Cooking Robots Enter Domestic Catering: A Threat to Chefs?
![]() 08/06 2025
08/06 2025
![]() 505
505

At the Chengdu Catering Technology and Intelligence Summit in July, multiple cooking robots, equipped with mechanical arms, seasoning boxes, and small pots, stole the show. These robots gracefully moved their mechanical arms, seasoning and stir-frying ingredients according to preset programs. The seamless process captivated the audience, prompting them to snap photos.

Conceptual diagram, not an actual robot
Artificial intelligence, including robots, has already permeated our daily lives. In the chain catering industry, AI is commonly used for ordering, meal preparation, accounting, and even restaurant operations. In the household consumer market, cooking robots tailored for home use are emerging, with prices ranging from a few thousand yuan for entry-level models to several hundred thousand yuan for high-end customizations.

Currently, many catering enterprises have recognized the immense potential of AI and are investing heavily in the research and development of algorithms and temperature control technologies. However, this integration has sparked numerous questions: Can cooking robots significantly reduce catering costs? Why have McDonald's and Starbucks, giants in the global chain catering industry, withdrawn their AI ordering systems? Will cooking robots and other artificial intelligences eventually replace chefs?
Chinese Cuisine Chains Rush to Embrace Intelligent Cooking Robots
From Unitree Technology's dancing robots to robot traffic police on the Bund, robots are becoming ubiquitous. During peak dining hours on Beijing's Guijie Street, a robotic dog distributes snacks to waiting customers. The intelligent inspection system developed by ChaBaidao and DeepSeek uses AI to inspect store hygiene, materials, and more, improving efficiency by 30%. Among these applications, cooking robots, integrated into the food preparation process, are a game-changer.
Traditionally, Chinese cuisine's low standardization and difficulty in uniforming flavors hindered large-scale development. However, Hunan chain catering enterprise BaWan has achieved a breakthrough with its self-developed intelligent cooking robots. According to media reports, BaWan's robots have undergone three generations of technological iteration, forming a mature and stable intelligent cooking system with over 550 stores.
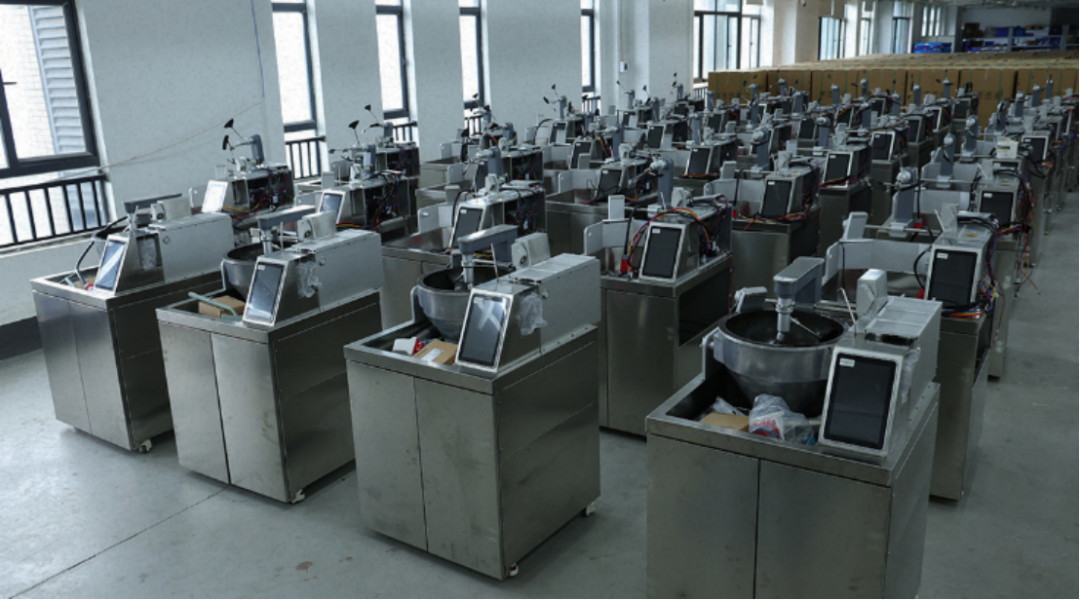

Picture of BaWan's third-generation cooking robot: Source, BaWan official website
Videos from store exploration bloggers show that this third-generation robot not only cooks various dishes precisely but also integrates automatic pot-washing, realizing full-process automation from cooking to cleaning. It can prepare a single serving in just 2-4 minutes, ensuring swift order fulfillment during peak hours from 11:30 AM to 1 PM.
In an 80-square-meter BaWan store, only three kitchen staff operate four devices simultaneously, significantly reducing reliance on chefs and alleviating the pressure of rising labor costs. With robots, the average meal price remains around 20 yuan, offering affordable dining.

Diagram of BaWan chain stores: Source, official website
Today, Chinese cuisine chain enterprises are clamoring for cooking robots. Unlike the decline of unmanned restaurants relying solely on technology and robotic equipment around 2019, more enterprises now choose to use robots to aid catering development. Well-known brands like Xiaocaiyuan and Laoxiangji have announced plans to procure intelligent robots this year. However, while Chinese cooking robots thrive, the American catering market presents a contrasting picture.
Starbucks Stumbles with AI Ordering: Catering Cannot Achieve "Full-Process Automation"
In July 2023, the Starbucks app in the United States experienced a severe system failure, erroneously notifying a large number of users that their orders were ready. This left many coffee lovers confused, checking their order records. Similar incidents occurred at McDonald's, where customers ordering water and ice cream through AI received ketchup and butter packets instead. In April 2024, Brian Niccol, the new CEO of Starbucks, announced during an earnings call that the Siren automation system launched in 2022 would be withdrawn, and plans were made to increase store staff.
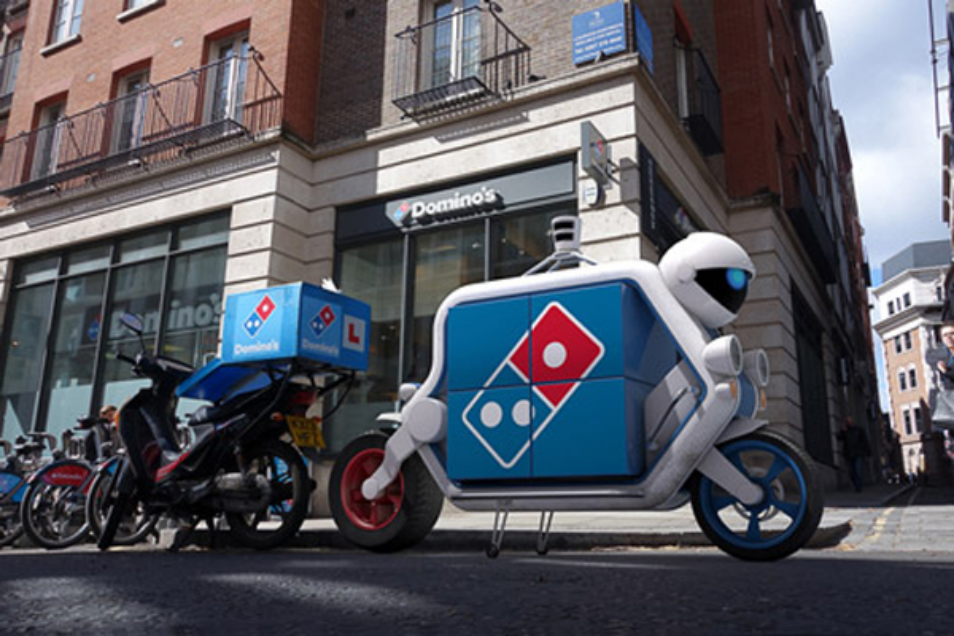

Domino's delivery robot
American chain catering enterprises have successfully integrated AI into food preparation. For instance, Domino's uses an AI robot to process online orders, sorting and allocating them quickly through intelligent algorithms, then delivering meals, improving peak-hour response speed by 40%. Pizza Hut's AI pizza inspection system detects ingredient completeness before baking, promptly identifying and adjusting issues, ensuring quality and reducing error rates by 20%.
These successes focus on standardized processes like order processing and quality inspection, suitable for AI's precision and efficiency. However, Starbucks and McDonald's mistakes reveal AI's shortcomings in complex service scenarios. Catering ordering is not just "process automation" but a comprehensive service integrating demand anticipation, emotional interaction, and market responsiveness, requiring flexible adjustments based on customer needs and market changes, posing challenges for current AI technology.

Starbucks' stumble highlights the limitations of current AI technology in catering ordering scenarios.
Firstly, complex scenarios lack sufficient data training. Catering ordering involves dynamic demands like different customer preferences and demand fluctuations, as well as non-standardized interactions like personalized recommendations and temporary adjustments. These require massive, segmented scenario data, unlike simple dish preparation. Currently, most catering AI's training data struggles to cover such complexities, leading to "efficient ineffectiveness."
Secondly, emotional experience is irreplaceable. For many, catering consumption involves emotional interaction. Internal Starbucks data shows stores providing emotional experiences, like coffee masters' demonstrations and personalized recommendations, have an average order value 18%-25% higher than ordinary stores, with a 37% increase in conversion rates. AI systems' mechanical responses, like a simple "your order is complete," fail to provide emotional care, leading to a drop in user satisfaction.

Starbucks hasn't abandoned AI technology; various AIs still assist during peak hours. But the focus has shifted to "serving experience upgrades," compensating for AI's emotional deficiencies through humanized services. This shift reveals that technology in catering ordering must balance efficiency and warmth.

Humans design, machines execute. This is the foreseeable future.
The emergence of cooking robots and AI ordering in catering has some practitioners worried about being replaced by technology.
For catering operators, especially large chains, robots in cooking bring significant advantages: They are emotionless, ensuring consistent quality; they avoid behavior like cutting corners, safeguarding dish quality; and they reduce management complexity and operational risks, improving overall efficiency.

This concern is valid. Robots will replace some human labor but not all. Those with unique skills or features will be retained, while others will transform.
So, how will this transformation occur?
Food host Liu Yiwei shared on his platform that he participated in a large-scale robot cooking model experiment in 2024, experiencing the advancement of robot cooking. If a master chef's skills are converted into precise parameter input systems, robots can execute at 80-90%, and when 100 robots operate under the same standards, dish taste can be completely consistent.
However, Liu Yiwei admitted that while robots can accurately reproduce dishes and follow preset programs, they cannot independently develop recipes, innovate flavors, or design ingredient pairings, requiring creativity and inspiration. In the future, chefs can be liberated from manual operations, transforming into "dish designers," focusing on creative tasks like recipe development and cooking logic optimization, endowing robots with more "creativity" while they focus on higher-level value creation.

For the catering industry, whether chefs or waiters, their core value lies in humanized service and discerning customers' potential needs, irreplaceable by current AI. Dish designers, excellent service personnel, and niche, specialty private kitchens all have scarce value and will exist in the market for a long time.
Robots can assist with basic procedural work, while humans handle creative design and emotional communication. In the future, human-machine collaboration will enhance food safety and cater to diverse dining experiences. Human-machine integration is the new trend in catering.
References
1. When the wind of robots "blows into" the kitchen, can cooking robots really replace chefs? NBD News
2. AI "workers" interact at the door, inspection systems introduce DeepSeek's artificial intelligence 3.0 on the tip of the tongue, Beijing Business Daily
3. McDonald's AI servers laid off, is catering AI a false proposition? Leikeji