【Annual AI Observation】 Targeting a $5 Trillion Market: Robotics' Cross-Industry Expansion - A New Consensus of the Era
![]() 01/04 2026
01/04 2026
![]() 450
450
Written by | Intelligent Relativity
As the calendar pages flip towards the end of 2025, China's robotics industry stands at a pivotal crossroads, on the cusp of commercial deployment and accelerating at breakneck speed. This year, embodied intelligence, epitomized by humanoid robots, has transcended the realm of laboratory concept validation, achieving a remarkable leap with over 50% growth, transitioning from mere 'stage demonstrations' to practical 'real-world applications.' A trillion-dollar industry is on the horizon, and amidst the myriad of buzzwords in the robotics sector, 'cross-industry integration' warrants a fresh perspective.
This year, it's no longer a solo performance by traditional robotics firms. Industrial titans from the automotive, electronics, and internet sectors have collectively entered the arena, leveraging their technological prowess, supply chain efficiency, and scale advantages. This has propelled the robotics industry from 'niche exploration' to a 'mass competition' phase, fostering a unique wave of 'cross-industry convergence' development.
Reflecting on the 2025 robotics landscape, each cross-industry player harbors distinct aspirations and objectives. Yet, their commonalities are evident: relentless product refinement, excellence in service delivery, and an unwavering pursuit of market demands. Only by adhering to these principles can they carve out a niche for survival in this uncertain technological odyssey.
The Rise of Cross-Industry Behemoths in the Robotics Blue Ocean: A Strategic Move
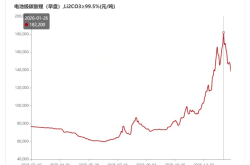
Corporate diversification is not a novelty. However, in 2025, few industries have attracted as many industry giants as the robotics sector. Data reveals that in the first eight months of 2025, primary market financing in the robotics field soared to RMB 38.624 billion, 1.8 times the entire year's total in 2024.
What fuels this surge of investment? The answers are multifaceted, but two factors have reached a consensus. Firstly, the blue ocean effect. Data indicates that in 2024, global industrial robot sales reached 542,000 units, with China accounting for 54% of the global total at 295,000 installations. In 2025, China's robotics market size is projected to exceed RMB 150 billion, representing 35% of the global market share. Some institutions predict that the Chinese market for embodied intelligence alone will reach RMB 400 billion by 2030 and surpass RMB 1 trillion by 2035, accounting for over 50% of the global share.
With such a colossal market at stake, it's natural to attract a multitude of players. However, from a business standpoint, cross-industry players adhere to certain patterns.
Firstly, the collective foray of automotive companies into robotics has become a trend. According to incomplete statistics by Cailian Press reporters, by the end of 2025, at least 20 companies have made cross-industry forays into humanoid robots. Among them, Chery unveiled the humanoid robot Mo Jia, BYD officially announced the mass production of core robot components, Changan introduced the humanoid robot product 'Xiao An,' and Geely collaborated with UBTECH to develop the Walker S1 humanoid robot serving the Zeekr 5G Smart Factory, all becoming focal points in the robotics sector at the time.
Why are automotive companies so enthusiastic about entering the robotics industry? This leads us to the second factor: technological homology. Data shows that various links in the automotive industry chain can deeply integrate with intelligent robots, with a supply chain overlap exceeding 60%. The answer from Chery Group Chairman Yin Tongyue is even more direct: 'A car is essentially a 'mobile intelligent robot.''
Moreover, technological homology is not exclusive to automotive companies venturing into robotics. Facing saturation in the traditional home appliance market, leading companies have swiftly entered the robotics market by leveraging their manufacturing, supply chain, and smart home ecosystem advantages. The underlying logic is the reuse of mechatronics and intelligent control technologies, combined with smart home scenarios and channel advantages, to seek new growth poles. Focusing on core components and complete machines of humanoid robots, they lower mass production thresholds through precision manufacturing and supply chain management capabilities. Consumer electronics companies like DJI, entering the robotics industry, follow the logic of quickly adapting to robot demands through accumulated technologies in micro-motors, precision structures, and sensors. Similarly, internet giants joining the robotics battlefield leverage their strengths in software algorithms, human-computer interaction, and scenario deployment. Players like ByteDance, JD.com, and Baidu can swiftly migrate technologies in AI large models, voice interaction, and visual algorithms, along with their own business scenarios like logistics and retail, for robot commercialization verification.
Therefore, cross-industry giants entering the robotics industry have already pondered whether and how they can succeed.
Collective Bets on Robotics: Seizing the Next Technological Anchor Point
As embodied intelligence emerges as the new trend in the tech industry, the robotics sector's heat carries another profound implication: it serves as a strategic anchor point for tech giants' transformation.
Let's first examine the automotive industry, currently the most actively transforming force. Traditional automakers and new energy players are viewing the robotics sector as their 'second curve.' Geely adopts a 'self-research + investment + ecological cooperation' trifecta approach, planning to invest RMB 5 billion over three years to conquer key areas like motors and reducers. Simultaneously, it builds an ecological landscape by leading investments in companies like Xingdong Era and Unitree Technology, aiming for full-sector coverage in 'humanoid + industrial + logistics' robots and full-scenario synergy in 'vehicle + road + cloud + factory,' completing the transformation from an automaker to a 'software-hardware integration' tech group. Chery's path involves seamless migration of technological and ecological capabilities, exemplified by this year's launch of the Mo Jia robot, which has achieved rapid mass production and delivery, entering markets in over 30 countries, and becoming the world's first humanoid robot to pass three core EU certifications. XPENG Motors takes an even more radical approach, directly positioning itself as a 'global embodied intelligence company,' connecting its product lines of electric vehicles, Robotaxi, and IRON humanoid robots through the 'Physical AI' strategy. The debut of its new-generation IRON humanoid robot sparked global doubts about human impersonation due to its natural, fluid catwalk performance and highly human-like posture.
Besides the aforementioned automotive companies venturing into robotics, giants like BYD, Changan, and GAC are not far behind, launching robot projects, mass-producing core components, or establishing dedicated companies. Leveraging the technological and production homology between automobiles and robots, they aim to seize industrial opportunities. The automotive industry's battle shifting to the robotics sector is now a foregone conclusion.
Home appliance companies are exploring another path: transitioning from 'tool manufacturing' to 'smart ecosystems.' The '2025 China AI Home Appliance Industry Development White Paper' predicts that future AI home appliances will trend towards the popularization of household robots. This undoubtedly presents a massive market opportunity, one that emerges from their core business. Against this backdrop, home appliance manufacturers naturally have a strong motivation to transform.
Midea is a typical representative. To advance frontier exploration in general-purpose humanoid robots, Midea has established a dedicated Humanoid Robot Innovation Center, focusing on developing platforms in various forms like humanoid and super-humanoid robots and creating solutions for industrial and commercial scenarios. Currently, Midea has built a complete R&D system from core components to complete machine systems. Its self-developed reducers and servo motors have entered mass production, with some products already in market applications, covering light-duty robots to heavy-duty robots weighing up to 300kg.
Similar stories are unfolding among home appliance manufacturers like Haier, Robam, and Stone Technology: Haier Group announced a 'home + industrial' dual-track strategy, fully entering the robotics field and embarking on a transformation from a home appliance giant to a new force in robotics. Robam Appliance established an Artificial Intelligence Research Institute to deeply explore AI-empowered kitchen robot application scenarios. Stone Technology, starting with intelligent cleaning robots, expanded its product portfolio to floor washers, washing machines, and lawnmowers, achieving full-scenario coverage in intelligent cleaning. Clearly, home appliance manufacturers venturing into robotics have richer levers, more specific entry points, and are more appealing to C-end users.
Internet giants' strategies lean towards achieving breakthroughs through strength: leveraging their technological and capital advantages, the natural alignment between the robotics sector and AI deployment capabilities offers ample imagination. Against this backdrop, internet giants act more directly and efficiently: ByteDance's Seed team released the general-purpose robot model GR-3, achieving precise execution of complex household tasks, with the R&D team expanded to 150 members, showcasing determination in self-research and production. Huawei launched the 'Kuafu' robot based on the HarmonyOS system, leveraging multi-device collaboration capabilities to bridge smart home and industrial handling scenarios, strengthening ecological interconnection advantages. Xiaomi invested over RMB 15 billion in the robotics field through a 'technology + capital + talent' tridimensional drive, not only feeding back robot R&D with technologies accumulated from its automotive and smart home businesses but also completing its industrial chain through investments in companies like Unitree Technology, aiming for seamless collaboration between robots and multiple terminals. JD.com announced an investment of over RMB 10 billion in resources, planning to assist a hundred robot brands in achieving sales exceeding RMB 100 million within three years, promoting intelligent robots into millions of terminal scenarios, and reconstructing the industry landscape as an ecological enabler.
Clearly, this competition in the robotics sector has become a future battlefield where giants have invested heavily. However, at its core, it remains a strategic reconstruction amidst the tech wave: on one hand, robotics business is the prime choice for enterprises to open up new growth poles and serves as a core carrier for integrating technologies, linking scenarios, and reconstructing ecosystems. Therefore, from automotive to home appliances, from the internet to advanced manufacturing, enterprises are leveraging robotics business to activate existing technological capabilities, build incremental ecological landscapes, and accelerate the transformation into tech ecosystem groups. Despite uncertainties in technological bottlenecks and commercial profitability, this transformation has become an irreversible trend that will continue to reshape the competitive landscape of the tech industry.
Numerous Challenges, but 'Just Get Started'
As cross-industry giants from automotive, home appliances, and the internet flood into the robotics sector, this seemingly vibrant strategic transformation conceals numerous challenges.
Technologically, amidst undefined paths, cross-industry players' core capabilities inevitably face 'incompatibility issues.' On one hand, current robotics technology routes remain unsettled, ranging from pure vision solutions to multi-sensor fusion and from hydraulic drives to motor drives, each with its pros and cons. Cross-industry players are prone to falling into the 'follow the trend and make mistakes' trap. For instance, while automotive companies excel in perception and planning technologies for intelligent driving, areas like precise motion control and bionic joint development for robots differ fundamentally from automotive technologies. On the other hand, internet companies' AI large model capabilities struggle to directly translate into physical control capabilities for robots, and home appliance manufacturers' manufacturing experience fails to meet the high-precision assembly demands of robots. More dangerously, some cross-industry players adopt a 'hot topic chasing' mindset, making technological沉淀 unlikely, let alone achieving scenario deployment.
When it comes to scenario commercialization, this is precisely the weak link for the entire industry. For cross-industry players, scenario adaptation has always been an arduous task: industrial scenarios demand extremely high precision and robust stability from robots, while unstructured scenarios like households and retail test robots' environmental understanding and interaction capabilities. Cross-industry players often struggle to quickly and precisely match diverse scenario demands.
Moreover, cost is another major consideration. While the localization rate of core components for humanoid robots gradually improves, mass production costs remain high. Automakers like BYD and GAC face immense challenges in supply chain integration and process optimization to achieve their goal of reducing costs to below RMB 200,000.
Despite these challenges, cross-industry players remain determined for the upcoming 2026. The current industry consensus is that mass production has begun, and the industry will enter a high-growth phase. Any difficulties can only be addressed through market expansion and continuous refinement. This requires cross-industry players to not only keep pace with technological paths but also strengthen scenario and supply chain collaboration to survive the 'knockout stage' in the robotics sector.
Clearly, this is a technological singularity filled with opportunities and challenges. The next chapter will reveal who can seize fleeting opportunities amidst transformation.
*All images in this article are sourced from the internet