Nissan's Financial Struggles: Can It Rebound?
![]() 05/19 2025
05/19 2025
![]() 621
621
In recent years, Nissan's most notable headline came in 2018 when "cost killer" Chairman Carlos Ghosn abruptly stepped down. Since then, the automaker has been mired in news of aging models, poor cash flow, and managerial turmoil. For several months, Nissan seemed poised to welcome a financial savior. However, in early 2025, news broke that Honda would merge with Nissan, only for the talks to be suspended within two months due to escalating disagreements over shareholding issues. This dashed Nissan's transactional prospects, leaving its future uncertain.

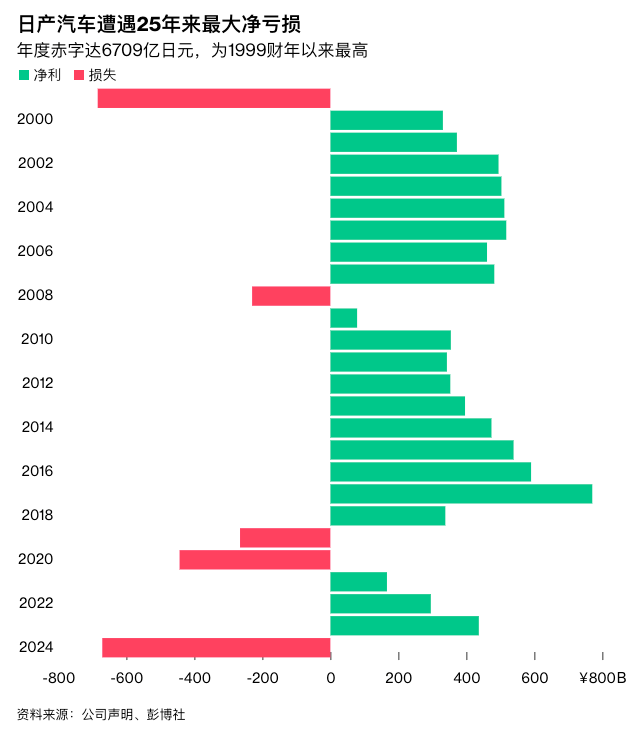
Matters worsened when U.S. President Trump imposed tariffs on imported cars, further complicating Nissan's hopes for a swift turnaround, given that nearly half of its U.S. sales come from imports. On May 13, Nissan announced its worst financial performance in 25 years, revealing a restructuring plan that included factory closures and layoffs of 20,000 employees to curb widening losses.
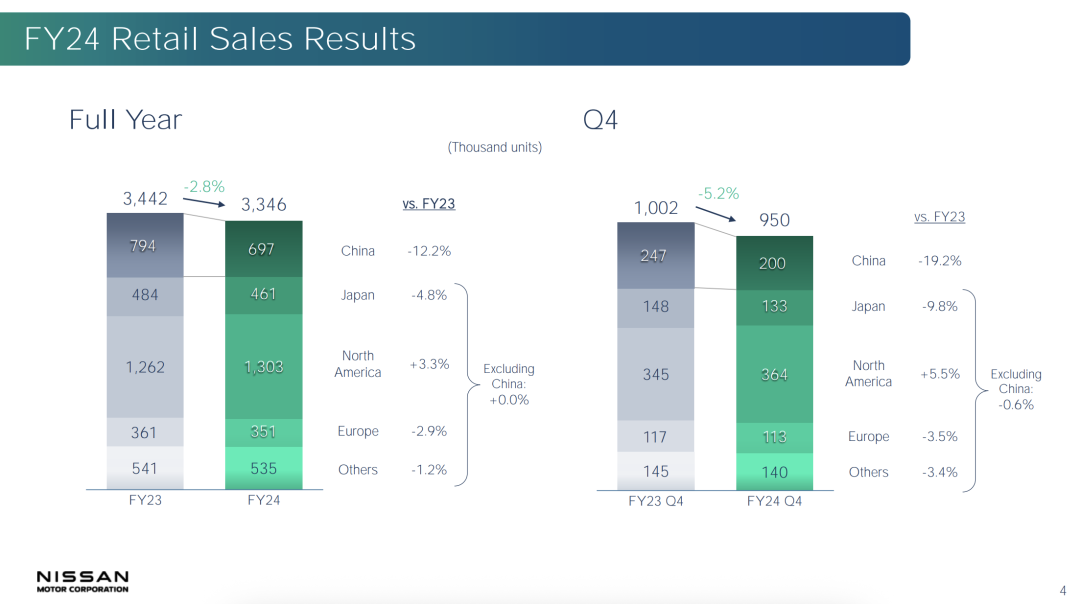
For fiscal year 2024, Nissan reported a net loss of 670.9 billion yen (approximately $4.5 billion), marking its largest annual loss since French automaker Renault rescued it from the brink of bankruptcy 25 years ago. Free cash flow turned negative, and the operating profit margin plummeted from 4.5% the previous year to 0.6%.
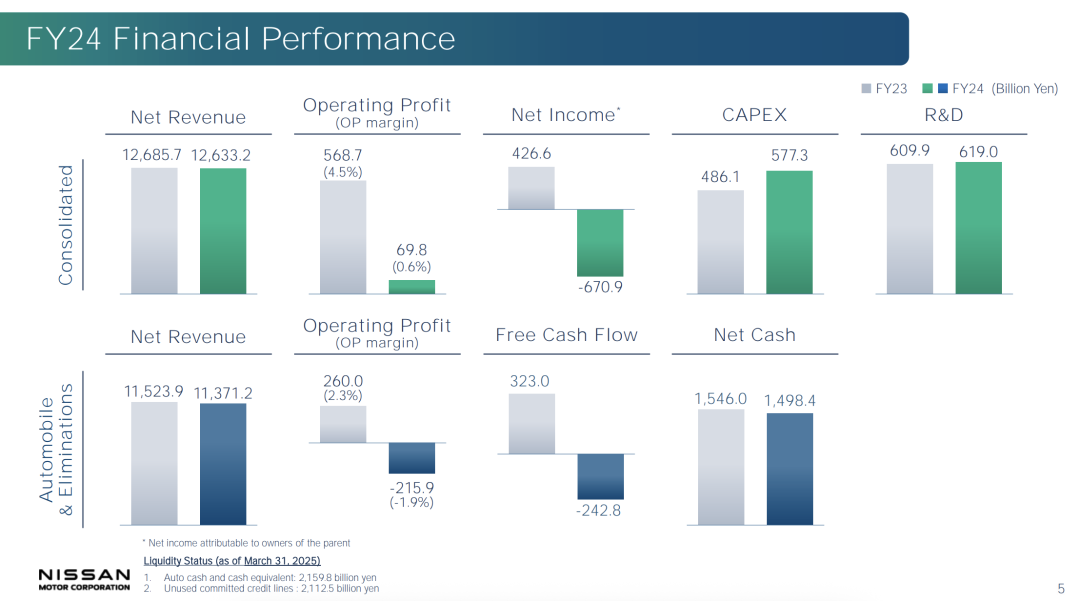
Nissan anticipates a decline in sales in the U.S., its largest single market, in 2025, even without considering the impact of tariffs. This is due to overcapacity and a lack of consumer demand. As Nissan bluntly stated in its recent investor report, "Fixed costs remain higher than the level that current revenue can support." To address this, Nissan plans to slash 500 billion yen in costs over the next three years by maximizing engineering and supply chain efficiency, which includes layoffs and workforce reduction. Following 9,000 job cuts last year, Nissan will lay off over 10,000 more starting in 2025, with 65% being production personnel, 18% sales and service personnel, and 17% R&D personnel.
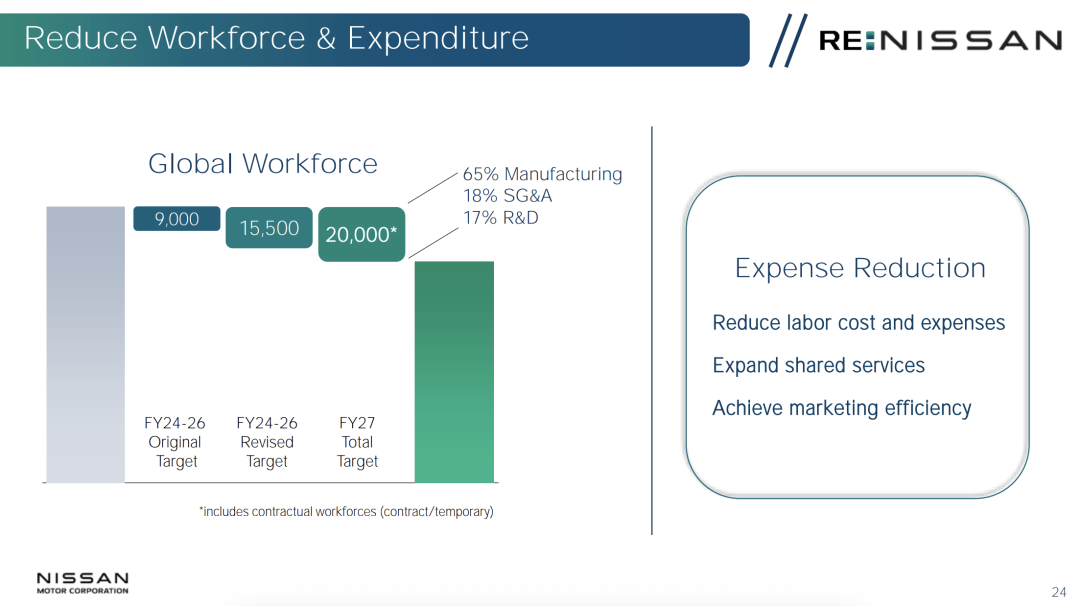
By closing factories and reducing capacity, Nissan aims to decrease the number of global factories from 17 to 10 and cut global annual production capacity from 3.5 million vehicles last year to 2.5 million, thereby boosting factory utilization from 70% to nearly 100%.
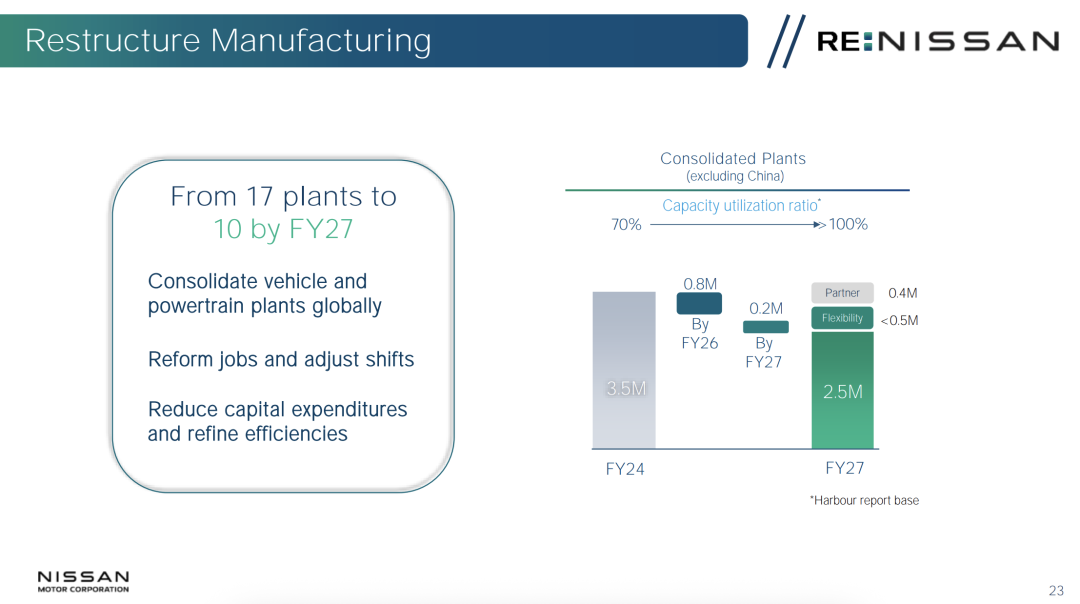
Reportedly, overcapacity was a crucial issue that led to the collapse of merger negotiations with Honda. What lies behind Nissan's plight? A decade ago, Nissan was heralded as an EV pioneer with the Leaf, the world's first mass-produced electric vehicle. However, over a decade later, its product line has become outdated, leading to inventory backlogs and price reductions. In China, for instance, competitors like Tesla and BYD have launched EVs with superior acceleration and range. In terms of hybrids, today's extended-range models and even BYD's DMI were inspired by Nissan's E-power launched in 2016, but Nissan failed to capitalize on this technology, shifting focus to bringing it to the global market in conjunction with local policies. As of the end of 2024, Nissan had produced only 1.5 million E-power vehicles globally, with over 1.2 million in Japan.
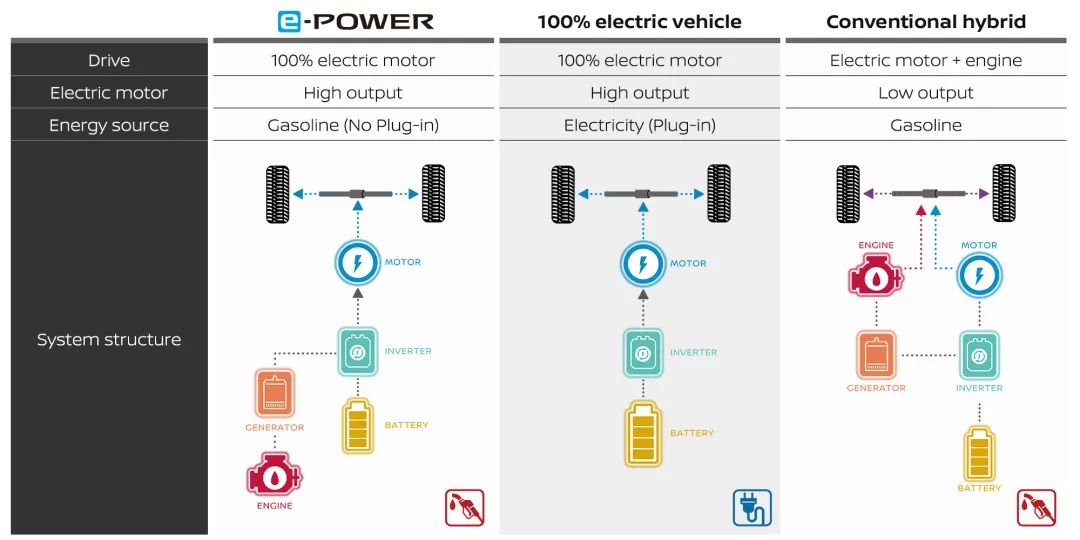
Consequently, by early 2025, Nissan still lacked the latest EV and hybrid technologies, hindering its ability to compete effectively in China and the U.S.
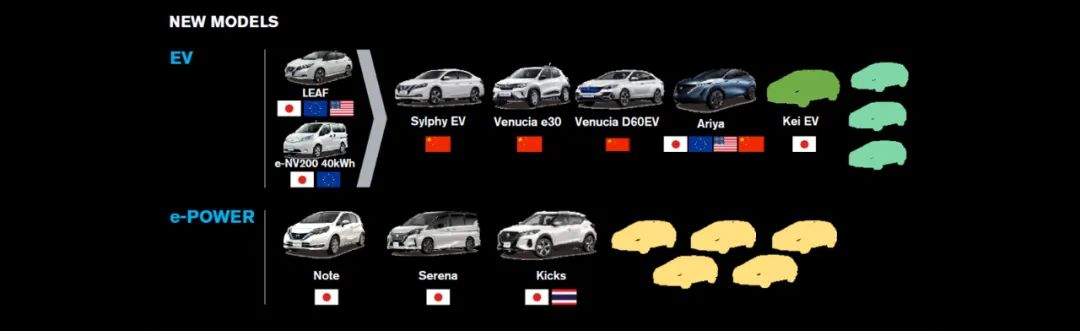
Moreover, Nissan's product planning and launch strategy has issues. It typically releases new models in clusters, followed by long periods without updates, leaving consumers without new products for extended periods. This forces dealers to reduce prices to attract buyers who might otherwise opt for more modern models from competitors. For example, sales of Nissan's most popular U.S. model, the compact crossover SUV Rogue, fell nearly 10% in 2024, prompting production cuts. Previously, the Japanese automaker discontinued the Titan full-size pickup truck, a slow-selling model designed specifically for the U.S. market. Most regrettably, Nissan transferred production of its largest and most profitable SUV models from the U.S. to Japan over the past decade, exposing its profits to the risk of Trump's import tariffs.
When did Nissan's troubles begin? The seeds may have been sown 25 years ago, after Nissan's last crisis. French automaker Renault stepped in, acquiring a controlling stake and sending "cost killer" Ghosn to turn the tide. Initially serving as Chief Operating Officer, Ghosn cut procurement costs, closed factories, and laid off 21,000 employees. Later as CEO and then Chairman, he accelerated new model launches to boost Nissan's global market share. While renowned for his cost management, he strictly controlled expenditures, resulting in models that ultimately lacked the innovativeness of competitors.

To meet Ghosn's sales targets, Nissan developed the habit of offering high price incentives to customers, especially in the U.S., and increasing sales to leasing fleet operators at the expense of profits. This strategy, also seen in Chinese companies now mired in sales and brand decline, prevented Nissan from fully leveraging the benefits of the Renault alliance through comprehensive product development cooperation. In 2018, the partnership crumbled when Ghosn was detained in Japan on suspicion of financial crimes. Since then, Nissan's outdated model lineup has plagued the company.
Why didn't Nissan's management address these issues? The company has a conservative business culture, and a series of leadership changes has made it difficult for management to reach consensus on solutions and stick to them. Ghosn's successor, Hiroto Saikawa, resigned as CEO in 2019 amidst a scandal involving excessive compensation, and other senior executives also left the company. His successor, Makoto Uchida, faced turmoil and eventually stepped down after years of failed negotiations with Honda. The little-known Mexican executive Ivan Espinosa was appointed CEO on March 11.

How does Nissan plan to rescue itself now? In addition to the aforementioned drastic measures of reducing capacity and current cost expenses, the new management's "RE:NISSAN" revitalization plan includes redefining market and product strategies and strengthening cooperation.

Redefining market and product strategies involves Nissan focusing on key markets and adopting tailored strategies for each. In North America, Nissan will adopt a self-developed approach, focusing on medium and large products. In China, it relies on the Dongfeng Nissan joint venture, highlighting Nissan's significant local development authority. For example, the recent Nissan N7 was entirely developed locally by Dongfeng Nissan, with plans to utilize China's production capacity for exports. In Japan, Nissan will focus on creating models with annual sales of 100,000 units, increasing prices, and developing K-cars with partners.

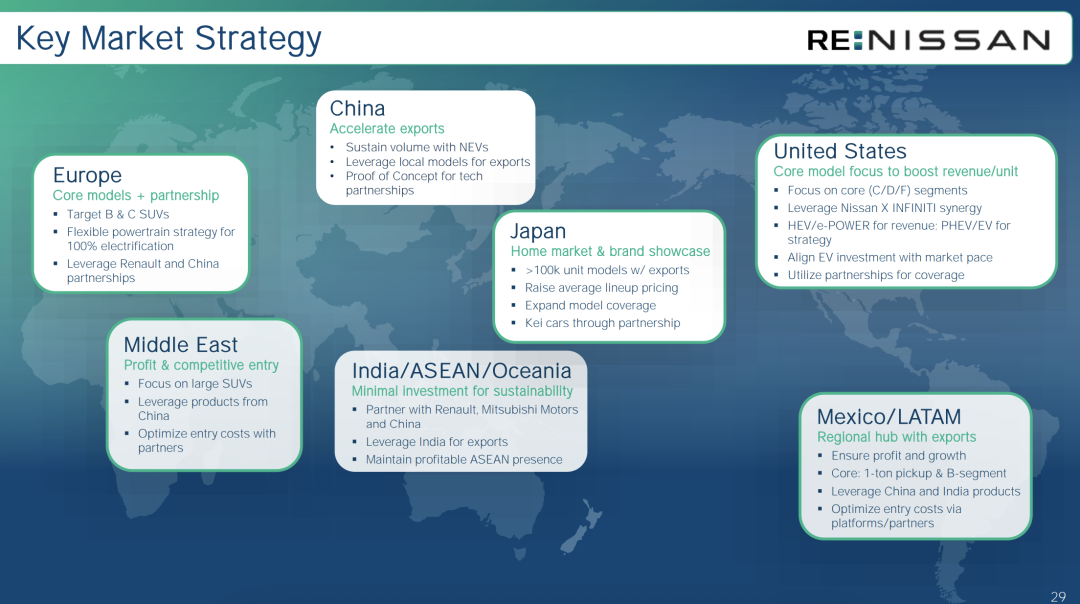
To strengthen cooperation, Nissan will generally partner with the Renault-Nissan alliance and Honda, leveraging the advantages of local partners in different regions, such as Dongfeng Nissan in China, Renault in Europe and India, and Mitsubishi in North America. It may even develop new partners.

What other options does Nissan have? The potential collapse of cooperation with Honda has reopened the door to multiple bids. One bidder is Taiwan's iPhone manufacturer Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd. (commonly known as Foxconn), which aims to leverage its electronics production experience to become an EV contract manufacturer. Even before Honda officially initiated negotiations, Foxconn had expressed interest in a deal with Nissan. As talks between the automakers fell apart, Foxconn expressed willingness to acquire Renault's stake in Nissan, and the two have been in contact. However, sources indicate that Nissan has restarted its search for a partner, possibly a U.S.-based technology company. In May this year, Nissan's CEO reiterated that the company is seeking new alliances while strengthening existing relationships.
Finally, let's consider the bigger picture. Does Nissan, Japan's first century-old automaker, have a future?
Reference articles and images
Nissan 2024 Financial Report PPT
Chinese and English transcripts of Nissan's 2024 financial report conference call * Reproduction and excerpts are strictly prohibited without permission - Access to reference materials: Join our knowledge planet to download a vast amount of reference materials from the official account, including the above reference materials.