The Transformative Impact of AI on Marketing
![]() 08/04 2025
08/04 2025
![]() 586
586

An In-Depth Look at AI in Marketing
By Wu Er
Edited by Zhang Xiao
55 million GMV and 13 million views—these aren't the impressive feats of a human celebrity but the "AI marvel" achieved by Baidu's "Digital Man Luo Yonghao" during its 618 live stream.
In this broadcast, AI accessed the knowledge base 13,000 times, akin to flipping through 130 copies of the "Dictionary of Chinese" in an instant. It generated 97,000 words of product explanations, equivalent to a typist furiously typing for 18 hours straight.
Tencent's "Wonderful Digital Man" also made its debut at the 2025 World Artificial Intelligence Conference (WAIC).
With 3,000 public digital avatars, 1:1 human voice replication, 24/7 unmanned live streaming, and a comprehensive AI tool, it slashes costs for short video production, user interaction, and sales conversion by 90%.
Across the ocean, during the NBA Finals live broadcast, an AI-generated advertisement emerged, costing a mere $2,000 and 48 hours, achieving over 95% cost reduction.
This isn't an isolated "AI case." As large models start autonomously generating ideas, optimizing delivery strategies, and predicting consumer trends, the fundamental logic of marketing is undergoing a qualitative shift from being a mere "efficiency tool" to a "strategic hub."
In response, traditional marketers feel a mix of excitement and unease.
Traditional 4A giant WPP saw a 2.7% year-on-year revenue drop in Q1, announcing its transformation with a self-developed AI hub costing GBP 300 million annually and a series of acquisitions. Its CEO bluntly stated, "We aim to transcend traditional identity solutions and become an AI-driven enterprise."
The acute contradictions facing AI marketing are emerging: SMEs becoming data vassals in the race for computing power, creatives fearing that human warmth will be swallowed by algorithms, and regulators grappling with black-box algorithms and copyright disputes...
According to iResearch's report, the penetration rate of intelligent marketing among Chinese enterprises reached 1.03% in 2024, and the AI marketing market size is projected to hit RMB 66.9 billion in 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 26.2%. By 2030, the AI advertising marketing market size is expected to exceed RMB 100 billion.
Driven by the rapid evolution of AI technology, the AI marketing market size continues to surge. So, what application values has AI brought to the marketing industry?
Firstly, it helps reduce costs and increase efficiency.
According to CMO Club marketing expert Hu Nanxi's observations, stores supporting GMV of RMB 1 billion used to require a 10-15 person operation team and an annual content production fee of RMB 2 million. Now, the same scale can be achieved with just 2-3 people and an investment in AI tools at the RMB 100,000 level.
The impact of AI on short video live streaming is particularly significant. AI can automatically identify the focus of live streaming scripts, such as fabric analysis, style comparison, cost-effectiveness emphasis, and precisely mark highlight segments. Within 30 minutes of live streaming, bulk live stream slices can be generated. Traditional MCN agencies need a team of 7-8 people to produce 8,000 videos per month, which is now reduced to 2 people. This model can drive GMV of RMB 30 million per month, contributing RMB 200-300 million in annual sales, and operators do not need an industry background, as simple interface interaction is sufficient to complete tasks.
Secondly, it upgrades user experience.
A digital artist on Xiaohongshu used AI to deconstruct McDonald's Big Mac into a "Bronze Taotie Pattern Tripod" and transform fries into a "Blue and White Porcelain Chopstick Bar." This set of AI images quickly went viral on the internet.

McDonald's promptly reposted on Weibo and swiftly launched the "AI Cultural Relic Replication Contest," inviting users to create "M-remembered heirlooms" with generative AI.
This is not only a successful marketing campaign but also reveals how AI continually reshapes user experience: users can freely choose materials like bronze, agate, and enamel to generate exclusive cultural relics, allowing brand symbols to achieve personalized fission. From artist creation to UGC explosion, AI evolves traditional "one-way brand output" into "mass co-creation," enabling real-time interaction. By analyzing young people's preference for national trends, the system predicts the potential for cultural relic memes to break out of the circle, transforming McDonald's from a fast food symbol to a cultural carrier.
Thirdly, it provides market insight and decision-making.
Netflix deeply transforms massive user data into market insights and drives key decisions, forming an intelligent closed loop of "watch-analyze-create-verify" throughout content development and marketing.
Netflix uses AI to analyze the vast data accumulated on its platform, such as over 95 billion hours of user viewing data, accurately identifying the potential of genre combinations and user preferences, achieving data-driven creative decisions.
For instance, analyzing the popularity of "dystopia + family ethics" elements contributed to the renewal decision of "Dark Glory." Simultaneously, AI deeply analyzes the regional preference characteristics of non-English content, which accounts for one-third of the total viewing time, successfully predicting the global transmission breaking point of the "violent aesthetics" symbol represented by the Korean drama "Squid Game."
On the content marketing side, Netflix uses AI technology to achieve personalized experiences tailored to each individual. The system intelligently generates and displays content cover images and trailers that best attract users' interests based on their viewing history and preferences.
For example, the movie "Good Will Hunting" displays the cover of Matt Damon and Minnie Driver for users who love romantic love themes, while highlighting Robin Williams' image for comedy lovers. Different versions of trailers are automatically generated for the series "Stranger Things," focusing on horror atmosphere or youth adventure elements, precisely matching user groups with different interests.
This highly personalized recommendation strategy significantly enhances user stickiness, contributing over 95 billion hours of viewing time.
Netflix's latest financial report data confirms the success of its AI-driven strategy. Revenue in the second quarter reached $11.08 billion, a year-on-year increase of 16%; profit was $3.13 billion. Its advertising business performed particularly well, with global monthly active users reaching 94 million, doubling from the same period last year. Its advertising effectiveness far exceeds the industry average, with brand favorability 8 times higher, sales conversion rate 162% higher, and purchase intention 3 times higher.
These remarkable achievements are achieved by the AI system real-time analyzing massive user behavior data and driving full-link decisions from content production, precision marketing to global distribution.
AI has become an indispensable engine for enhancing marketing efficiency and effectiveness, deepening user connections, and optimizing strategic directions. The underlying force driving the realization of these values is the rapid evolution of AI technology itself in algorithms, computing power, and data application.
Looking back at the development of AI marketing, its technological evolution has mainly gone through three stages:
Stage 1 (2015-2020): Rule engine dominance, exemplified by Facebook's precision-targeted advertising;
Stage 2 (2021-2023): Generative AI breakthrough, like ChatGPT writing advertising copy;
Stage 3 (2024-): Multi-Agent collaboration, such as Amazon's closed-loop system of "demand forecasting-production-logistics."
The technological evolution of AI marketing is undergoing a paradigm shift from "single-point intelligence" to "system collaboration," with the core being the upgrade from single-point tools to a multi-Agent autonomous collaboration ecosystem.
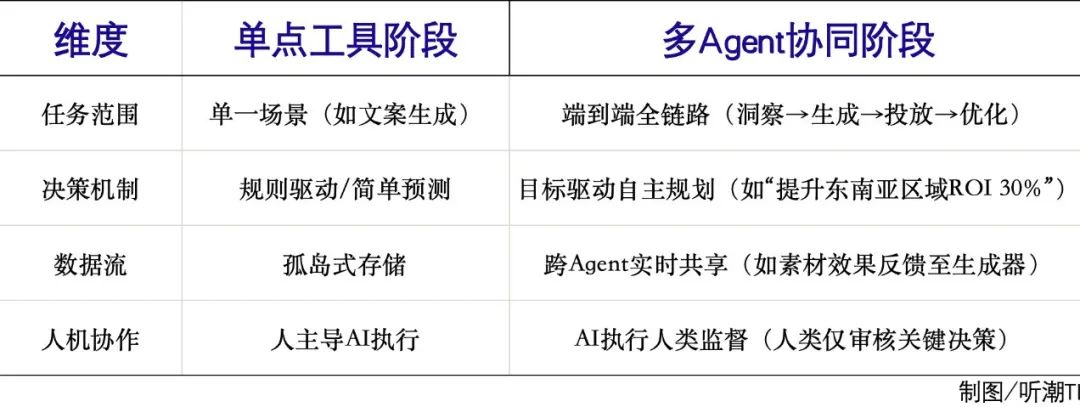
Currently, AI marketing has covered all links of the marketing chain, including automated insight, strategy generation, multimodal content generation, intelligent delivery and optimization, and effect attribution. Among them, the development of content generation and intelligent delivery is particularly prominent.
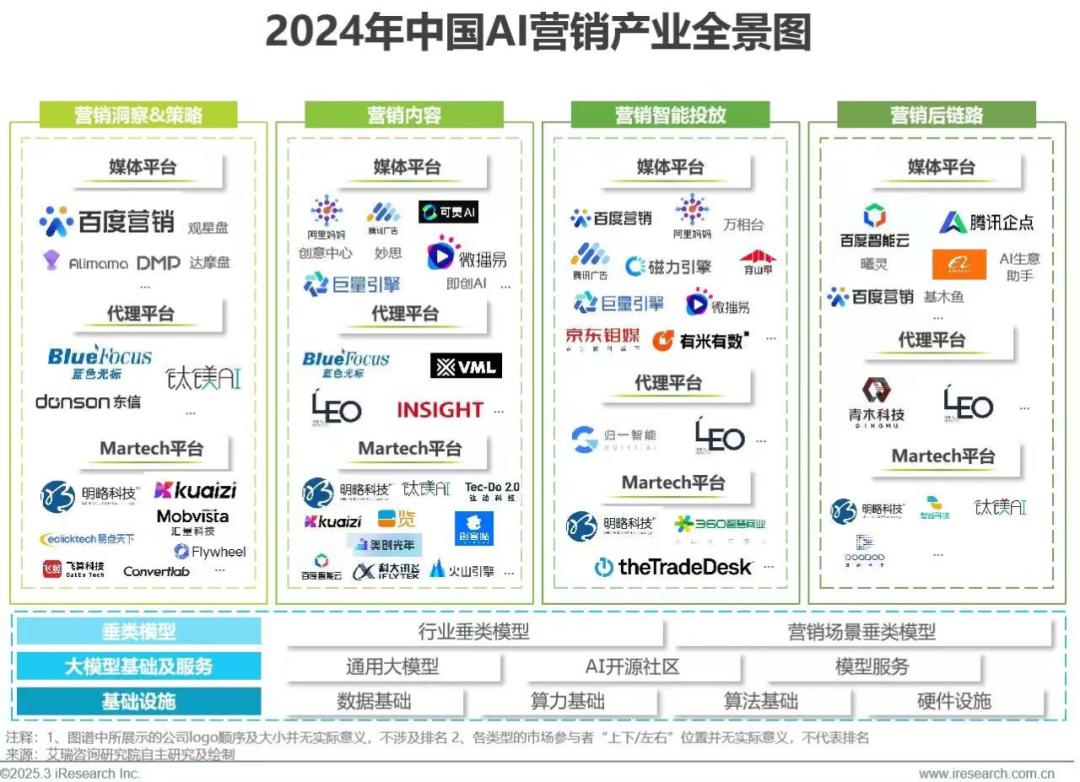
Image/iResearch
Taking Alibaba as an example, Alimama, as Alibaba's digital marketing middle platform, has built an AI marketing system spanning the entire chain of "insight-strategy-content-delivery-attribution."
By integrating 1 billion consumer behavior trajectories inside and outside the Taobao and Tmall groups, it constructs a model of "opportunity crowd-brand assets-conversion path" to real-time mine high-potential customer groups. Midea Air Conditioner analyzed users' willingness to leave information through AI interactive components, accurately reaching potential customers, and increasing the ROI of the entire store by 40% during the 618 period.
In terms of marketing insights, "Product Site-wide Promotion" automatically selects products with GMV growth potential through AI intelligent product selection, including high-quality new products, potential products, and opportunity hit products, differentiating labeling and allocating resources.
In terms of content generation, it intelligently releases content productivity from image to video in one click across the entire chain. During the 618 period, Alimama's AIGC creative capabilities cumulatively helped over 2 million merchants double their creative material efficiency. "AI Image-to-Video" supports merchants to quickly generate videos from scratch with up to 10 images; "AI Instant Video" helps merchants in various industries such as apparel, fast-moving consumer goods, home appliances, 3C digital products, home furnishing, and home appliances increase CTR by up to 170%.
In terms of delivery optimization, Uni Desk's dynamic optimized material combination and cross-media frequency control strategy help merchants with intelligent delivery. The "Net Transaction Bidding" mode can identify and block instant refund users through AI, reducing the refund rate of delivery plans by 18%.
In terms of effect analysis, Uni Desk realizes full lifecycle management of "seeding-searching-transaction-repurchase."
Alimama's entire AIGX technology system, including AIGB intelligent bidding, AIGC creativity, AIGE simulated delivery environment, etc., has comprehensively and deeply functioned in various e-commerce links.
Not just e-commerce, AI marketing has widely penetrated numerous industries such as gaming, fast-moving consumer goods, finance, and overseas expansion. Especially in the fields of e-commerce and overseas expansion, multi-Agent collaboration has become a standard configuration.
This is mainly due to two advantages. On the one hand, these industries have accumulated billions of user behavior data, providing a solid foundation for AI accurate prediction; on the other hand, their conversion links are short, realizing a closed loop of "exposure-click-payment," with clear and direct effect attribution.
a. Power games on the supply side: Winner-takes-all and survival in the cracks
Cloud giants, AI platforms (such as OpenAI, Anthropic), and large media platforms (such as Google, Meta, ByteDance) rely on their absolute advantages in technology, data, computing power, and ecosystem to form a strong monopoly in marketing service supply.
Taking Amazon as an example, its AI strategic layout is deeply integrated and extremely extensive. From building basic models (such as Nova), selling underlying computing power (such as Trainium chips), providing infrastructure platforms (such as Bedrock), to applying AI throughout Alexa smart assistants, distribution systems, advertising businesses, and even quantum computing (such as Ocelot chips). This comprehensive layout across all layers of the AI technology stack significantly distinguishes it from competitors who typically focus on a single field.
In terms of resource reserves, Amazon has a robust operating cash flow, reaching $113 billion since the last quarter and holding $94 billion in cash. Its first-quarter performance in 2025 was impressive, with revenue increasing by 9% year-on-year to $155.7 billion and net profit reaching $17.1 billion, a significant increase of 64% year-on-year. Its strong financial strength supports Amazon's vertical integration from chips to applications in the AI field.
In terms of investment, the company's capital expenditure in the first quarter was as high as $24.3 billion, and the planned capital expenditure for the entire year of 2025 reached $100 billion. Most of this will be invested in AI-related areas, including data center construction, network equipment upgrades, AI hardware development, and generative AI capability building. This annual planned expenditure is close to one-sixth of its total revenue last year.
Significant AI investments have begun to translate into business growth, with its advertising business achieving a 19% year-on-year increase in the first quarter, generating revenue of $13.9 billion.
Looking back domestically, Tencent recently announced its "AI Product Application Panorama" for the first time, and Tencent is building its own infrastructure covering the entire chain of AI marketing. Meanwhile, with WeChat and QQ, two national-level applications, its real-time user behavior data and traffic entry points at the billion level are significantly squeezing the survival space of small and medium-sized marketing service providers.
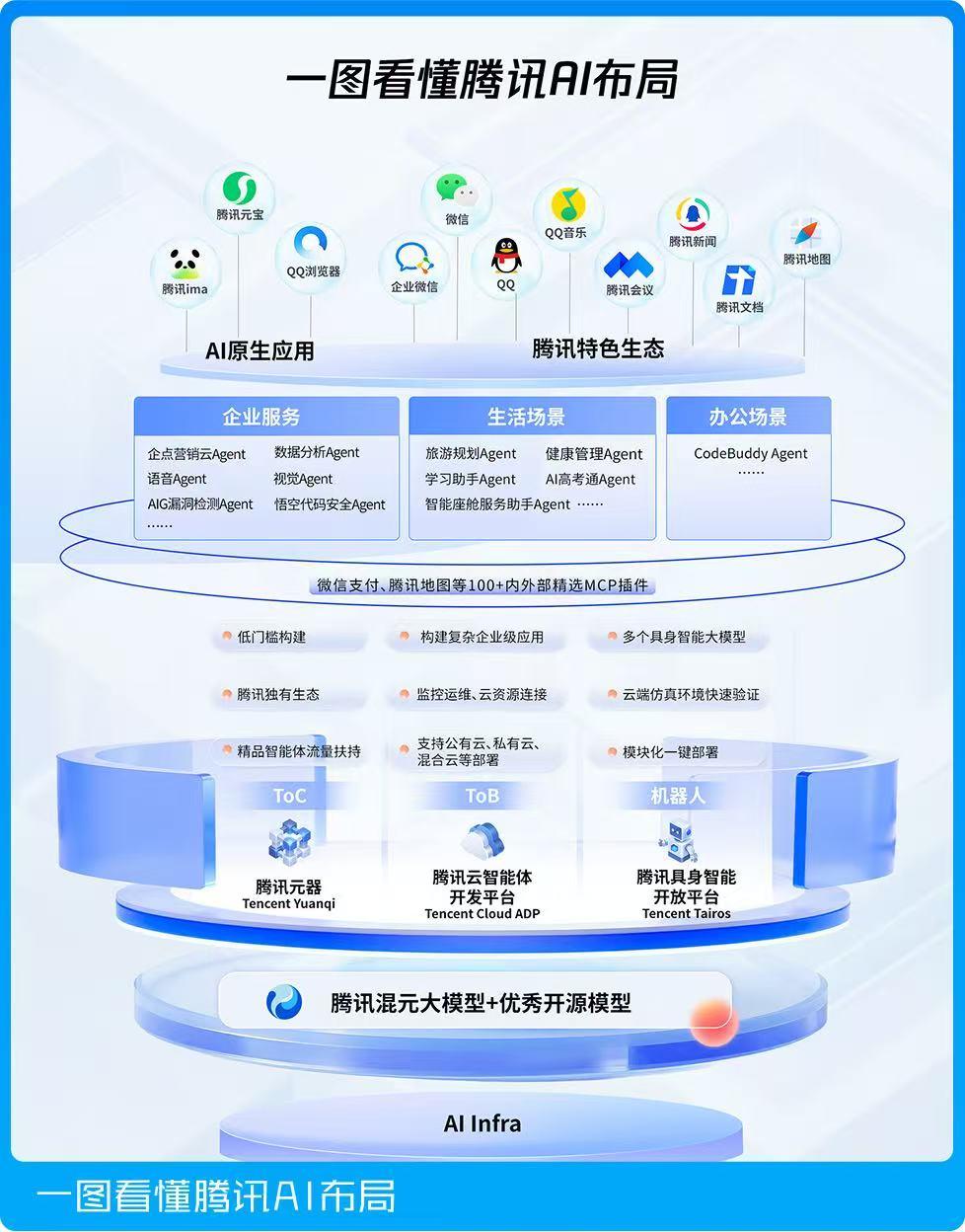
Facing the monopoly pressure from giants, small and medium-sized marketing service providers are deeply trapped in a triple dilemma: technological homogeneity, intensified customer loss, and narrowing financing channels.
Most small and medium-sized service providers depend heavily on fine-tuning open-source models, their functions largely confined to single-purpose tools like copywriting generation, and often lacking the capability for multi-agent collaboration. Despite numerous service providers claiming to offer "fully managed" solutions, empirical tests reveal that their creative output diversity only reaches approximately 30% of that of leading systems.
As leading brands establish their own AI teams, smaller service providers are compelled to shift their focus to regional markets in search of sustainability. For instance, Shushangyun has successfully stabilized its market share in Southeast Asia by offering deeply localized "language-payment-logistics" customized services.
Against this backdrop, transitioning into specialized agents within vertical fields has emerged as a vital avenue for many small and medium-sized service providers.
Concurrently, for grassroots roles such as copywriters, designers, and optimizers, the risk of job displacement due to AI substitution is on the rise.
b. The Digital Divide on the Demand Side: A Stratified World for Brands
On the marketing demand side, monopolization by giants exacerbates the digital divide.
Leading brands are rapidly integrating AI into their brand strategies, making significant investments to promote AI marketing either through building in-house AI capabilities or deep collaborations with top platforms.
L'Oréal established the generative AI beauty content lab CREAITECH, training large models tailored for the beauty industry. This initiative provides localized content and creativity for TikTok and Instagram across 20 markets in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. Additionally, to innovate in R&D, L'Oréal collaborated with IBM to create the world's first AI foundation model specifically designed for cosmetic formula design, aiming to enhance sustainable production capabilities.
Nike acquired the consumer data analysis company Celect to develop a privatized demand forecasting engine, firmly grasping core data sovereignty.
Essentially, leading brands are evolving from mere "AI users" to "rule conspirators" by deeply collaborating with platforms to jointly reshape traffic allocation algorithms and industry discourse power.
Conversely, small and medium-sized enterprises, constrained by their limited data volumes, struggle to effectively utilize data resources, leading to poor marketing outcomes and ultimately becoming free data fuel for platforms.
While AI marketing lowers the technological threshold, it further widens the "digital divide" caused by resource disparities.
c. Migration of Traffic Entry Points: GEO Becomes Mainstream
With the rise of generative AI, AI search is swiftly becoming the primary means for people to access information. Against this backdrop, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) has emerged.
In June 2024, scholars from the Indian Institute of Technology, Princeton University, and independent researchers jointly published the paper "GEO: Generative Engine Optimization," formally introducing the concept for the first time.
GEO fundamentally differs from traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
First, their target objects are distinct. SEO focuses on traditional search engines like Baidu and Google, aiming to enhance a website's ranking in search results. In contrast, GEO targets generative AI engines such as ChatGPT and DeepSeek, aiming to prioritize content in AI-generated direct answers.
Second, their optimization methods vary. SEO emphasizes optimizing website structure and keyword placement, whereas GEO emphasizes content structuring and authority, requiring adaptation to AI's semantic understanding capabilities and placing greater emphasis on semantic relevance.
Third, their results are presented differently. SEO optimization results present as link lists that users must click to view. Conversely, GEO-optimized content may be directly integrated into AI engines' structured answers.
According to Coherent Market Insights, the global AI search engine market is projected to reach $43.63 billion by 2025 and grow to $108.88 billion by 2032, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 14% from 2025 to 2032.
From an application perspective, the web search segment is anticipated to account for the largest share of the global market (61.7%) in 2025. Technologically, generative AI will dominate (54.2%).
The rise of GEO signifies a shift in traffic inlets from traditional search engines to AI-native interaction scenarios. Essentially, it represents a "disintermediation" revolution in how users access information. As ChatGPT, social recommendations, and scenario-based shopping guides directly generate decision-making advice, brands must restructure their content strategies to compete for "source sovereignty" within AI cognitive systems.
So, who stands to benefit from this traffic revolution?
First, open AI platforms (such as ChatGPT and DeepSeek).
As algorithmic hubs, they control information sources and directly recommend branded products for commercialization through a three-stage process of "knowledge retrieval → context integration → answer generation." Furthermore, their AI agency capabilities, akin to Amazon's "Buy for Me," can complete cross-platform price comparison and the entire payment process, achieving ultimate simplification from "demand description → transaction closure."
Second, social ecosystems (such as TikTok and WeChat).
They leverage the advantage of "scenario-based inlets," seamlessly connecting content and consumption through immersive recommendation engines. A notable example is TikTok Shop, which triggers immediate purchasing behavior through "video keywords + AI commentary."
Third, vertical GEO service providers focusing on specific industries or scenarios.
Take the startup GEO service provider "Profound" as an example. According to PR Newswire data, as of June 2025, its platform processed over 100 million AI search queries per month, serving users in 18 countries globally. More importantly, its optimization solutions can increase clients' brand voice share in AI answers by 25%-40% within 60 days.
However, GEO startups like Profound face a double squeeze:
First, the impact of traditional SEO transformation enterprises. Relying on customer resources and mature ecosystems accumulated during the SEO era, these enterprises expand into the GEO field, giving them a first-mover advantage.
Second, deep conflicts with large model platforms.
The essence of GEO services is inherently adversarial to large model platforms. This adversarial nature stems from GEO's core operating model, which involves analyzing keyword weights, generating optimized content, and increasing the probability of AI recommendations. Their entire strategy is built on "guessing" the underlying algorithms of large models.
Essentially, this is a strategy of finding "loopholes" within the existing algorithmic framework rather than fundamentally cracking the algorithmic principles—it is closer to "reverse engineering" the algorithms. Therefore, every core algorithmic upgrade by large model platforms can instantly invalidate previous GEO service providers' optimization efforts.
This contrasts sharply with the SEO era. Algorithm adjustments by traditional search engines like Google and Baidu typically occur on a monthly basis and have relatively transparent rules. However, the iteration speed of large models may now be measured in weeks, with highly opaque rules, further exacerbating the plight of GEO service providers and raising a key challenge—ambiguity in effect attribution. When a brand's exposure in AI search results increases, it becomes difficult to ascertain whether it is due to GEO optimization strategies or adjustments to the algorithmic weights of large models.
Additionally, as GEO leads the traffic revolution, the "hidden power" in its algorithmic operating mechanism must be vigilantly monitored.
First, there are hidden dangers in platform algorithmic hegemony. Brands may manipulate AI's judgments of "authority" through specific markers, while ordinary users only see the "objective" conclusions presented by AI. This lack of transparency in rules essentially constitutes a form of digital authoritarianism.
Second, there is capital-driven information monopoly. Large brands buy out core professional information sources within vertical fields with exorbitant budgets, leaving small and medium-sized enterprises without even the opportunity to be "seen" by AI, exacerbating inequality in information access.
More alarmingly, if AI platforms follow the example of search engines by quietly opening "paid recommendation" slots (similar to advertising slots) in generative answers while deliberately obscuring the recommendation mechanism, it will create a "double black box." Users may mistakenly believe they are receiving neutral information when in fact they are exposed to soft advertisements from paying entities. In critical areas like healthcare, such practices, if left unregulated, could directly delay patient treatment and endanger life and health safety.
d. Business Ecosystem Reconstruction: Traditional Behemoths vs. Emerging Forces
As AI permeates the entire marketing chain, encompassing advertising creativity, content generation, precise placement, and intelligent customer service, marketing is no longer the exclusive domain of traditional advertising companies.
Technology giants (such as Meta, Tencent, and ByteDance) are constructing new marketing ecosystems leveraging their digital and intelligent infrastructure. For instance, Meta has announced its intention to fully AI-ize its advertising business by 2026, relying on Facebook and Instagram platforms.
Meanwhile, the rise of vertical AI marketing companies is further compressing the survival space of traditional 4A companies, leading to shrinking revenues and market share. Under this pressure, layoffs, business contractions, mergers, and transformations have become industry trends:
The century-old J. Walter Thompson (JWT) merged with the digital marketing company Wunderman.
Omnicom Group plans to acquire Interpublic Group for $13 billion.
Publicis Group is accelerating its AI transformation, making 12 acquisitions in the past year to cover the entire marketing chain.
WPP Group is undergoing layoffs and business restructuring due to declining performance and customer loss.
Facing the contraction of vertical scenarios, many small and medium-sized agencies are compelled to delve deeper into regional markets in search of differentiated survival strategies. For example, Shushangyun focuses on the Southeast Asian market, building localization barriers through "language-payment-logistics" deep customization services to withstand the impact of AI efficiency.
Taking the global advertising giant WPP as an example, under the multi-faceted pressures of market loss, growth deceleration, and organizational inefficiency, WPP views AI as a critical turning point for survival and is fully promoting transformation.
At its peak, WPP had over 3,000 offices in 12 countries and more than 400 independently operated agencies, forming a global service network.
However, WPP currently finds itself in a precarious situation. Its 2024 financial report shows revenues of only $18.426 billion, a year-on-year decline of 0.7%. Regional markets have suffered setbacks, with declines of 2.7% in the UK, 0.7% in North America, and 2.6% in other regions. The decline in China was particularly significant, reaching 20.8%.
Simultaneously, it lost several top clients, including Coca-Cola's North American business, Mars Group's media business, and Paramount's business.
By the end of 2024, WPP's total workforce stood at 108,044, a decrease of 6,129 from the end of 2023.
In 2025, WPP is facing a transformational challenge for survival, viewing AI as a key strategy to break the deadlock. Previously, WPP and tech giant NVIDIA announced a collaboration to launch an AIGC content engine based on Omniverse Cloud, signifying WPP's shift from "labor-intensive creativity" to "AI industrial production."
WPP will invest over £400 million annually in AI development, ranging from developing its AI marketing system WPP Open to launching Open Intelligence, the industry's first large marketing model, to establishing AI delivery centers. WPP is making a significant bet on AI transformation.
On the other hand, emerging service providers represented by vertical AI agents are rapidly gaining traction.
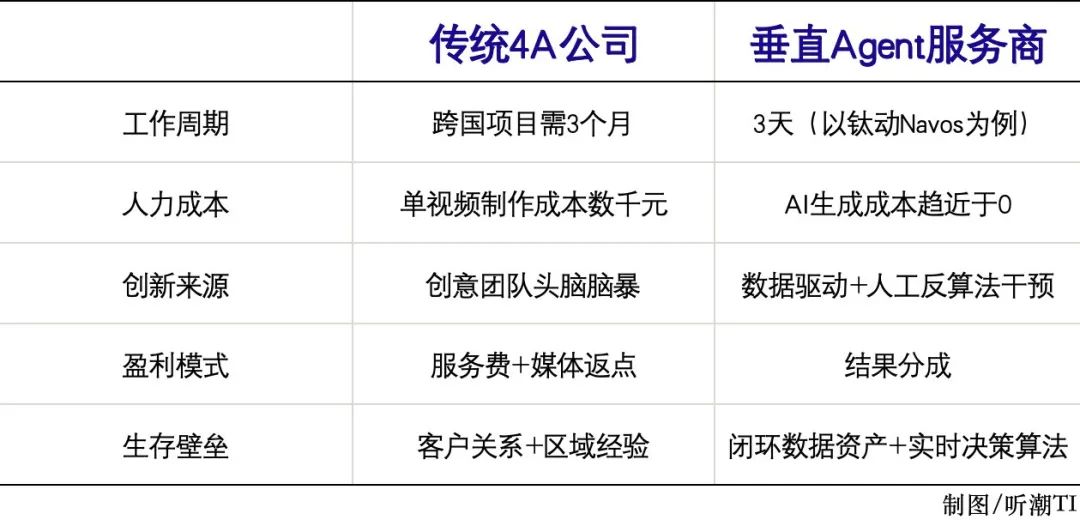
Navos, unveiled at the 2025 World Artificial Intelligence Conference (WAIC), employs a multi-agent collaborative architecture, focusing on addressing the full-link needs of overseas marketing, encompassing planning, hit analysis, content generation, intelligent placement, and data analysis optimization.
Taking TikTok women's clothing marketing as an example, Navos first analyzes platform data and material to extract popular creatives. It then generates targeted materials in bulk, such as 30-second real-person try-on videos featuring cost-effective and simple styles for white-collar workers. Finally, it completes fully automated placement and data insight optimization.
Navos can complete a full campaign that would traditionally take a 4A advertising company three months in just three days, potentially increasing human resource efficiency by dozens of times.
Youche Technology provides full-link AI marketing services for the automotive industry, spanning content generation, intelligent editing, and precise placement.
On January 1, 2025, it produced an AI creative ad for Chery's high-end brand Starway, which took only 10 days from planning to completion. This represents a significant reduction in time compared to the traditional 6-8 weeks, and the production cost was a fraction of the traditional method.
Simultaneously, independent AI creative studios are becoming an emerging trend, fueled by AI's substantial reduction in the technical thresholds and costs of creative production.
At the 2025 WAIC exhibition, Keling launched its creative workbench "Lingdong Canvas," providing creators with a powerful intelligent canvas and creative assistance functions. It supports multi-image reference generation and precise character consistency control, enabling a one-stop creation experience from conception to finished product.
This platform empowers individual creators to independently produce multimodal marketing content, a task previously requiring a team of ten. Currently, Keling AI boasts over 45 million creators across 149 countries and regions, testifying to the success of its model.
At the heart of this model lies a transformation in roles. AI handles basic content creation and production, allowing studios to focus on higher-value insights, creative ideation, and strategic decision-making.
In the future, small AI-driven creative studios will likely become the norm, particularly for resource-constrained small and micro-enterprises, where they will serve as indispensable "creative engines".
AI's impact on work patterns is evident. In Microsoft's internal code repository, 20%-30% of the code is AI-generated. Its CTO predicts that this proportion will rise to 95% by 2030.
The marketing field is also undergoing significant changes. As AI reshapes the industry, roles like copywriters, designers, data analysts, and placement optimizers are being efficiently replaced.
However, this is not the end of professions but an opportunity for transformation, much like typists in the print media era transforming into copy editors.
Executors transitioning into strategists/architects require comprehensive product, technology, and system capabilities, focusing on areas that AI cannot easily replace, such as marketing insights, value delivery, and emotional shaping.
Those transforming into AI trainers/tuners use industry knowledge and brand assets to refine AI models, ensuring outputs are precise and aligned with brand tonality.
The separation of basic execution tasks elevates the unique human values of creativity, strategic thinking, and emotional connection to the forefront.
As "minute-level output surpassing weekly human effort" becomes standard, the biggest professional risk is not being replaced by AI but clinging to outdated models and refusing to embrace the new paradigm of human-machine collaboration.
The evolution of individual marketers will inevitably drive the restructuring of marketing organizations, primarily reflected in three trends:
First, building cross-functional agile teams to break down departmental barriers and achieve deep integration and agile collaboration across marketing, technology, and data capabilities.
Second, enhancing AI literacy organization-wide, making AI tool application and data insight capabilities the organization's core competitiveness.
Third, accelerating offshore outsourcing of human resources. For instance, Manila, Philippines, has emerged as a large-scale "AI review outsourcing center," handling content review tasks for many European and American brands. Incomplete statistics indicate that major tech companies employ over 100,000 content reviewers in the Philippines, with Facebook alone employing about 20,000 locally.
Beneath the surface of AI marketing's prosperity lie profound ethical dilemmas and value disruptions.
In March 2023, ChatGPT leaked user chat records due to technical vulnerabilities, exposing sensitive information like names, email addresses, and credit card details. OpenAI not only failed to promptly report to regulatory agencies but also used the data for model training without user authorization, leading to a €15 million fine from GDPR.
Concurrently, writers filed a class action lawsuit accusing OpenAI, Microsoft, and other enterprises of using millions of books without permission to train AI models, exposing regulatory blind spots regarding copyright ownership and data usage.
These incidents highlight the collapse of data sovereignty and regulatory challenges in AI development.
While AI marketing can enhance efficiency, it may come at the cost of emotional warmth. Twilio data shows that 87% of Hong Kong brands deploy AI customer service to accelerate response times, with 67% of enterprises recognizing its efficiency. However, only 17% of consumers believe brands achieve personalized interaction, and 74% of local consumers abandon purchases due to AI customer service lacking "humanity".
More severely, the "authenticity trap" of AI-generated content exacerbates the trust crisis. AI digital humans costing only $5,000 can precisely induce elderly groups to purchase inferior products through pre-set algorithms optimizing scripts like "lonely elderly conversational databases" and "health anxiety scripts".
This rationality of technological tools crushing human values turns marketing from "value delivery" into "emotional manipulation".
GEO may be alienated into an "algorithmic-level monopoly" tool. A leading enterprise in a regional building materials market manipulates AI recommendations for the "top ten brands of waterproof materials" through industry whitepaper insertions, forming an algorithmic information cocoon. This not only misleads consumer decisions but also squeezes the survival space of small and medium-sized enterprises.
Algorithm recommendation systems may lead to the rise of algorithmic hegemony and unfair imbalances.
The limitations of future AI marketing do not lie in tool failure but in the systematic aphasia of humanity within algorithms. When technology becomes a commercial belief in the name of "cost reduction and efficiency enhancement," human emotional warmth, creativity, and ethical judgment are marginalized.
To address the triple dilemma of data sovereignty collapse, emotional temperature stripping, and algorithmic hegemony rise, the future of AI marketing lies in constructing a "symbiotic marketing" system centered on human wisdom, warmth, and ethics, with AI as the enabling engine, achieving human-machine co-evolution.
a. Multi-Agent Collaboration Becomes Marketing Infrastructure
Multi-Agent collaboration is becoming the foundational design of AI marketing engines, driving the reconstruction of the industry's underlying logic. Its core trend is the agentization of the entire marketing chain.
Euromonitor International's report predicts that the marketing and sales market size of AI Agents in China will reach approximately 44.2 billion yuan by 2024. On one hand, AI Agents enhance the value of SaaS services; on the other hand, there is a significant growth in demand for customized AI Agent functions. This is expected to show explosive growth in the next five years, reaching a market size of trillions of yuan.
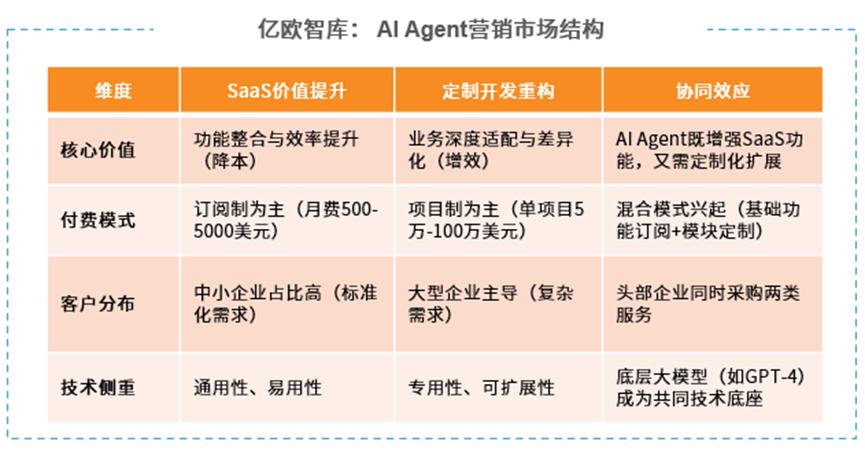
Figure/Euromonitor International
From 2024 to 2028, the penetration rate of AI autonomous decision-making technology in enterprises will increase from 0 to 15%. Given that 93% of enterprises are SMEs, it is estimated that the penetration rate of AI Agents in Chinese SMEs will increase from 0.5% to 15% from 2023 to 2028; for large enterprises, the penetration rate is expected to rise from 3% to 25%.
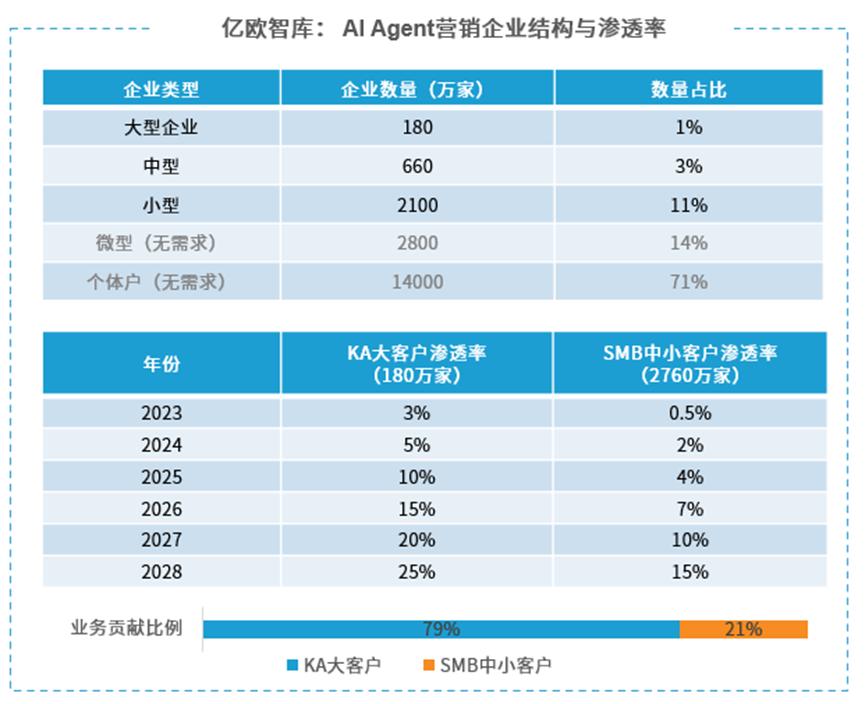
Figure/Euromonitor International
Taking Tencent as an example, Tencent AI Marketing covers the entire link from market insight to delivery optimization through technologies like Agents, digital humans, AIGC, and data analysis, realizing a fully automated closed loop for the entire process.
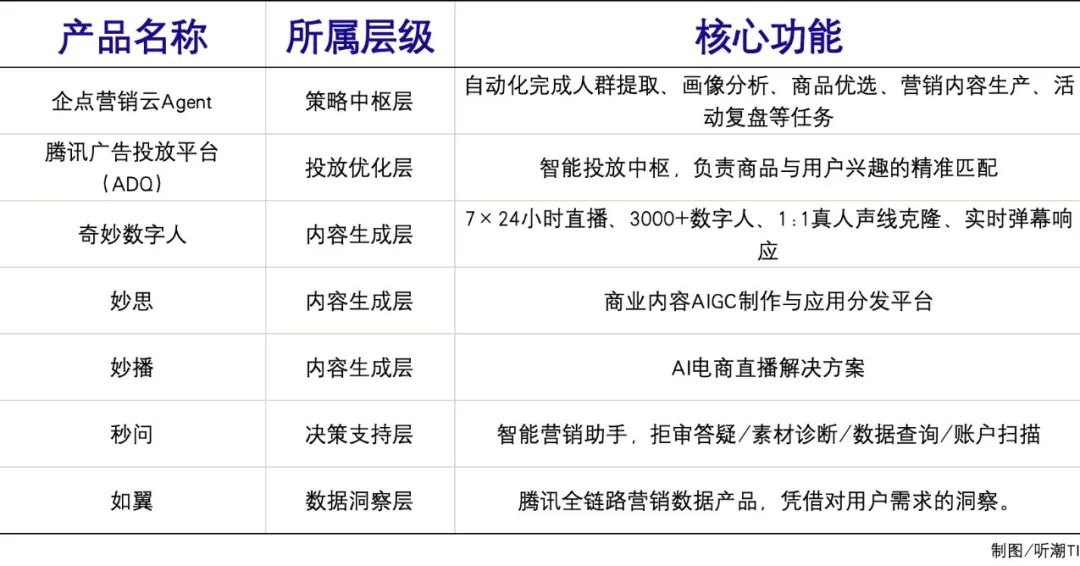
Tencent AI Marketing Agent Matrix
Data Insight → Content Creation: Analyzing regional consumption preferences with Wing, and Miaosi automatically generating adapted short video scripts and digital human materials.
Smart Delivery → Real-time Interaction: ADQ accurately pushes content based on user interest tags, and Miaobo uses a "live streaming brain" to analyze live chat comments in real-time and adjust its script.
Effect Optimization → Strategy Iteration: Miaowen diagnoses advertising delivery issues, and Qidian Marketing Cloud's MA engine automatically triggers member repurchase strategies.
AI Agent technology is deeply penetrating the entire marketing process, forming a value closed loop of "Insight-Creation-Delivery-Optimization-Interaction" through the division of labor and collaboration among multiple AI Agents. An autonomously coordinated AI Agent network has become the infrastructure for AI marketing.
b. Popularization of Predictive Marketing
Predictive marketing is moving towards widespread adoption, as evidenced by Meta and the University of Washington's jointly released AI preference prediction system PrefPalette on July 28, 2025. This system, akin to having "mind-reading abilities," can not only predict user behavior but also clearly explain its reasoning logic.
In tests conducted on 45 different communities on the Reddit platform, PrefPalette achieved an average accuracy rate of 84.9%, a 46.6% improvement over GPT-4o.
Notably, the system exhibits varying accuracy rates across different community types. In highly academic communities like history Q&A, it achieves an excellent accuracy rate of 91.6%, whereas in more casual communities, it achieves a slightly lower accuracy rate of 69.4%. This indicates that the clearer the community norms, the more accurate the AI's predictions. History Q&A communities have strict academic standards and clear quality requirements, whereas general communities are more inclusive of diverse response styles.
One of PrefPalette's standout features is its interpretability. The system can clearly explain the reasons for its predictions, for example, emphasizing the importance of detail in history Q&A communities. This transparency enables people to truly understand the AI's decision-making process.
AI is shifting from analyzing the past to accurately predicting future needs and consumer behavior, and predictive marketing will become prevalent. For instance, e-commerce platforms can dynamically analyze user decision-making attributes, such as "price sensitivity" or "quality orientation," and generate personalized product descriptions.
c. Reshaping of Pricing Models
As mentioned earlier, Youche Technology and TopOn Technology have both adopted or partially adopted the "RAAS" (Result as a Service) model.
Its core is to directly deliver measurable marketing results to clients, rather than merely providing traditional SaaS tools.
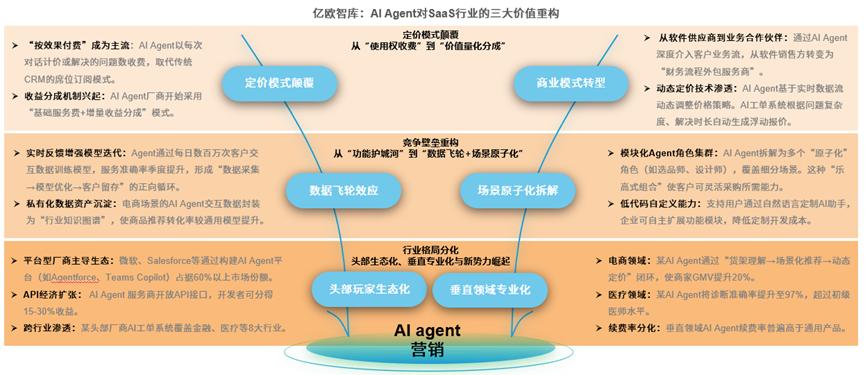
Figure/Euromonitor International
The rise of this model is supported by the traditional marketing pain point of ambiguous effect attribution, while AI makes marketing effects more quantifiable and predictable.
This is redefining the way marketing value is assessed and driving "performance-based pricing" to become the mainstream.
Essentially, AI marketing is undergoing a profound transformation from "selling tools" to "selling results." The core demand for client payments has shifted from acquiring functions to acquiring visible business outcomes. This signifies a fundamental restructuring of the marketing value chain driven by technological change.
The rise of the "performance-based pricing" model further symbolizes a paradigm shift in the entire marketing industry, from "resource-intensive" (competing on budgets and channels) to "capability-intensive" (competing on data closed-loop capabilities and results delivery capabilities).
d. Reanchoring of Human Roles
As AI takes over the efficiency engine of marketing, from massive data analysis to personalized delivery, from 7x24 live streaming to batch material generation, the coordinates of human value are being reanchored: returning to the beacon of strategy, the hotbed of emotions, and the compass of ethics.
AI's liberation of repetitive labor paradoxically frees up immense space for human creativity, as evidenced by the explosion of 45 million creators on the Canva AI platform.
As the CTO of Dentsu Group stated at a marketing technology summit, "Let algorithms analyze behavioral data and let humans return to desire insight. This is the underlying protocol for human-machine symbiosis."
This means:
Humans become "soul architects," defining the core of the brand and mapping out long-term visions, holding onto unchanging value anchors amidst the flood of technology.
They transform into "cultural decoders," deciphering the emotional codes of groups, translating regional customs, generational anxieties, and collective memories into "temperature instructions" that AI can understand.
They serve as "moral calibrators," drawing a red line before algorithmic bias and commercial temptations, safeguarding brand values and social contracts.
As technology iterates at the speed of light, the intangible gleams of humanity—profound empathy for pain, persistent questioning of meaning, and value choices in ambiguous areas—become the ultimate scarce barriers.
Just as AI can optimize the sugar curve of a bubble tea, it cannot replicate the thrill on the tip of a teenager's tongue when they sneak a sip from their grandmother's teapot.
Ultimately, AI marketing is not merely a tool upgrade but a profound revolution that touches the industry's foundations, restructures power dynamics, disrupts the nature of work, and challenges ethical boundaries. It interweaves multiple complex contradictions, including efficiency leapfrogging and cost restructuring, monopoly by giants and digital divides, job replacement and capability evolution, innovation explosions, and ethical constraints.
Only by embracing technology while adhering to humans' unique strategic foresight, emotional connections, and ethical boundaries, and pursuing responsible AI applications, can we build a solid foundation for human-machine symbiosis. In this AI marketing revolution, humans are not being replaced but are, instead, reanchoring their irreplaceable value coordinates amidst the efficiency of AI.