35% decline. The core reason for the profit slump is their products' inability to meet AI-driven high-end storage demands, remaining reliant on traditional consumer electronics markets, which are being squeezed by high-end products like HBM, leading to a double decline in orders and profits.
AI Demand and Capacity Allocation Extend Industry Shortage Until 2027
The performance divergence among memory chip concept stocks essentially reflects the industry's structural transformation. From 2025-2026, the global memory chip industry is undergoing a 'demand restructuring, capacity allocation, and technological upgrading' triple transformation, driving sustained price increases. This tight supply situation is expected to persist until 2027, offering long-term opportunities for domestic manufacturers.
AI Demand Reshapes the Memory Market, Making High-End Products 'Strategic Assets.' The primary driver of this memory chip price surge is the 'rigid hunger' for high-performance storage in AI infrastructure. A high-performance AI server requires 8-10 times more DRAM and three times more NAND flash memory than traditional servers. Storage costs now account for 35%-40% of total AI server hardware costs, up from 20%.
HBM, in particular, is indispensable for AI large model training, boosting bandwidth over tenfold through 3D stacking technology. Giants like OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft are paying hefty premiums to secure capacity, with orders already booked beyond 2027.
This demand is not a short-term fluctuation but a long-term structural shift. As AI transitions from training to large-scale inference applications, 'storage-as-computation' technology becomes a core path for cost reduction and efficiency gains, further driving high-end storage demand. Data shows that DRAM industry revenue surged 30.9% quarter-on-quarter to USD 41.4 billion in Q3 2025, while enterprise SSD revenue jumped 28% quarter-on-quarter to USD 6.54 billion, hitting annual highs and confirming the AI-driven demand explosion.
Leading Manufacturers Shift Capacity to 'High-Margin, High-End' Products, Widening Supply-Demand Gaps in Mid-to-Low-End Markets. Faced with the high-profit allure of AI demand, Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron—controlling over 90% of the global DRAM market—have made clear strategic choices. They are allocating over 80% of new advanced capacity to HBM and server-grade DDR5 while actively cutting or halting production of mature products like DDR4.
Critically, producing 1GB of HBM consumes three times the wafer area of traditional DRAM. Even with wafer fabs operating at full capacity, the capacity left for traditional sectors like mobile phones, PCs, and automotive has shrunk dramatically. This capacity allocation directly causes supply-demand imbalances in mid-to-low-end markets. Price-wise, from late 2024 to December 2025, 16GB DDR4 memory module prices skyrocketed by 1,800%. Samsung raised NAND flash memory supply prices by 100% in Q1 2026, far exceeding earlier forecasts of 33%-38%.
The global memory chip supply-demand imbalance provides a rare substitution window for domestic manufacturers. Beyond Biwin Storage and GigaDevice's high growth, ChangXin Memory Technologies saw its 2025 DRAM shipments rise 50% year-on-year, increasing its global market share from 6% to 8% and achieving its first annual profit, with net profit ranging from RMB 2 billion to RMB 2.5 billion. Its DDR4 products are steadily replacing imports in domestic consumer electronics and industrial sectors.
Yangtze Memory Technologies achieved breakthroughs in QLC and TLC NAND flash memory technologies, with 2025 shipments ranking among the global top ten. Its consumer-grade SSD products, leveraging cost-effectiveness, captured over 12% of the domestic market share last year.
In the packaging and testing segment, Tongfu Microelectronics (002156.SZ) forecasts a net profit of RMB 1.1 billion to RMB 1.35 billion, with a year-on-year growth rate of up to 99.24%. The company raised RMB 4.4 billion for storage packaging and testing capacity upgrades, becoming one of the few domestic firms capable of handling HBM packaging and testing orders.
Meanwhile, domestic manufacturers are accelerating capitalization and supply chain collaboration. GigaDevice completed its H-share listing in January 2026, issuing shares at HKD 162.00 each and raising a net amount of HKD 4.611 billion (approximately RMB 4.2 billion) for NOR Flash and DRAM technology R&D. ChangXin Technology filed for a STAR Market IPO, seeking to raise RMB 29.5 billion for advanced DRAM production line construction, marking a shift from 'technological breakthroughs' to 'scale expansion' in domestic memory.
The 'super cycle' for memory chips in 2025-2026 is fundamentally an industry transformation driven by the AI technological revolution and global capacity restructuring. The performance divergence among domestic concept stocks is a true reflection of this transformation. Leading firms leverage technological and scale barriers to secure high-end orders, while niche market dark horses achieve explosive growth through precise layout . Conversely, firms with technological lag and poor adaptability struggle in the cycle, intensifying the industry's 'Matthew effect.'
From an industry outlook, the memory chip shortage is expected to persist until 2027, with some institutions projecting it could extend to 2028. AI servers and data centers will continue to drive industry growth. TrendForce forecasts that the global memory chip market will reach USD 551.6 billion in 2026, up 134% year-on-year.
For domestic manufacturers, this presents both substitution opportunities and technological challenges. Only by continuously increasing R&D investment, addressing shortcomings in high-end fields, and promoting supply chain collaboration can they secure a more prominent position in the global memory chip competition.
From Shengma Finance's perspective, investors should view industry divergence rationally. The performance growth of leading firms and high-quality players in niche segments is sustainable, warranting focus on technological barriers and order backlogs. Firms reliant on traditional businesses and lacking core competitiveness should be monitored for further profit declines. With AI technology's continuous penetration and accelerated import substitution, the memory chip industry will undergo deeper structural transformations, reshaping the global semiconductor industry's competitive landscape.
END
Follow us for more exciting content.
Original content by Shengma Finance. Unauthorized reproduction prohibited.