Hyundai Mobis's 2025 Transformation: Betting on Seven Key Technologies to Seize Future Mobility Tracks
![]() 09/01 2025
09/01 2025
![]() 641
641
Produced by Cheena Tech
Amidst the accelerated electrification and intelligent transformation of the global automotive industry, Hyundai Mobis's role is subtly evolving.
Historically, it served as the "behind-the-scenes factory" for the Hyundai Motor Group, primarily supplying core components like brakes, steering systems, and lighting. However, as we approach 2025, Mobis is increasingly resembling a proactive player seeking change – no longer content with merely supporting but aiming to occupy a more prominent position in the future mobility industry chain.
This transformation is evident in the technological directions Mobis is pursuing: from windshield holographic displays and electro-mechanical braking to steer-by-wire, software-defined vehicles, electrification systems, semiconductors, and robotics. These technologies cover nearly all key aspects of intelligent mobility.
Simultaneously, Mobis is becoming more aggressive in its global expansion and capital operations, establishing deeper ties with OEMs in markets like North America, Europe, and China through regional manufacturing centers and R&D hubs.
Behind this strategy lies a clear logic: during the pivotal moment of the automotive industry's transformation, automotive parts companies can only solidify their position in future competition by simultaneously mastering cutting-edge technologies, securing customer resources, and maintaining financial stability.

01 Product System Driven by Cutting-Edge Technology
Hyundai Mobis's strategic vision is clear: to lead the transformation of mobility. This vision revolves around three core strategies – "mastering cutting-edge technology, focusing on profitability, and accelerating global customer expansion" – forming a closed loop encompassing technology research and development, product implementation, and global layout.
In terms of cutting-edge technology, Mobis is building its competitiveness in future vehicles and intelligent mobility through seven key areas: windshield displays, software-defined vehicles, electro-mechanical braking, steer-by-wire, electrification components, automotive semiconductors, and robotics.

◎ The Windshield Display embodies Mobis's forward-thinking in interactive experiences. Through collaborations with ZEISS and Envisics, utilizing holographic optical film and computer-generated holography, Mobis aims for mass production from 2028 to 2029, offering OEM customers high-end design flexibility and enhancing consumers' intuitive driving safety and information visualization experience.
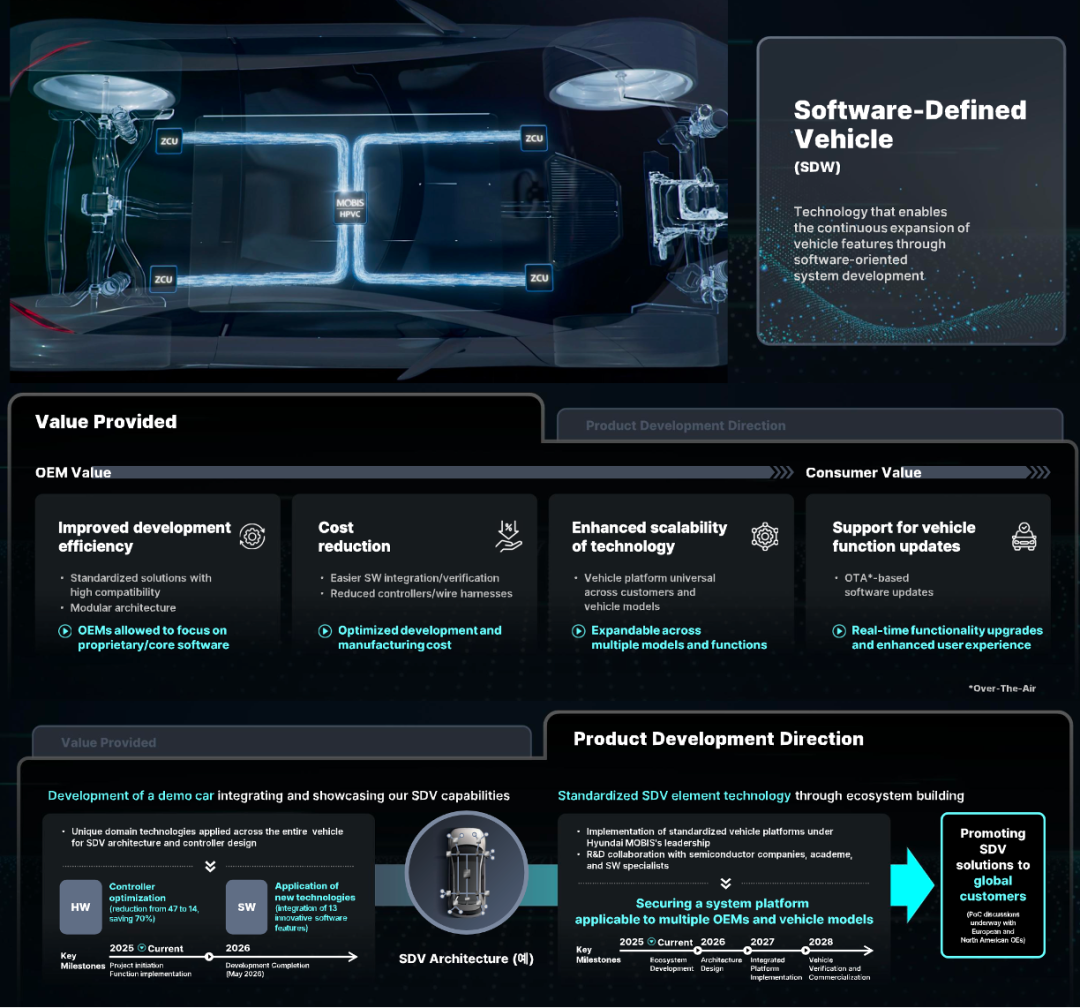
◎ Software-Defined Vehicles (SDV) enable OTA upgrades and continuous feature expansion through modular architecture, standardized development, and common vehicle platforms across customers and models. Mobis has mapped out a clear path, starting from project initiation in 2025 to global customer promotion by 2028, collaborating with semiconductor companies and academia in R&D.

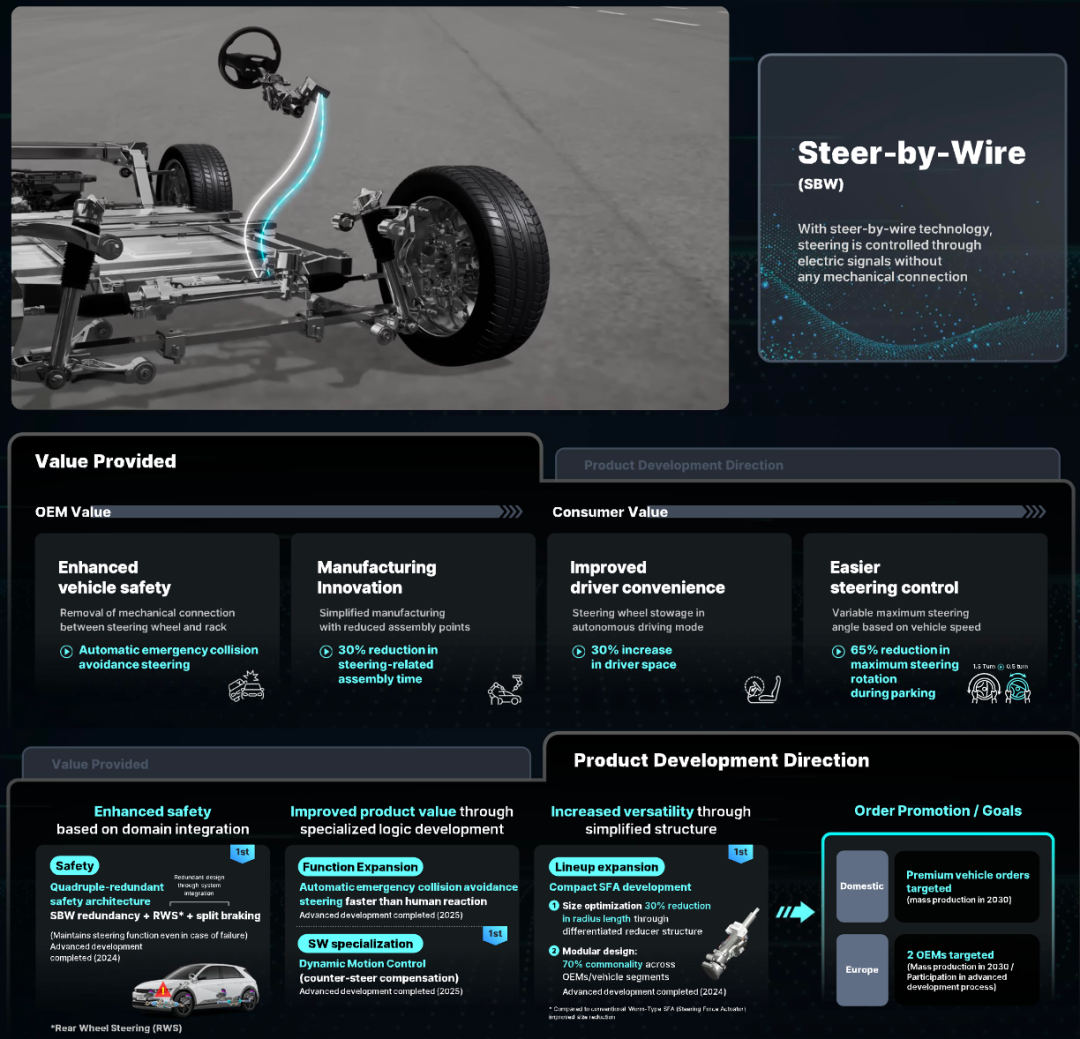
◎ In chassis and safety technology, the Electro-Mechanical Braking System (EMB) and Steer-By-Wire (SBW) achieve precise control of braking and steering through wire control technology, enhancing vehicle response speed and safety redundancy while optimizing manufacturing and assembly efficiency. EMB applies braking force through independent motors, reducing braking distance and maintenance costs, with mass production expected in 2025 and expansion into orders from mainstream automakers in Europe and the US. SBW improves autonomous driving safety and driving space through modular design and multiple redundancies, aiming for mass production in domestic high-end models by 2030 and expansion into the European market.
◎ In electrification components, Mobis promotes the development of CTP (Cell to Pack) and X-in-1 integrated power conversion systems through three technical routes: battery safety, charging convenience, and cost accessibility. With thermal diffusion prevention, 800V high-voltage systems, 22kW high-power ICCUs, and high-energy-density battery solutions, Mobis achieves improvements in range and charging efficiency while reducing system costs.

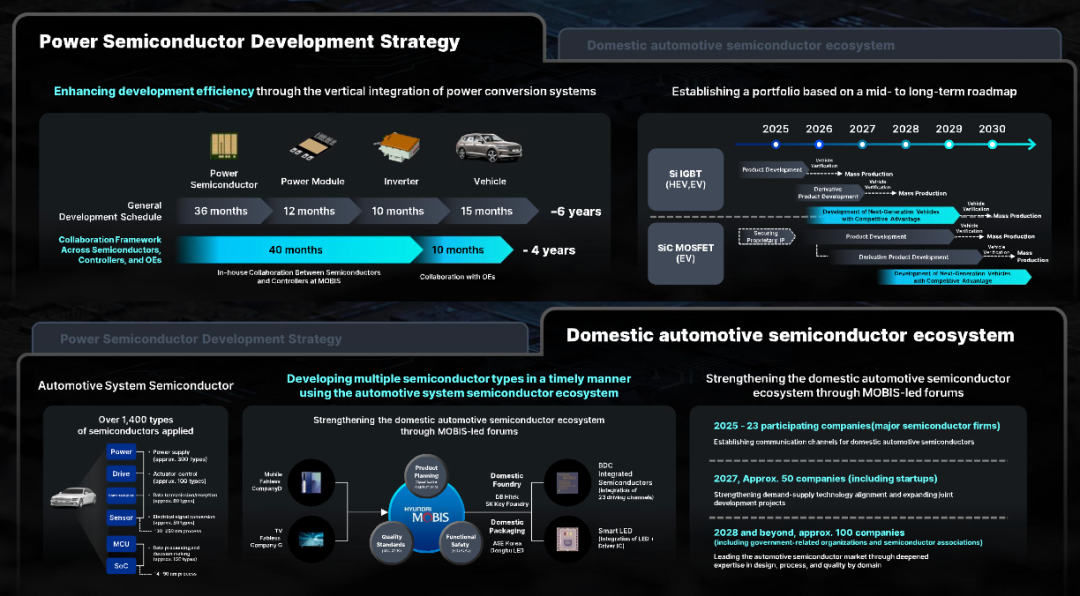
◎ The semiconductor business is crucial for Mobis to build autonomous control and core competitiveness. System semiconductors establish a local automotive semiconductor ecosystem through the development of network SoCs and BMICs; power semiconductors achieve vertical integration of inverters and power conversion systems through the development of Si IGBTs and SiC MOSFETs. Combined with robotics technology, Mobis accumulates experience in the actuator field, expanding from automotive parts mass production capabilities to robot core components, fostering a technology transfer effect.

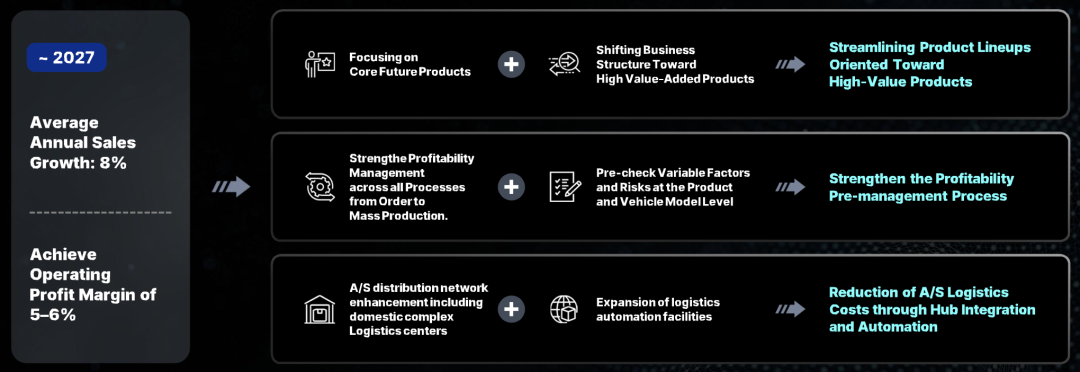
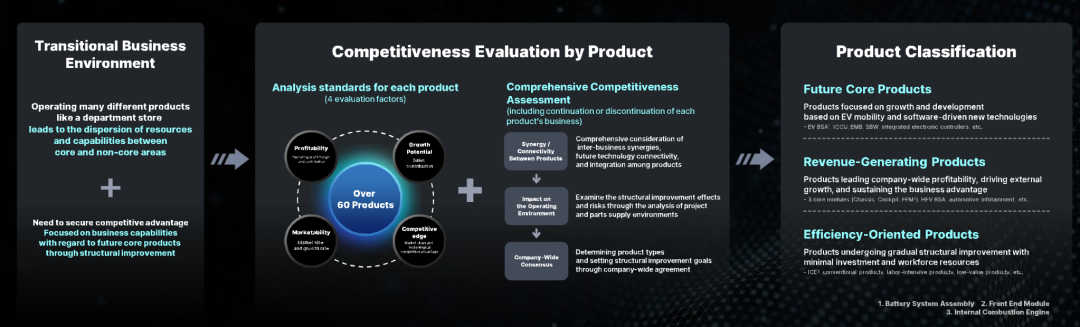
Enhancing profitability hinges on product line streamlining and resource allocation. Mobis concentrates R&D investment on core products, optimizes product development profit and loss management processes, and reduces costs through the deployment of global logistics and manufacturing hubs. The target for 2027 is an average annual revenue growth rate of 8% and an operating profit margin of 5-6%, achieving synchronized growth in quality and efficiency through an increase in core product revenue share and optimization of non-core products.
02 Global Customer Expansion and Financial Strategy
Global customer expansion forms another cornerstone of Hyundai Mobis's strategy.
Gradually moving beyond local market dependence to emerging and global high-end markets, Mobis enhances customer penetration through joint development models and regional localization strategies.
◎ Focusing on Ford, GM, and Rivian in the North American market, supplying core components such as braking systems and display systems;
◎ Covering Stellantis, Polestar, and VW in the European market, breaking through with complex modules and steer-by-wire systems;
◎ Leveraging the foundation of Hyundai/KIA in the Indian market and aligning with local automakers' development needs to gradually foster order growth;
◎ In the Chinese market, promoting global competitiveness through technology feedback and HUD/AR/LiDAR products.

In terms of financial strategy, Mobis maintains robust and flexible capital operations. With revenue of 57.2 trillion Korean won and an operating profit margin of 5.4% in 2024, it faces challenges from EV demand fluctuations and geopolitical risks.
To achieve the 2027 targets of an 8% CAGR in revenue and an operating profit margin of 5-6%, the company has devised a three-year cash utilization plan totaling 9 trillion Korean won. Of this, approximately 6 trillion Korean won will be invested organically in manufacturing hub expansion and future growth engines, approximately 3 trillion Korean won will be invested inorganically in mergers and acquisitions and partnerships, and 3-4 trillion Korean won will be returned to shareholders through dividends and share buybacks, ensuring stable returns.
The global hub layout not only optimizes manufacturing and logistics costs but also supports the rapid growth of the electrification business. Regional manufacturing and R&D centers in North America, Europe, and India establish a one-stop service capability of "local design-delivery," flexibly responding to uncertainties in the EV market and catering to diverse customer needs through CTV technology, cylindrical/prismatic battery solutions, and differentiated powertrain designs.
Concurrently, through independent R&D of semiconductors and software platforms, Mobis realizes synergies from hardware to software, further strengthening strategic ties with customers.
Summary
Hyundai Mobis's story is one of self-breakthrough for traditional parts suppliers, gradually shifting from "supplying parts" to "providing solutions" through technology investment and global layout, and striving to find a balance between growth and stability through financial robustness and shareholder return policies.
Transformation comes at a cost. High R&D and manufacturing investments require time to pay off, and industry uncertainties – such as fluctuations in electric vehicle demand, geopolitical factors, and semiconductor cycles – may make this path even more challenging.






