Top 10 Global Chip Giants: The Latest Ranking Unveiled!
![]() 08/06 2025
08/06 2025
![]() 671
671

Earlier this year, I compiled a list of the top 10 chip giants based on the financial reports released by leading global semiconductor companies. Now, six months have passed, and with the ongoing disclosure of Q2 financial reports, the chip market has undergone significant changes.
Let's revisit these chip giants, delving into the evolution of the semiconductor market in the first half of the year based on Q1 rankings and data, coupled with Q2 revenue performance.
01
Leading Chip Companies: The Latest Ranking
The companies selected this time refer to the top 15 semiconductor companies published by WSTS in Q2 last year, including NVIDIA, Samsung, Broadcom, Intel, SK Hynix, Qualcomm, Micron, AMD, Infineon, MediaTek, TI, ST, among others.
Based on the Q2 2025 performance of these companies, I have compiled the latest ranking for the new quarter. (NVIDIA's Q2 revenue data is forecast data)
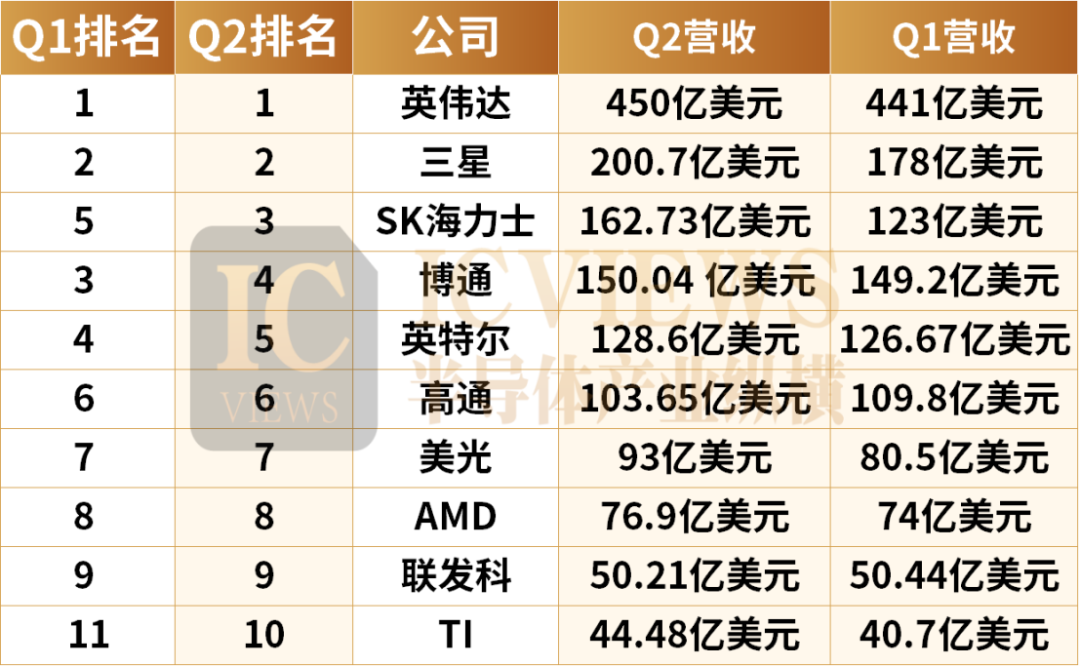
It's worth noting that due to differences in annual calculation methods among semiconductor manufacturers and the fact that some revenue data has undergone exchange rate conversion, there may be discrepancies in the rankings based on revenue comparison results. These rankings are for reference only. Additionally, due to the diversification of Apple's business sector revenue, the company has not been included in this ranking.
NVIDIA's financial report data was released later than that of other semiconductor companies and is expected to be published by the end of this month. According to NVIDIA's Q1 forecast data, the company's revenue in Q2 is projected to reach $45 billion (±2%).
Samsung's Q2 revenue for the DS department, encompassing the storage business, was KRW 27.9 trillion (approximately $20.07 billion), marking a 11% increase quarter-on-quarter and a 2% decrease year-on-year. Operating profit stood at KRW 0.4 trillion (about $290 million), a 64% decrease quarter-on-quarter and a 94% decrease year-on-year, falling below the KRW 1 trillion mark for the first time in six quarters.
Broadcom's Q2 (as of May 4, 2025) revenue amounted to $15.004 billion, a 20% increase year-on-year; GAAP net profit reached $4.965 billion, surging 134% year-on-year.
Intel's Q2 revenue was $12.86 billion, a 0.2% increase year-on-year but exceeding market expectations; net profit was a loss of $2.92 billion, higher than the loss of $1.61 billion in the same period last year.
SK Hynix's Q2 revenue was KRW 22.23 trillion (about $16.273 billion), a 35% increase year-on-year and a 26% increase quarter-on-quarter; operating profit was KRW 9.21 trillion (about $6.74 billion), a 68% increase year-on-year and a 24% increase quarter-on-quarter; net profit was KRW 6.9962 trillion (about $5.121 billion), a 70% increase year-on-year. The operating profit margin was 41%, and the net profit margin was 31%.
Qualcomm's Q2 revenue was $10.365 billion, a 10% increase year-on-year, with adjusted net profit of $2.67 billion, a 25% increase, but falling short of market expectations, leading to a 4.7% drop in share price after market close.
Micron's Q2 (as of May 29, 2025) revenue was $9.3 billion, a 15% increase quarter-on-quarter and a 37% increase year-on-year; under Non-GAAP, operating profit was $2.49 billion, and the operating profit margin rebounded to 26.8% from 24.9% in the previous quarter; net profit was $2.181 billion, a 22.3% increase quarter-on-quarter and a 210.7% increase year-on-year.
AMD's Q2 revenue was $7.69 billion, a 32% increase year-on-year, with an estimate of $7.43 billion. Adjusted gross margin was 43%, compared to 53% in the same period last year and an estimate of 43.1%. Adjusted net profit was $781 million, a 31% decrease year-on-year, and adjusted earnings per share were $0.48, compared to $0.69 in the same period last year and an estimate of $0.49.
MediaTek's Q2 revenue was NT$150.369 billion (about $5.021 billion), a 1.9% decrease quarter-on-quarter and an 18.1% increase year-on-year; net profit was NT$28.064 billion, a 2.2% decrease quarter-on-quarter and a 17.7% increase year-on-year.
Infineon's Q2 (as of June 30, 2025) revenue was €3.704 billion (about $4.275 billion), flat year-on-year and a 3% increase quarter-on-quarter. Profit was €668 million, with a profit margin of 18.0%.
TI's Q2 revenue was $4.448 billion, a 16% increase year-on-year and a 9% increase quarter-on-quarter. Operating profit increased by 25% year-on-year to $1.563 billion; net profit was $1.295 billion, a 15% increase year-on-year.
ST's Q2 net revenue was $2.77 billion, with a gross margin of 33.5%, an operating loss of $133 million, and a net loss of $97 million (equivalent to diluted earnings per share of -$0.11). On a non-GAAP basis, net operating profit was $57 million, and net profit was $57 million (equivalent to diluted earnings per share of $0.06).
ADI's Q2 (as of May 3, 2025) revenue reached $2.64 billion, a 22% increase year-on-year. This growth exceeds the general expectations of Wall Street analysts and indicates that the analog chip industry is gradually emerging from the trough and entering a recovery cycle.
NXP's Q2 revenue declined by 6% year-on-year to $2.926 billion, slightly higher than analysts' expectations of $2.9 billion. Although revenue increased by 3% quarter-on-quarter, Non-GAAP operating profit declined by 13% year-on-year to $935 million.
02
Leading Chip Companies: Major Highlights
In previous articles, we observed the following key points in the semiconductor market from the Q1 performance reports of the top 10 chip giants: explosive growth in data center business; differentiation in the storage market; continued popularity of custom ASICs; and demand for automotive chips hitting a trough.
Entering Q2, it's evident that these trends have generally persisted and become more pronounced.
NVIDIA's Financial Report: Stirring Up New Ripples
If we discuss which chip giant has been the most noteworthy in the first half of this year, NVIDIA undoubtedly stands out.
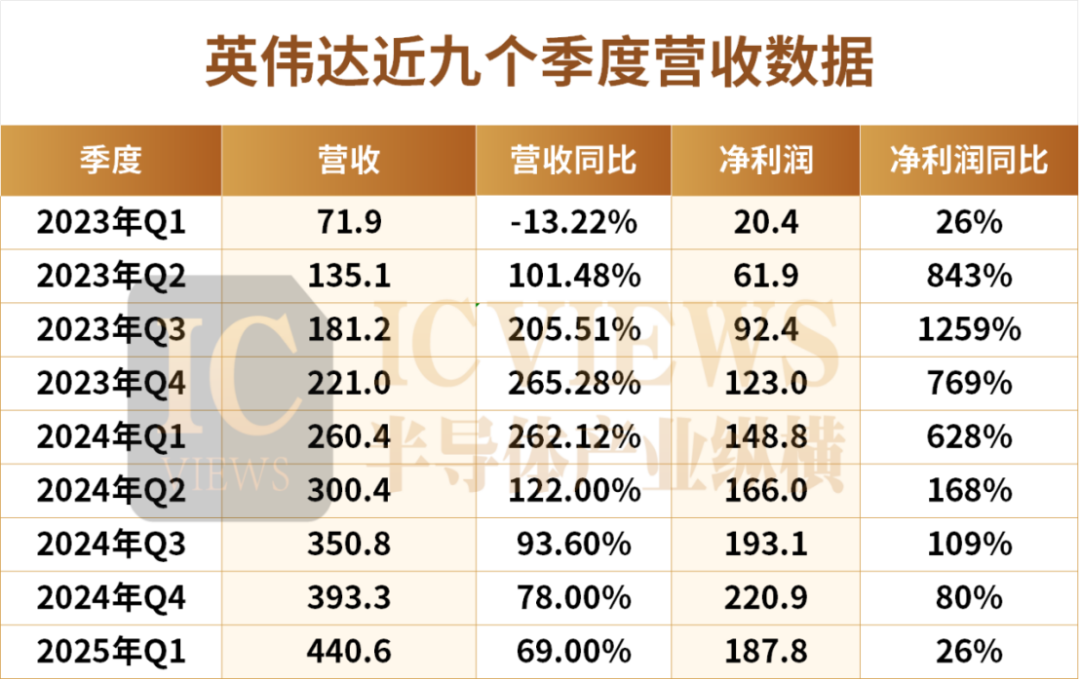
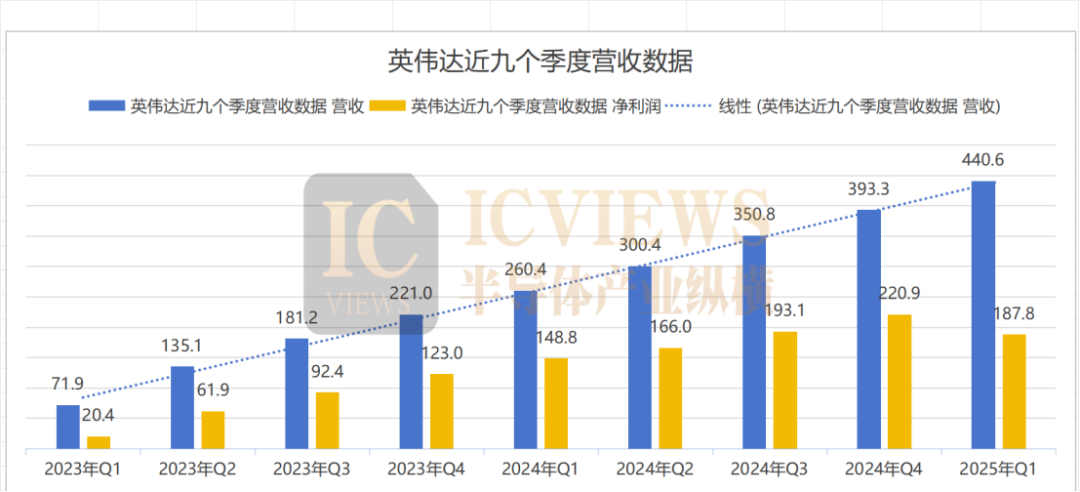
Looking back at the past year, NVIDIA's growth rate has been astonishing, with its quarterly revenue increasing by over 200% year-on-year multiple times.
NVIDIA's revenue forecast for Q2 is slightly lower than the market expectation of $45.9 billion, primarily due to uncertainties in Chinese market policies and adjustments in the supply chain ramp-up pace.
In April this year, the U.S. government decided to ban NVIDIA from selling its H100 chips to the Chinese market. The H100 is an AI accelerator designed specifically for the Chinese market to comply with U.S. export restrictions. Based on NVIDIA's Hopper architecture, the H100 features advanced CoWoS packaging technology. The H100 is more suitable for vertical model training and inference but cannot meet the training needs of trillion-parameter large models.
Subsequently, on July 15, NVIDIA announced the resumption of supply of the China-specific H100 computing chips. NVIDIA stated that the U.S. government had assured NVIDIA of granting the license, and the company hoped to start delivery as soon as possible.
However, throughout the second quarter, NVIDIA's revenue in China was significantly impacted. NVIDIA had previously warned that this could result in a $5.5 billion inventory write-down and up to $15 billion in lost revenue.
Does this mean that NVIDIA may not be able to maintain its previous high growth rate in Q2? In fact, it's not the case.
Morgan Stanley previously issued a research report stating that despite the short-term financial pressure caused by the "H100 sales restriction," improved GB200 supply and explosive growth in inference demand are the key drivers of NVIDIA's future growth, and performance in the second half of the year may see an acceleration inflection point.
AMD's data center business performed somewhat worse in the new quarter. In Q2, its data center business revenue increased by 14% to $3.2 billion, slightly lower than market expectations of $3.25 billion.
Betting on HBM: SK Hynix and Micron Score Big
As an HBM supplier inextricably linked to NVIDIA GPUs, SK Hynix has also hit the fast lane, and Micron's revenue has also entered a new phase.
While everyone is focused on how NVIDIA's GPUs are revolutionizing the world, SK Hynix has become the one providing the most critical and scarce "shovels" for the "gold diggers."
In Q2, with sales of KRW 21.8 trillion, SK Hynix surpassed Samsung Electronics, which has long occupied the top spot (KRW 21.2 trillion), to win the championship in global storage market sales (including DRAM and NAND).
Analysts said that although Samsung and Micron are catching up, it is widely believed in the industry that SK Hynix's leading position "will continue until 2025 and may extend to 2026."
Last year, Micron announced the start of mass production of HBM3E high-bandwidth memory, with its 24GB 8H HBM3E product to be supplied to NVIDIA and applied to NVIDIA's H100 Tensor Core GPU. In April this year, industry insiders revealed that Micron's HBM3E 12-layer product had passed NVIDIA's quality tests and began mass production, to be equipped on the AI accelerator "Blackwell Ultra (GB300)."
Thus, Micron became the second company after SK Hynix to supply the currently mainstream product HBM3E 12-layer to NVIDIA.
On the other hand, Samsung Electronics' Q2 storage business revenue declined year-on-year, and its HBM market share also plummeted from 41% in the same period last year to 17%, lagging behind competitors such as SK Hynix and Micron.
Its performance pressure mainly stems from two aspects: First, U.S. export restrictions on China have restricted storage chip sales channels, leading to inventory write-downs; second, HBM products have lagged behind in technological credibility and customer expansion, failing to pass the rigorous quality tests of core customers such as NVIDIA.
ASICs and Automotive Chips: Both Trending Upwards
Custom ASICs have been hot topics since 2025, but no new hot events have led to further market heating up in this quarter.
AI revenue growth is primarily driven by the demand for data center AI acceleration chips from hyperscalers (such as Google, Meta, ByteDance). These customers seek to reduce their dependence on NVIDIA's general-purpose GPUs through customized ASICs while improving training and inference efficiency.
The automotive chip market has truly hit bottom and is crossing the winter.
From Q1 this year, the revenue of the automotive chip market fell short of expectations, a common performance among chip giants, but the clarion call for market recovery has also sounded.
TI stated that the peak of the automotive market came a year later than that of the industrial sector, with the industrial sector peaking in the third quarter of 2022 and the automotive sector peaking in the third quarter of 2023. Therefore, it can be expected that the automotive industry will be the last to recover.
In terms of specific data, TI's industrial market grew by more than 15% year-on-year and about 15% quarter-on-quarter in Q2, but the automotive market grew by mid-single digits year-on-year and fell by low-single digits quarter-on-quarter, indicating a slower recovery pace.
ST's Q2 automotive chip sales were also slightly lower than expected. Although revenue from the personal electronics and industrial sectors increased, these growths were far from offsetting the decline in the automotive business. This structural imbalance reflects the strategic risk of STMicroelectronics' over-reliance on the automotive industry.
However, NXP stated that "the two-year surplus of automotive chip inventory may finally end this year." This statement by NXP CEO Kurt Sievers is undoubtedly exciting news for the entire industry struggling in the inventory quagmire.
He further explained that the inventory levels of most Tier 1 automotive customers are either close to normal or have already reached normal levels.
03
Semiconductor Market Size Surges in the First Half of the Year!
According to data from the World Semiconductor Trade Statistics (WSTS), the global semiconductor market size reached $346 billion from January to June this year.
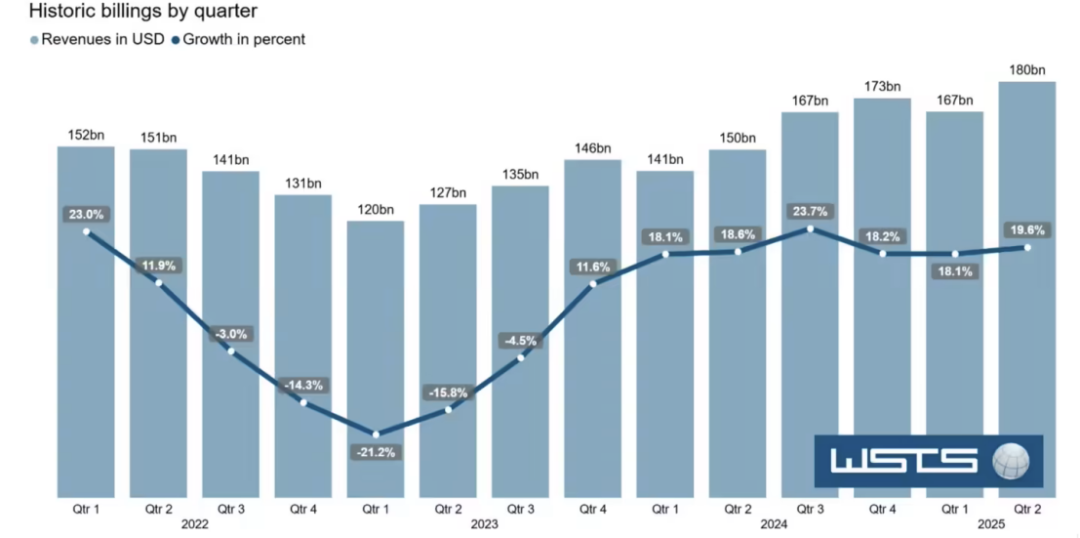
Divided by time, the market size in the first quarter was approximately $167 billion, an increase of 18.1% year-on-year; the second quarter was approximately $180 billion, an increase of 19.6% year-on-year.
Divided by category, the logic semiconductor market size increased by 37% in the first half of the year, while the storage semiconductor market grew by 20%, sensors by 16%, and analog and discrete devices both increased slightly by 4%. In contrast, discrete devices and optoelectronic devices experienced quarter-on-quarter declines of 4% and 0.5%, respectively.
WSTS also revised upwards its forecast for the full-year 2025 global semiconductor market size to $728 billion, a 15.4% increase compared to 2024; while the semiconductor market size in 2026 is expected to reach $800 billion, a further year-on-year increase of 9.9%.
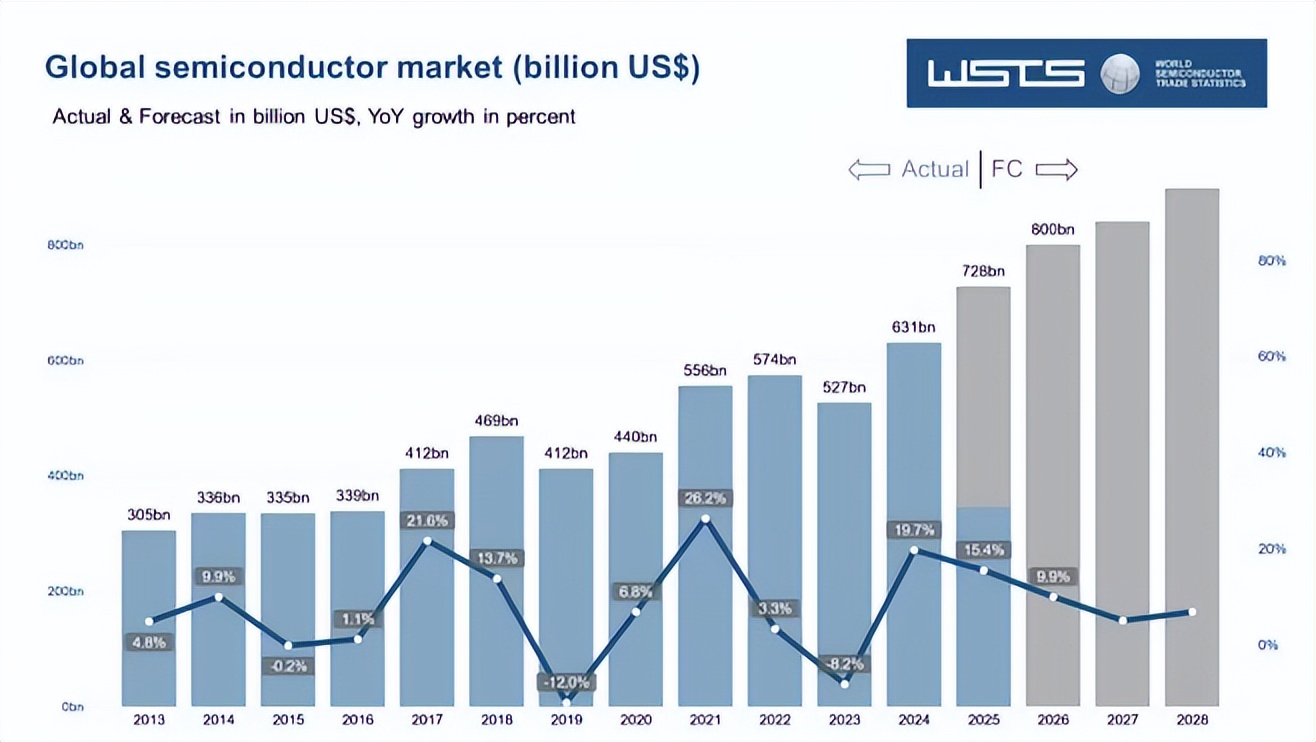
In the future, AI infrastructure will become the primary growth driver of the semiconductor market. With the continuous development of large language model technology, especially the current trend of training with trillions of parameters, enormous computing power is required to generate tokens (output content of generative AI). Currently, it is observed that enterprises are expected to invest approximately $1.5 trillion in IT from 2025 to 2028, of which more than $325 billion will flow to AI platforms and infrastructure.
This also implies