Collaborating with UBTECH: Huawei Aims to Craft a "HarmonyOS Universe" for Robotics, Can It Replicate HarmonyOS Success?
![]() 05/15 2025
05/15 2025
![]() 573
573
Huawei has demonstrated its prowess in assisting not just the automotive industry but also in the burgeoning field of robotics.
Huawei is poised to establish a new "HarmonyOS Universe" within the robotics sector.
From the introduction of the term "robot" by Czech writer Karel Capek in 1921 to the Unitree robots dancing at the 2025 Spring Festival Gala, the robotics industry has finally reached a moment of explosive growth after more than a century.
On May 12, Huawei signed strategic cooperation agreements with UBTECH and Tencent Cloud, alongside Ecoman Technology, in Shenzhen. While Tencent and Ecoman Technology signed a cooperation agreement solely for cloud services, Huawei's engagement is comprehensive, encompassing innovative collaboration with UBTECH in product technology R&D, scenario applications, and industrial systems.

(Image source: Generated by Doubao AI)
As early as 2022, Huawei collaborated with the robot unicorn CloudMinds Robotics (though rumors suggest this robot company has since faced bankruptcy). By late 2024, Huawei explored robot applications in 5.5G network scenarios with China Mobile and Ubtech Robotics. Partnering with UBTECH, one of the Four Dragons of Embodied Intelligence, marks Huawei's formal entry into the field of humanoid robots.
The robotic "HarmonyOS Universe" has arrived!
In recent years, numerous companies from various fields have ventured into robotics, including automakers like Tesla, XPeng, and BYD, as well as appliance giants such as Midea and Haier. Depending on their strengths and market strategies, some companies have opted for independent robot development, while others have chosen to collaborate with the supply chain.
The collaboration between UBTECH and Huawei stands out. Huawei announced it will provide technological innovations like Ascend, Kunpeng, Huawei Cloud, and large models, along with its expertise in R&D, production, and supply. Coupled with UBTECH's full-stack humanoid robot technology, this will enhance robot efficiency across industrial and household scenarios, accelerating their commercialization.
From the official announcement, Huawei's cooperation with UBTECH is deeply integrated, encompassing data center computing power, Huawei Cloud services, large model technology support, and comprehensive empowerment for UBTECH in R&D and production supply. While Huawei has registered the "MATEROBOT" trademark, it remains uncertain whether it will independently produce robots.
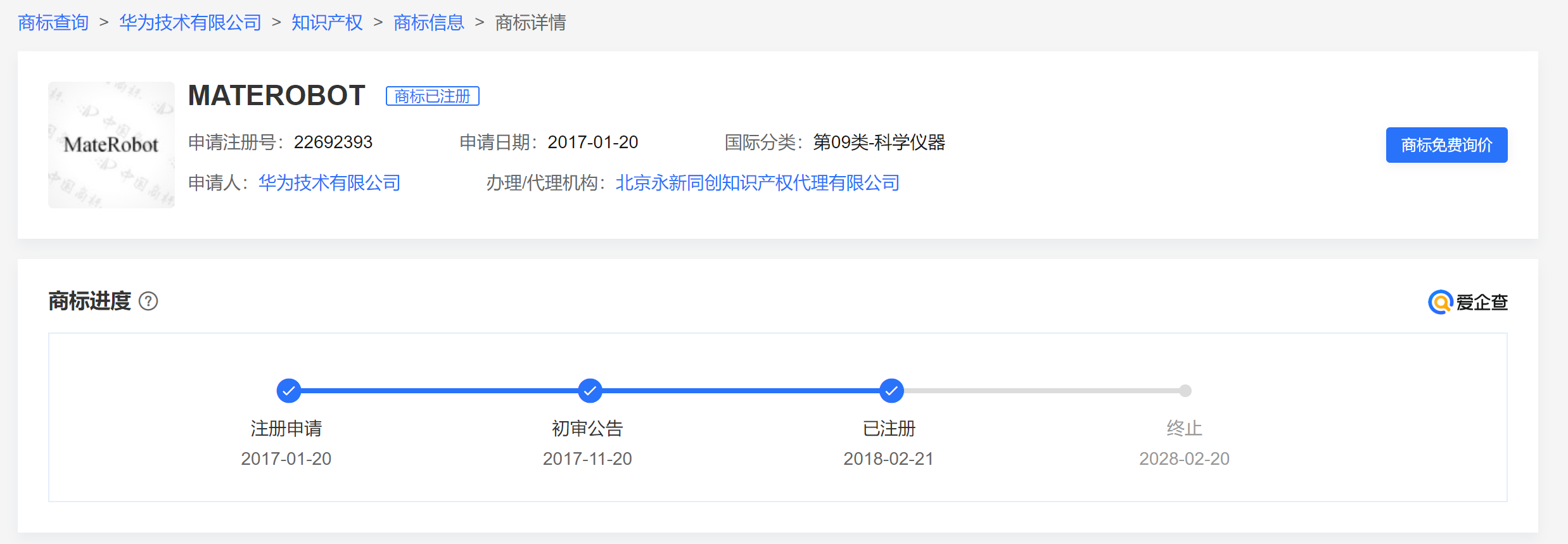
(Image source: Screenshot from Aiqicha)
Huawei's collaboration model with UBTECH echoes its HarmonyOS Intelligence strategy. After entering the automotive industry, Huawei proposed three cooperation models—Smart Selection, Hi, and components—transforming into a supplier rather than a car manufacturer.
Both the automotive and robotics industries are capital-intensive and require significant entry costs. Despite being a domestic mobile communication giant, Huawei faces considerable risks in these sectors. However, excelling in the supply chain can generate substantial revenue, comparable to that of automakers. For instance, Bosch's 2024 revenue reached 90.3 billion euros, and ZF's was 41.4 billion euros, both exceeding domestic automakers like Great Wall and Changan.
Upon entering the humanoid robotics industry, Huawei is likely to replicate its automotive strategy, creating a brand akin to HarmonyOS Intelligence and collaborating with robotics manufacturers to empower them with its technological prowess and brand influence. This will accelerate the mass production and commercialization of humanoid robots, enriching their application scenarios. With HarmonyOS Intelligence as a precedent, Huawei's robotics brand endeavor should not prove challenging.

(Image source: HarmonyOS Intelligence)
Regarding whether Huawei will independently produce robots, the company has yet to comment. Supply chain enterprises like Fenda Technology, Anlian Ruishi, Hengtong Optoelectronics, Hanwei Technology, iSoftStone, and Runhe Software have announced collaborations with Huawei in robotics, suggesting potential plans for in-house robot manufacturing.
However, the robotics industry is just entering large-scale mass production, with numerous participants and more anticipated. For example, NIO has expressed interest in entering the robotics industry. The risks in robotics may surpass those in the new energy automotive sector. Therefore, Huawei may empower its supply chain partners' outcomes, such as UBTECH or other deeply collaborating robotics enterprises, rather than independently producing robots.
In the first year of robot mass production, Huawei aims to be a vital support.
From the publication of regulations like the "Industrial Robot Industry Specification Conditions (2024 Version)" and the "Measures for the Administration of Industrial Robot Industry Specification Conditions (2024 Version)" to Unitree robots dancing at the Spring Festival Gala and the emergence of "embodied intelligence" and "intelligent robots" in National Two Sessions reports, various signs indicate increasing domestic support for the robotics industry.
Simultaneously, enterprises like Unitree Technology, UBTECH, Zhiyuan Robotics, and Tesla have announced plans for humanoid robot mass production in 2025, with expected capacities exceeding 1,000 units this year. Tesla CEO Elon Musk stated in an interview that thousands of Optimus humanoid robots will be produced this year, with capacities increasing tenfold next year to 50,000 to 100,000 units. Domestic media and netizens have dubbed 2025 the "first year of humanoid robot mass production".
(Image source: UBTECH)
However, as humanoid robots enter mass production, robotics enterprises face another challenge: penetrating industrial and household service markets.
XPeng, Tesla, and BYD have automobile factories, enabling their robots to initially assist on production lines. Even if costs exceed hiring employees, it serves as a robot test. Robotics startups lack this characteristic and must prove the superiority of robotic employees to enterprises before factory entry, incurring additional costs.
Huawei's entry will undoubtedly provide technical support to partners like UBTECH. Training large models suitable for robots requires computing power and data. As one of China's top three cloud service providers (alongside Alibaba Cloud and Tencent Cloud), Huawei Cloud possesses large-scale data centers and has developed high-performance chips like Ascend and Kunpeng, offering computing power support to partners.
Huawei's self-developed assisted driving solution can also enhance robots' spatial perception and decision-making capabilities. Li Xiang, CEO of NIO, once stated that the ultimate form of an automobile is a spatial robot, and achieving L4-level autonomous driving is crucial for NIO's entry into robotics. In terms of spatial perception and decision-making, autonomous vehicles and robots share a common origin. Huawei's assisted driving technology is robust and can empower partners by leveraging its end-to-end large model technology for intelligent driving, helping robotics enterprises create more powerful large models for robots.
Beyond technology, Huawei offers two significant advantages to robotics enterprises. The first is sales expansion capability. With multiple large-scale production bases in cities like Shenzhen, Huizhou, and Dongguan, and collaborations with automakers like Thalys, Chery, JAC, and BAIC, UBTECH, which partners with Huawei, may send its robots to Huawei's factories or those of brands collaborating with HarmonyOS Intelligence.

(Image source: Generated by Doubao AI)
The second advantage is brand empowerment. Currently, due to technological immaturity, humanoid robots primarily target the B-end market, where brand influence demand is low. However, as robots enter household service scenarios, C-end market consumers place greater emphasis on brands. Thalys' transformation from Dongfeng Xiaokang to a leader in China's new energy automotive industry is largely attributed to Huawei's influence.
Once robots enter household scenarios, they will become part of smart homes, and it's crucial they can connect with other smart ecosystems. Requiring specific apps for remote robot control would compromise the user experience. By accessing Huawei's smart ecosystem, UBTECH robots can be voice-controlled anytime, anywhere, similar to cars integrated with HarmonyOS Intelligence.
Robotics enterprises must consider both technology and market, and few enterprises can provide these advantages. Huawei is one such entity. With robots poised for large-scale mass production this year and potential capacity doubling next year, Huawei is well-positioned to be a "golden assist" for its partners.
As the robotics industry heads towards a trillion-dollar market, choosing the right direction is crucial.
In 2024, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang stated in an interview that robot technology would achieve significant breakthroughs within 2-3 years and become as ubiquitous as automobiles. In the interview's comments section, Musk noted that robots' popularity would surpass that of cars by tenfold. While robot product maturity will take time, industry insiders have outlined the sector's vast potential.
The challenge is that, like the new energy automotive industry, robotics presents both opportunities and risks. CloudMinds Robotics, which collaborated with Huawei in 2022 and once had a higher valuation than Unitree Technology, now faces a liquidity crisis due to a broken capital chain. According to a Sohu News report, CloudMinds Robotics has been laying off employees consecutively, leaving only about 10 employees in its Beijing R&D center, which once housed 50 to 60.

(Image source: CloudMinds Robotics)
Perhaps mindful of the risks, Huawei aims to create a second HarmonyOS Intelligence in robotics. Enterprises like XPeng, Tesla, and Xiaomi have strong brand influence and may not need deep collaboration with Huawei. If needed, they can follow a route similar to HarmonyOS Intelligence's Hi and component models, seeking technical support from Huawei.
Apart from Unitree Technology, which gained fame through the Spring Festival Gala, other robotics startups are only well-known within the industry. Collaborating with Huawei can address multiple challenges, including data centers, technology, and brand influence, accelerating robot mass production and functional upgrades.
Robotics enterprises need a first-mover advantage to establish a market foundation. The first batch of enterprises to mass-produce humanoid robots for the C-end market stands a chance to gain a title akin to the "Big Three of New-Energy Vehicle Startups." While UBTECH possesses strong technical expertise, it can fully unleash its potential only with Huawei's empowerment, testing products in B-end scenarios and leveraging Huawei's brand influence to explore the C-end market.
Source: Leitech