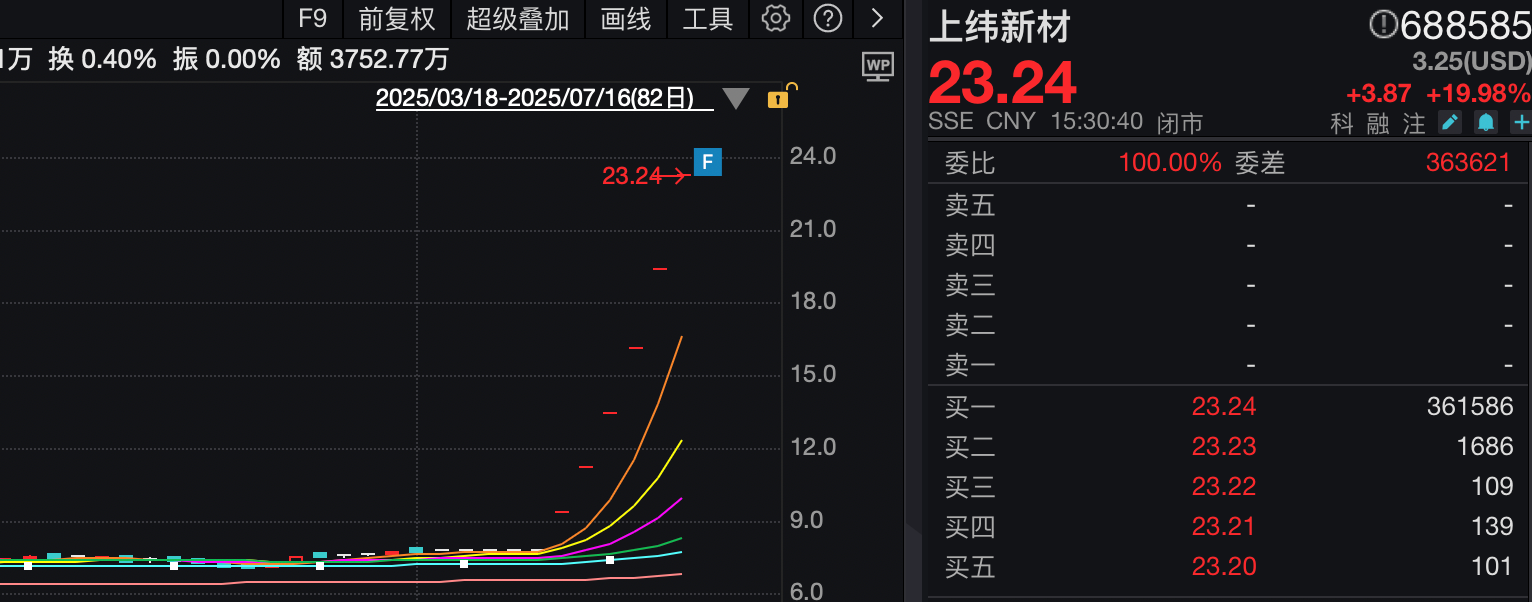
SWANCOR's Six Consecutive 20cm Daily Limits Spark Interest in Humanoid Robots
![]() 07/16 2025
07/16 2025
![]() 467
467
With six straight days of hitting the 20cm daily limit, SWANCOR has emerged as the most closely watched company in the A-share market.
In related news, some media outlets reported that Zhiyuan Robotics recently secured strategic investment from Chia Tai Robotics, a subsidiary of the Chia Tai Group.
SWANCOR's surge has also ignited the sector, with stocks related to the humanoid robot concept, such as RDI, Weichuang Electric, and Fuda, performing exceptionally well.
The robot sector is now becoming increasingly crowded.
Companies like Huawei have long been involved in humanoid robots, Unitree Robotics gained fame during the Spring Festival Gala, and giants like Tesla and BYD have also set their sights on this field.
From Boston Dynamics to Honda, and then to OpenAI and Microsoft, the advent of the generative AI era has ushered in a new wave of competition in robotics.
Robots are composed of three key technical modules: motion, sensing, and AI. For traditional robots, excellence in just one of these areas often suffices. For instance, industrial robots primarily focus on motion control, while cleaning robots emphasize navigation and sensing.
However, humanoid robots must be versatile across various application scenarios, rather than being limited to single tasks in specific settings. This complexity demands higher technology integration and fusion, modeling of larger datasets, and stronger language and command understanding capabilities. Previously, AI data and models were developed in isolation, leading to slow iteration speeds and high, unreducible costs.
The rise of large models has significantly altered this landscape.
In just a few years, the number of model parameters has soared from billions to trillions. Subsequently, large models have evolved from single-modal large models (text, speech, vision) to general AI with multi-modal fusion. This enables the direct integration of voice, vision, decision-making, control, and other technologies with humanoid robots, comprehensively enhancing their capabilities.
In April 2023, AI company Levatas collaborated with Boston Dynamics to integrate ChatGPT and Google's speech synthesis technology into the Spot robot dog, successfully enabling human interaction.
The rapid evolution of underlying technologies has showcased the potential for large-scale commercialization of humanoid robots, with major global technology companies actively making attempts and preparations. However, based on the current situation, humanoid robots still have a long way to go before truly becoming a fixture in thousands of households.
Firstly, the capabilities of humanoid robots on the market are still relatively limited and lack substitution benefits.
For example, household service humanoid robots do not yet have the ability to fully replace human daily services, and those used for commercial guidance and reception can only answer simple questions, failing to address all customer inquiries.
Consequently, humanoid robots lacking rigid substitutes are still not very appealing to end consumers.
It is also evident from the product positioning of participants that the current focus remains on exploring B-end scenarios. For instance, the first batch of mass-produced Tesla bots are likely to be deployed in superfactories, while UBTech is focused on exploring the application of humanoid robots in related industrial scenarios such as new energy vehicles and 3C electronics in collaboration with enterprises.
Secondly, many shortcomings in basic technologies remain unresolved. For instance, the robot's battery needs to support continuous operation for up to 20 hours, but most humanoid robots currently work for less than 2 hours. Another example is cost, which easily reaches tens of thousands of dollars, a price that obviously cannot be widely adopted. Manufacturing costs need to be reduced by 15%-20% annually in the future.
While humanoid robots may not be a profitable business within the next three years, they are an industry that cannot be ignored in the long term. Starting from the industry's first principle, the value of humanoid robots lies in replacing high-cost human labor, which is a highly certain event.
As for the current technical and cost issues, they will not be long-term problems.
Taking cost as an example, as long as continuous commercialization can be achieved, any new technology and product will move from high prices to low prices, as seen with computers, smartphones, electric vehicles, etc. In the past, the cost of a single humanoid robot such as Honda's ASIMO and Boston Dynamics' Atlas was as high as $3 million and $1.9 million, respectively. Now Tesla can achieve $20,000, and it will definitely go lower in the future.
The same applies to technology, which will continue to iterate and upgrade. Due to the immaturity of lithium battery technology, when Boston Dynamics launched the first-generation humanoid robot Atlas in 2013, it still needed to be powered by cables. However, when the second-generation Atlas was launched in 2016, it utilized independent lithium batteries.
Musk predicts that the long-term demand for humanoid robots will reach 10 billion units. Even if only one-tenth of this expectation is met, the industrial space will still be immense.
With the largest population and manufacturing industry, China is already the world's largest robot consumer market, with strong demand in both B-end and C-end markets in the future. Furthermore, China's software and hardware technologies in the field of robots are not far behind. The combination of these two factors fundamentally determines that China has great potential to produce a group of robot companies that can compete globally.
Currently, the leading domestic humanoid robot enterprises are UBTech and CloudMinds, founded in 2012 and 2015, respectively. From a realistic perspective, compared to UBTech and CloudMinds, the domestic humanoid robot enterprises that will truly emerge in the future are likely to be major companies such as Xiaomi and ByteDance. Major companies have obvious advantages in terms of talent, capital, market, and brand. Moreover, although UBTech and other companies started earlier, they have not established a strong leading edge, and the current revenue share of UBTech's humanoid robots is only in the single digits.
The visibility and profitability of upstream players are much stronger. Analyzing the material costs of robots, reducers, servos, and controllers account for 35%, 20%, and 15% of the cost of industrial robots, respectively, totaling 70%. Considering that humanoid robots have more joints and degrees of freedom, the proportion of these components may be even higher.
The reducer field boasts many players, including Han's Motion, Leadshine, Tongchuan Technology, Zhongdalide, Guomao, etc., all of which have certain production capacity. However, there is only one clear leader: Green Harmonic Drive. The company has established a virtuous development cycle of "R&D - expansion - profitability - re-R&D - re-expansion." As a manufacturing enterprise, Green Harmonic Drive has achieved a net profit rate of over 30%, which is no small feat.
The differentiation in the servo motor field is relatively obvious. High-end production capacity is primarily held by foreign companies such as Mitsubishi, Yaskawa, Fanuc, and Siemens. Inovance, Jiangte Motor, Jiangsu Leili, Leisai Intelligence, Haozhi Electromechanical, etc., are concentrated in the mid-to-low-end field, with Inovance being the clear leader. In 2022, Inovance's market share in the domestic servo field reached 21.5%, an increase of 5 percentage points compared to 2021. With the combination of domestic substitution and the increase in robot production, Inovance's potential expectations are also relatively high.
In the controller field, domestic controller enterprises are highly fragmented. Although there are a number of professional controller enterprises such as Canoo, Wansun Automation, Googol Tech, Invt, and Haide Control, they have not yet formed effective market competitiveness. The current localization rate is less than 20%, and their future success remains to be seen.
In the long run, humanoid robots are a promising field with immense potential. Short-term speculation is meaningless; what is needed is long-term tracking and attention to identify those key enterprises.
Disclaimer
This article involves the content of listed companies and is based on the author's personal analysis and judgment using information publicly disclosed by listed companies in accordance with their legal obligations (including but not limited to temporary announcements, periodic reports, and official interaction platforms, etc.). The information or opinions in this article do not constitute any investment or other business advice, and Market Value Watch will not bear any responsibility for any actions taken as a result of adopting this article.
——END——







