Spring Festival Highlights High Fuel Consumption of Extended-Range and Plug-In Hybrids, Propelling Pure Electric Vehicles to Consolidate Market Leadership
![]() 01/29 2025
01/29 2025
![]() 643
643
In recent years, extended-range and plug-in hybrid technologies have surged in popularity among new energy vehicles, effectively addressing range anxiety. However, the Spring Festival holiday brought to light several shortcomings, with high fuel consumption emerging as a critical issue, potentially sidelining these already challenged technologies.

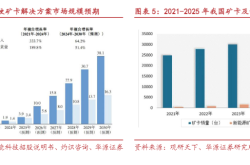
Market data from China's new energy vehicle sector for the first eleven months of 2024 reveals that sales of pure electric vehicles reached 5.552 million units, while sales of plug-in hybrids and extended-range vehicles totaled 4.044 million units. Pure electric vehicles accounted for 57.9% of domestic new energy vehicle sales.
Before 2023, pure electric vehicles held a larger share of the new energy vehicle market. During the first eleven months of 2024, plug-in hybrids and extended-range vehicles witnessed an 80.2% year-on-year growth, significantly outpacing the 21.9% growth of pure electric vehicles. Consequently, the market share of pure electric vehicles has gradually declined.
The rapid growth of plug-in hybrids and extended-range vehicles can be attributed to their ability to alleviate range anxiety, catering to both daily commuting and long-distance travel. Their small-capacity batteries suffice for short commutes, while fuel engines support long-distance travel, offering the best of both worlds.

Nevertheless, during the Spring Festival, the limitations of plug-in hybrids and extended-range vehicles became apparent. Their fuel consumption is substantially higher than that of traditional fuel vehicles, and their battery power systems offer limited assistance during long-distance travel.
The high fuel consumption of these vehicles stems from their reliance on fuel engines once battery power is depleted during long journeys. In extended-range vehicles, the fuel engine drives a generator to produce electricity, which powers the electric motor. Due to their power system characteristics and heavier vehicle bodies compared to fuel vehicles, fuel consumption during long-distance travel is significantly higher, with extended-range vehicles exhibiting even greater consumption.
Most of these vehicles are unsuitable for charging at service stations during long-distance travel due to their small battery capacity. To prolong battery life, they employ slower fast-charging technologies, resulting in extended charging times. With a typical battery range of less than 120 kilometers, high-speed travel consumes more power, reducing the actual range to less than 70%. This necessitates charging every two service stations, causing significant inconvenience. Many car owners opt to forgo charging and rely solely on fuel engines for long-distance travel.
In hindsight, car owners have also experienced the inconvenience of small battery capacity in daily use. With limited battery capacity, owners need to charge every two to three days, which can be inconvenient. Unless owners have private charging stations, many forgo purchasing private parking spaces.
The full exposure of the drawbacks of plug-in hybrids and extended-range vehicles is likely to steer consumers towards pure electric vehicles when purchasing new energy vehicles. This trend is favorable for pure electric vehicle sales and will further solidify their dominant position in the new energy vehicle market.
Globally, the proportion of plug-in hybrids and extended-range vehicles in the new energy vehicle market is minimal. In 2024, outside of China, pure electric vehicle sales increased by 16%, while plug-in hybrid sales grew by only 4%. This underscores the low acceptance of plug-in hybrids in overseas markets. Additionally, recognition of new energy vehicles in international markets remains low. In the European market, new energy vehicles account for only about 20% of the new car market, while in the US market, this figure is merely 7%.
This phenomenon is beginning to impact the domestic market, leading to a decline in the proportion of new energy vehicles in the new car market in November and December 2024. Weekly sales data indicates that in November 2024, new energy vehicles accounted for 55% of the new car market, while in the penultimate week of December 2024, this figure dropped to 42%. In 2025, the proportion has further declined to 39%, below 40%.
This shift suggests that consumers were previously heavily influenced by marketing. However, the experiences of plug-in hybrid and extended-range vehicle owners are now influencing potential buyers. New energy vehicles fall short of marketing claims, and there is a significant disparity between plug-in hybrids and extended-range vehicles and their promotional promises. Consumers should thoroughly understand the pros and cons of various technologies when purchasing a car and not be swayed by media propaganda.