Onsemi Microelectronics's STAR Market Challenge: Founder's Absence and Special Voting Rights Stir Debate
![]() 04/14 2025
04/14 2025
![]() 504
504
Autonomous and controllable development is imperative.
Wu Wei, Investor Network
Amidst the surge in domestic semiconductor substitution, Beijing Onsemi Microelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Onsemi Microelectronics") has witnessed its revenue skyrocket from 923 million yuan to 21.01 billion yuan over the past three years, achieving a compound annual growth rate of 50.88%, attributed to breakthroughs in 5G RF front-end chips. With its impressive growth, Onsemi Microelectronics' application for listing on the STAR Market has recently been accepted.
However, despite shipping over 2 billion chips annually, the company has incurred cumulative losses of 805 million yuan from 2022 to 2024 and remains unprofitable. Notably, despite support from industry giants such as Huawei's Haibo Investment and Xiaomi Fund, issues like high inventory levels, liquidity pressures, and management changes have clouded the company's IPO journey.
Hidden Concerns Amid Rapid Expansion
Founded in 2012, Onsemi Microelectronics' early development was fraught with challenges. According to Tianyancha, the company's shareholders and senior executives have undergone numerous changes since its inception. In 2015 and 2016, Onsemi Microelectronics was listed in the abnormal business operation directory due to "inability to contact the registered residence or business premises" and "failure to submit annual report information as required."
Nonetheless, with the emergence of founder and actual controller Qian Yongxue, coupled with the booming domestic substitution demand in the semiconductor industry, Onsemi Microelectronics' fortunes have dramatically transformed. In 2020, investment institutions such as Xiaomi Fund and Huawei's Haibo Investment invested in Onsemi Microelectronics, and the company's 5G RF front-end chips and RF SoC chips gradually gained market recognition.
Onsemi Microelectronics' core product, the 5G RF front-end chip, directly competes with overseas giants like Broadcom and Skyworks. In 2024, related revenue reached 1.79 billion yuan, accounting for 85.21% of total revenue, and it has entered the supply chains of top global mobile phone brands, including Samsung, Xiaomi, Honor, OPPO, and even Apple.
Under the synergistic effect of "capital + orders" from customers like Huawei Haibo and Xiaomi Fund, Onsemi Microelectronics' revenue surged from 923 million yuan in 2022 to 21.01 billion yuan in 2024, with a compound annual growth rate of 50.88%. Besides the successful deployment of RF front-end chips, the company's RF SoC chip products have also been introduced into products of renowned customers such as Alibaba, Xiaomi, HP, Kaadas, Holitech Technology (301011.SZ), and Sunray Medical.
However, Onsemi Microelectronics' rapid expansion also harbors hidden concerns. Firstly, the company's supply chain management capabilities have not kept pace with its business growth, leading to significant inventory write-downs. Its production and sales ratio dropped from 101.18% in 2022 to 87.98% at the end of 2024.
As a result, Onsemi Microelectronics' inventory book balance increased from 645 million yuan to 920 million yuan from 2022 to the end of 2024, marking a cumulative increase of 42.6%. During this period, the company provisioned a cumulative amount of 485 million yuan for inventory write-downs, with a cumulative loss of 244 million yuan. The inadequacy of supply chain management has eroded a significant portion of Onsemi Microelectronics' profits.
Besides insufficient supply chain management, Onsemi Microelectronics, which has suffered long-term losses, also faces liquidity pressures. From 2022 to 2024, Onsemi Microelectronics incurred cumulative losses of 805 million yuan, and the company's asset-liability ratio increased from 17.82% in 2022 to 42.33% in 2024.
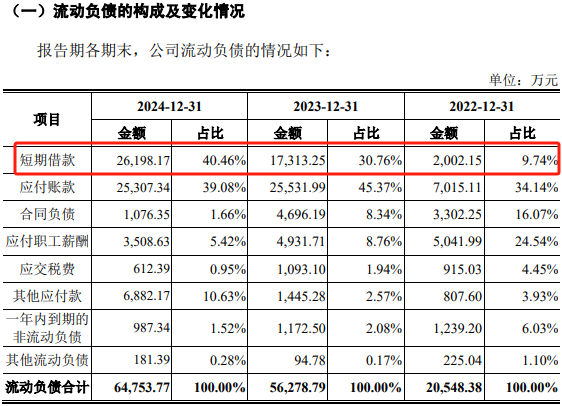
Data Source: Prospectus
Among Onsemi Microelectronics' liabilities, short-term borrowings exhibited the most significant growth, increasing from 20.0215 million yuan in 2022 to 262 million yuan at the end of 2024, a 12-fold increase over three years. With the rapid growth of interest-bearing liabilities, Onsemi Microelectronics' interest expenses also increased from 1.0931 million yuan in 2022 to 6.5496 million yuan in 2024, nearly a five-fold increase over three years.
Balancing Under Special Agreements
To fuel its development, Onsemi Microelectronics has conducted multiple rounds of financing, resulting in a relatively dispersed shareholding structure with up to 72 shareholders before the issuance. The withdrawal of co-founder Yang Qinghua has garnered market attention. According to the prospectus, when Onsemi Microelectronics was founded in 2012, Yang Qinghua held 75% of the company's shares and was the controlling shareholder. However, Tianyancha records indicate that the actual controller Qian Yongxue became a director of the company in 2015 and gradually came to the forefront.
It's worth noting that in the gambling agreements signed between early investors such as Nanjing Ruida and Wang Xinfu and Onsemi Microelectronics and its shareholders, Yang Qinghua and Qian Yongxue were jointly the main obligors. However, in 2019, co-founder Yang Qinghua abruptly withdrew from Onsemi Microelectronics' management, ceasing to serve as the company's director and general manager, and instead operating Suzhou Hantianxia, which, according to its official website, also focuses on RF filter research and development, directly competing with Onsemi Microelectronics. Currently, Suzhou Hantianxia has completed its C round of financing. The prospectus does not provide an explanation for Yang Qinghua's sudden withdrawal.
In contrast to Yang Qinghua's withdrawal, current Chairman Qian Yongxue firmly controls the company through a special voting rights mechanism. As of the prospectus signing date, Qian Yongxue directly holds only 3.86% of the company's shares but controls a total of 62.43% of Onsemi Microelectronics' voting rights through controlling shareholding platforms such as Beijing Xinke and Nanjing Tongxin, as well as the special voting rights mechanism, thereby becoming the actual controller of the company.
Specifically, except for special circumstances like modifying the company's articles of association and changing the voting rights of Class A shares, the shares held by Qian Yongxue and the entity he controls, Beijing Xinke, are Class A shares, which have 10 times the voting rights of Class B shares. To establish Qian Yongxue's position as the actual controller, Onsemi Microelectronics also stated in the prospectus that "there is no situation where the shareholders of the issuer (Onsemi Microelectronics) control the company through agreements."
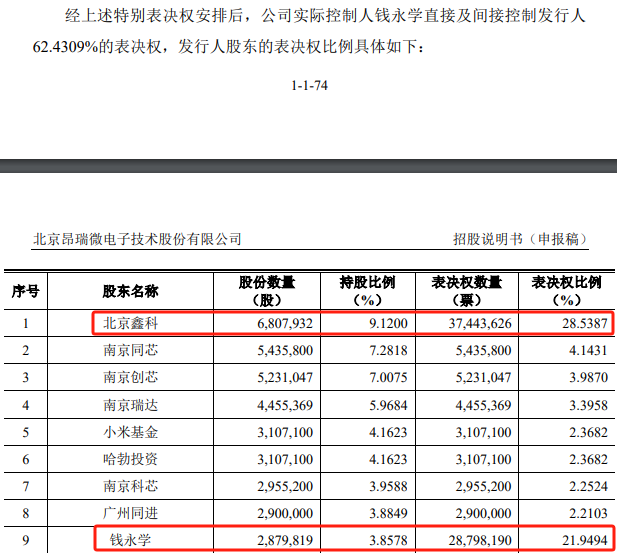
Data Source: Prospectus
Public information indicates that regulatory authorities scrutinize the listing of enterprises without actual controllers. Companies such as CoreMotion (688582.SH), AMEC (688012.SH), and Qizhong Technology (688352.SH) were questioned about their lack of actual controllers when applying for listing on the STAR Market; among them, Qizhong Technology even changed its description of the actual controller, identifying the Hefei SASAC as the actual controller for the first time before the company's listing, which differed from the time of application.
Onsemi Microelectronics' IPO journey is both a microcosm of domestic semiconductor substitution and a delicate balancing act between risks and opportunities. Tempted by policy dividends and market space, the company faces operational risks like customer dependence, inventory management, and liquidity pressures, as well as governance-level issues such as the founder's withdrawal and concentrated control. These constitute a "double-edged sword" that investors must remain vigilant about. As the halo of domestic substitution fades, whether the enterprise can establish a robust technical barrier in its scale expansion and find a power balance point in its governance structure will determine its ability to truly breakthrough in the fiercely competitive global RF front-end market. (Produced by Siwei Finance) ■
Source: Investor Network