Who is Quietly Rising in the "Urban Race" of Humanoid Robots?
![]() 01/17 2025
01/17 2025
![]() 537
537
2024 is heralded as the inaugural year of humanoid robot commercialization. In this milestone year, humanoid robots manufactured in Hangzhou have frequently captured headlines on the global internet.
Unitree Technology's release of the B2-W robot dog demonstration video garnered worldwide attention; CloudMinds Robotics' "Jueying X30" was deployed for power tunnel inspection in Singapore; and NVIDIA's list of partners in the humanoid robot sector includes Unitree Technology's H1 humanoid robot among six domestic manufacturers...
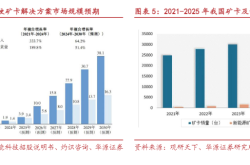
As a crucial race in future industries and a vital direction for nurturing and generating new productive forces, the humanoid robot industry is rapidly advancing into the commercialization phase. According to GGII (Gao Gong Robotics Industry Research Institute), it is estimated that the global penetration rate of humanoid robots in service robots will reach 3.5% in the next three years, with a market size exceeding US$2 billion. By 2030, the global market size is projected to surpass US$20 billion. How will Hangzhou, renowned as the pioneer city of the digital economy, secure a competitive edge in this vast market?
Hangzhou Humanoid Robot Industry Planning
Hangzhou stands at the forefront of promoting the industrialization of robots. Data from the Firestone Creation Industrial Data Center reveals that currently, Hangzhou boasts over 200 robot-related enterprises, with a robot industrial output value of RMB 15 billion in 2023. The city has gathered 10 specialized and innovative "little giants" across various industrial links, including robot component production, complete machine manufacturing, and system integration.
To further capitalize on the humanoid robot race, in December 2024, the Hangzhou Municipal Government issued the "Hangzhou Humanoid Robot Industry Development Plan (2024-2029)", emphasizing a focus on "optimal bodies + powerful brains" and accelerating the construction of an integrated innovation system and a comprehensive industrial chain ecosystem for humanoid robot R&D, design, manufacturing, and application. This blueprint outlines a roadmap for the development of Hangzhou's humanoid robot industry in the coming years.
Regarding the spatial layout of the humanoid robot industry, the "Plan" proposes to establish a humanoid robot production and research transformation leading area, a production and research integration demonstration area, and a collaborative manufacturing development area, leveraging the overall development layout of the West Lake Science and Technology Innovation Corridor and the East City Intelligent Manufacturing Corridor, alongside the scientific research and industrial resource endowments of various regions.
Table: Spatial Layout of Hangzhou's Humanoid Robot Industry
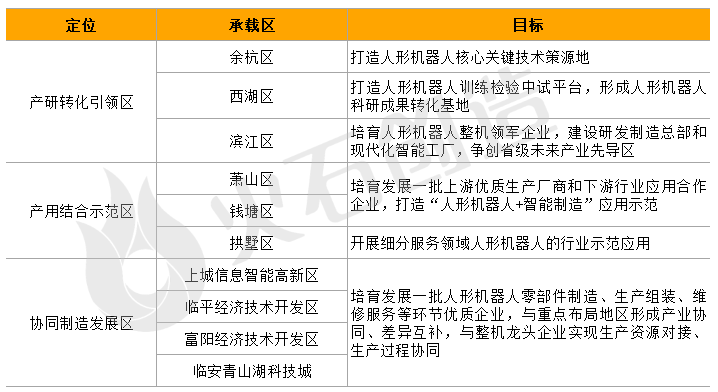
Source: Compiled by Firestone Creation based on public information
This policy will significantly propel the growth of Hangzhou's humanoid robot industry. Dr. Feng Lei, deputy director of the Firestone Creation Industrial Research Institute, stated:
On one hand, the "Plan" will foster the development of a technological innovation system. It proposes the establishment of an integrated innovation system, incentivizing enterprises to increase investment in humanoid robot R&D. For instance, enterprises can forge closer industry-university-research collaborations with universities and research institutions to jointly undertake key technology research.
On the other hand, the "Plan" will nurture the full industrial chain ecosystem. It emphasizes the construction of a comprehensive industrial chain ecosystem, encouraging closer cooperation between upstream and downstream enterprises. In the manufacturing sector, large enterprises can drive the advancement of component suppliers, enhancing component quality and supply stability. In the application sector, enterprises are urged to expand the application of humanoid robots into more fields, such as medical rehabilitation and education, forming a complete industrial ecosystem loop and bolstering the industry's overall competitiveness.
Hangzhou's Humanoid Robot Industry Foundation
Artificial intelligence serves as the "brain" for robots. Hangzhou enjoys a first-mover advantage in the field of artificial intelligence, gathering numerous AI technology R&D institutions and high-tech enterprises. For example, the "China Cloud Valley" project is a significant cluster of the AI industry in Zhejiang Province, housing renowned enterprises like Alibaba and Hikvision.
In terms of hardware manufacturing, Hangzhou excels in research on intelligent sensing and control technology for robots and the R&D of complete machine systems, particularly in the realms of intelligent robots and humanoid robots.
Regarding scientific research capabilities, Hangzhou boasts innovation platforms such as Zhejiang University, Westlake University, BUAA Hangzhou Innovation Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, Zhejiang Robotics and Intelligent Equipment Innovation Center, and Alibaba DAMO Academy. This robust research infrastructure enables Hangzhou to establish an early-mover advantage in the field of humanoid robots.
In Feng Lei's perspective, Hangzhou's advantages in developing the humanoid robot industry are primarily manifested in three aspects:
First, technological R&D strengths. Companies like Unitree Technology have accumulated extensive technical expertise in fields such as robot dogs. Technological achievements in balance control and adaptability to complex terrains of robot dogs can provide technical support for stable walking and complex environment operations of humanoid robots. In industry-university-research collaborations, Zhejiang University offers theoretical support in robot dynamics modeling, new sensor applications, and deep learning algorithm optimization, supplying high-end talent and cutting-edge technology to local humanoid robot enterprises.
Second, industrial ecosystem strengths. In robot component manufacturing, there are numerous enterprises engaged in producing high-precision motors, reducers, and other key components, such as Sankai Electromechanical and Zhenzheng Weidun. In software development, companies like CloudMinds, Qianxun Technology, and Westlake Robotics develop specialized operating systems and control software. Additionally, institutions focused on robot testing and certification, like Hangzhou Cyber, Hangzhou Oute, and SGS, provide product quality testing and certification services to enterprises. The gradual refinement of the industrial chain fosters further agglomeration and development of the humanoid robot industry.
Third, market strengths. Leveraging its robust e-commerce and logistics industry foundation, Hangzhou's humanoid robots can efficiently execute tasks like shelving and unshelving goods with their flexible limbs and intelligent vision systems, presenting broad market application scenarios.
Feng Lei believes that within the Yangtze River Delta region, Hangzhou is at the forefront of humanoid robot technological innovation. Compared to cities like Shanghai and Suzhou, Hangzhou boasts its own advantages in terms of the number of robot enterprises and the completeness of industrial supporting facilities.
Furthermore, Hangzhou and Ningbo have forged a strong complementary relationship.
In terms of industrial chain division of labor and collaboration, Ningbo, as the hub of humanoid robots in Zhejiang, excels in areas such as large-scale robot production equipment and precision mold manufacturing. Conversely, Hangzhou shines in software algorithms and intelligent control. The two cities can achieve an organic "hardware + software" integration, enhancing the overall performance of humanoid robots.
In terms of market expansion and collaboration, Ningbo boasts a relatively developed manufacturing and port logistics industry, with substantial demand for industrial robots and logistics robots. Enterprises from both cities can collaborate to promote the application of humanoid robots.
Suggestions for the Development of Hangzhou's Humanoid Robot Industry
Overall, Hangzhou already possesses a solid industrial foundation. In the fiercely competitive "Urban Race" of humanoid robots, how can it further harness its strengths? In this regard, Feng Lei suggests:
First, accelerate the cultivation of high-end talent. Humanoid robots fall under an interdisciplinary field, and there is a relative shortage of versatile talent proficient in both mechanical engineering and artificial intelligence and software development. Enterprises may need to invest higher costs in attracting talent from other regions or strengthen their in-house talent development systems. This can be achieved through collaborations with universities to develop tailored professional courses, nurturing talent that meets the demands of the humanoid robot industry.
Second, address the reliance on imports for key components. Hangzhou enterprises partially depend on imports for key components of humanoid robots, such as high-performance motors and high-precision reducers. It is imperative to increase investment in the research and production of key components, and cultivate local component suppliers through technological innovation and industrial policy guidance, thereby elevating the localization rate of key components.
Third, actively participate in the formulation of industry standards and enhance global influence. The humanoid robot industry is progressing rapidly, and current industry standards are still evolving. It is essential to strengthen cooperation with other cities and institutions domestically and internationally, and actively engage in the formulation of industry standards. For instance, in terms of safety standards and performance evaluation standards for humanoid robots, strive for more discourse power to regulate the production and market competition of local enterprises, while elevating the influence of Hangzhou's humanoid robot industry nationally and even globally.