The Ascent of Non-Humanoid Robots: A 2025 Industry Financing Overview
![]() 11/03 2025
11/03 2025
![]() 608
608
Presented by Zhineng Technology
While Tesla captures the limelight in the AI era with its 'humanoid robots,' a more pragmatic wave of non-humanoid robots is quietly but significantly transforming industries.
From domestic cleaning and pool maintenance to industrial inspections, surgical procedures, and agricultural tasks, intelligent machines not designed to mimic humans are making their way into our daily lives, offering unparalleled efficiency, precision, and functionality. The empowerment of AI extends far beyond humanoid forms, as evidenced by both consumer and industrial applications.
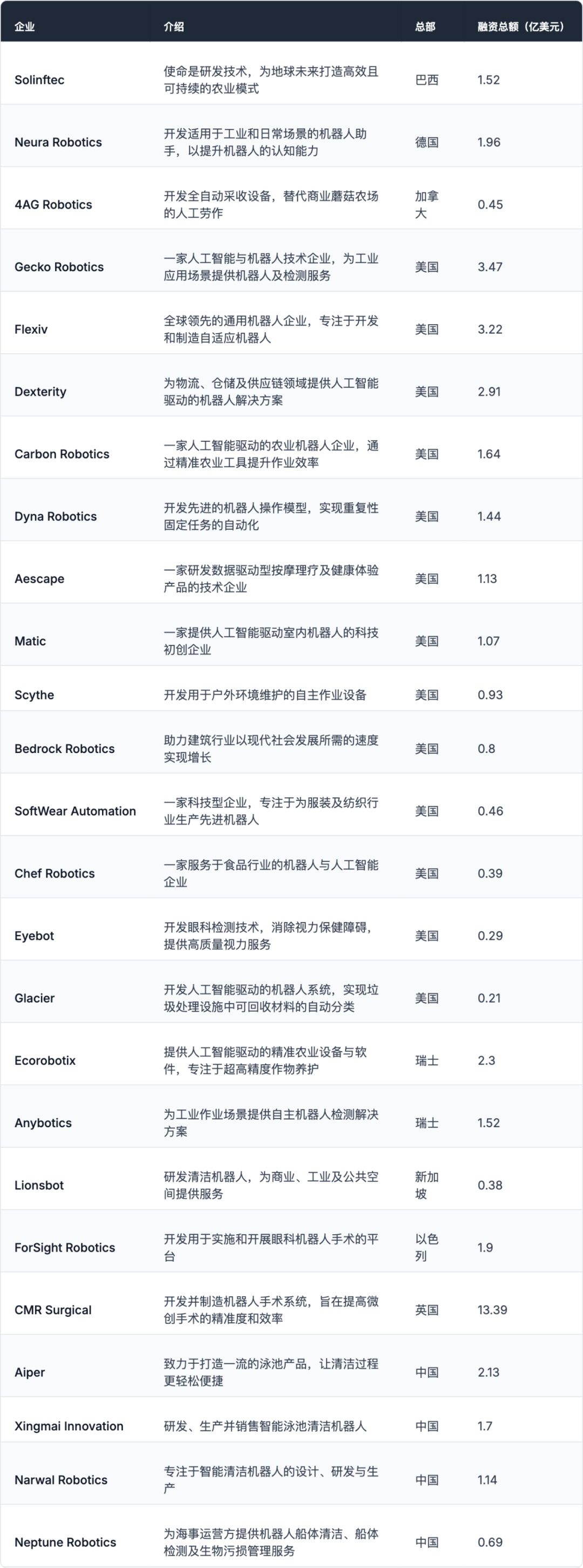
● In the United States, firms such as Gecko Robotics, Flexiv, and Dexterity have each secured over $200 million in funding. Their primary focus lies in industrial inspections, adaptive robotics, and intelligent warehousing, seamlessly integrating robots into frontline production processes.
The healthcare sector is also experiencing rapid advancements, with Aescape providing intelligent physiotherapy services and CMR Surgical enhancing the precision of minimally invasive surgeries through robotic technology. The latter has notably raised $1.3 billion in funding, the highest globally in this field.
● In Europe, Switzerland's Ecorobotix and Anybotics are at the forefront of industrial and agricultural automation, while Germany's Neura Robotics aims to develop robot assistants capable of 'comprehending the world.'
● In China, cleaning robots remain a focal point. Companies like Aiper, Xingmai Innovation, Yunwhale, and Neptune Robotics are developing intelligent cleaning or underwater robots, with total financing surpassing $500 million, highlighting China's strong competitiveness in life service and specialty robot sectors.
01
Consumer Market:
Transitioning from 'Human-Like' to 'Human-Replacing'
In the nascent stages of household automation, the market's pursuit of 'humanization' was nearly unanimous. Robots were envisioned to 'look like humans' and interact in a human-like manner.
However, by 2025, a fundamental shift in capital and technology trends is evident: Consumers are no longer seeking 'smiling assistants' but rather prioritizing 'tools that can thoroughly mop floors, effectively clean pools, and provide precise massages.'
◎ China's Yunwhale Intelligence, which completed a $100 million Series E financing in April, exemplifies this trend by updating home cleaning robots with features such as 'AI adaptive hot water mopping,' 'LiDAR navigation,' and 'dirt detection.'
◎ Similarly, U.S. startup The Bot Co. has raised $300 million in cumulative financing since last year, developing a new generation of household robot systems. Investors' bets clearly indicate that automated cleaning has become a breakthrough application for AI in home scenarios.
Pool cleaning serves as another prime example.
◎ Xingmai Innovation secured $140 million in financing in September, launching the Beatbot, priced at $3,000, and touted as the 'world's first AI-driven five-in-one pool cleaning robot.'
◎ Its competitor, Yuanding Intelligence's Aiper Scuba Max Pro, garners market attention with its intelligent pool mapping and mobile app control capabilities.
Both companies, hailing from China, demonstrate global competitiveness in consumer-grade intelligent hardware. AI is increasingly penetrating more 'experience-driven' scenarios.
◎ New York's Aescape received $83 million in financing in March to expand its fully automated AI massage services. These robots represent continuous breakthroughs in AI-driven human-machine interaction, sensory feedback, and tactile control.
From cleaning to relaxation, robots are gradually infiltrating various 'low-attention but high-value' aspects of human life. Their common feature is 'non-humanoid,' but more fundamentally, it's a shift towards 'de-humanization.'
Technology is reverting to its core focus on functionality and efficiency. Capital's pursuit of companies like Narwal, Aiper, and Aescape signals that AI hardware is transitioning from conceptual stages to real-life pragmatism.
02
Industrial and Professional Sectors:
Climbing the Value Chain
Compared to the high visibility of consumer markets, industrial and professional applications of non-humanoid robots resemble an 'invisible force,' characterized by larger investments, higher technical barriers, and greater long-term value.
Surgical robots are among the most capital-intensive directions.
◎ UK-based CMR Surgical has raised $1.1 billion in cumulative financing, including a $200 million round in April this year, focusing on soft tissue surgery. Its robotic platform assists surgeons in high-precision operations, significantly reducing intraoperative risks.
◎ Israel's ForSight Robotics secured $125 million in Series B financing in June, specializing in ophthalmic surgery automation. Through high-resolution vision and precise robotic arm control, medical robots are evolving from 'replacements' to 'enhancers'—becoming intelligent assistants for doctors.
In the industrial sector, non-humanoid robots exhibit stronger structural innovation.
◎ Switzerland's Anybotics raised $150 million to develop inspection robots with quadrupedal designs capable of climbing, obstacle avoidance, and inspection tasks in complex industrial environments.
◎ China's Flexiv completed a $100 million Series C financing this summer, developing AI-controlled flexible robotic arms for versatile applications in assembly, inspection, and packaging.
Both examples embody the fusion trend of 'animal-like morphology + AI control algorithms,' granting robots greater autonomy and environmental adaptability.
Agricultural automation is another emerging frontier.
Switzerland's Ecorobotix and the U.S.'s Carbon Robotix automate farm management through laser weeding and precision spraying, reducing pesticide use while boosting crop yields and sustainability.
Capital's focus on this sector reflects the potential of non-humanoid robots in addressing labor shortages and modernizing agriculture.
Non-humanoid robots are becoming a critical pillar of industrial intelligence, sharing a common trait: They surpass human limitations without the need to mimic human forms.
Whether performing micron-level surgical operations, navigating complex terrain for inspections, or managing precision agriculture, AI-driven non-humanoid robots demonstrate autonomous cognition and decision-making capabilities that surpass traditional mechanical automation. Their foundational support stems from continuous breakthroughs in AI algorithms, sensor fusion, energy management, and materials science. Moreover, their commercialization pathways are more controllable and scalable than those of humanoid robots.
Summary
The current robotics craze often centers on 'humanoid' narratives: machines capable of walking, talking, and mimicking human emotions.
However, from both market and engineering perspectives, the true drivers of productivity leaps are often machines that do not need to 'resemble humans.' Powered by AI, these robots achieve optimal solutions for specific tasks through lower energy consumption, higher precision, and stronger adaptability. Such products are poised to lead in completing commercial loops, forming extensive application networks that span from households to industries.






