Navigation Lane Plus Ads: Baidu Map's Dual-Edged Monetization Strategy
![]() 05/14 2025
05/14 2025
![]() 506
506

Recently, Baidu introduced a controversial feature: placing ads on the virtual lanes of its navigation interface. Many drivers have complained about frequent pop-up ads for "Dongpeng Special Drink" on 3D virtual lanes, with some segments even featuring voice announcements that cannot be manually disabled.
According to Jiemian News, this ad collaboration is a customized project worth tens of millions of yuan.
Dongpeng Beverage, the other party involved, saw its stock price dip by 3.9% on May 12, while the broader food and beverage index rose by 0.38%.
Public opinion swelled rapidly, with some netizens arguing that since the software is free, monetization through ads is understandable. Others, however, contended that "navigation software can sell ads, but not at the expense of users' sense of security," suggesting that such ads may violate the Advertising Law's clause on not affecting users' normal use of network services and potentially breach restrictions on driving interference under the Road Traffic Safety Law.
This contentious innovation highlights yet another instance where Baidu has prioritized commercial monetization over user rights, this time impacting user safety.
I. Baidu Map's Ad Frenzy
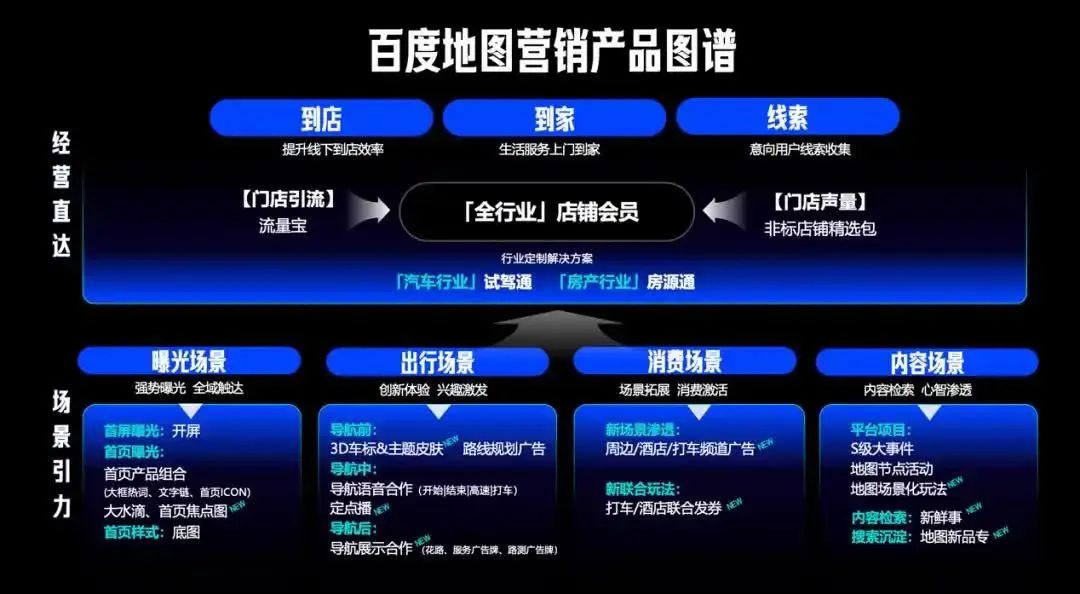
Baidu Map's ads permeate various scenarios, interfaces, and locations.
The "2025 Baidu Map Marketing Plan" outlines its "Scenario Gravity" strategy, which spans the entire user travel cycle from exposure, travel, consumption to content.
Under exposure scenarios, Baidu Map offers resources such as splash screen ads, homepage exposure, and base map skin changes.
In travel scenarios, before, during, and after navigation, Baidu Map captivates users through innovative experiences like 3D car logos, navigation voices, and navigation display ads. For instance, brands can customize broadcasts to play when targeted users pass specific locations.
In consumption scenarios, Baidu Map connects new consumption avenues such as ride-hailing, hotels, and surrounding areas. During the Spring Festival travel period, for example, Baidu Map collaborated with Wanglaoji for voice navigation and channel exposure.
In content scenarios, Baidu Map stimulates users' content search and consumption decisions through ecosystems encompassing news, Deepseek intelligent reasoning, and new product specials.
For enterprises seeking advertising, Baidu Map provides abundant marketing resources and precise targeting. For users, however, pervasive ads, especially those related to personal safety, significantly impair the user experience, giving an impression of overzealous commercialization.
Generally, map navigation platforms do not charge C-end individual users, with B-end advertising being the primary monetization method.
Google Maps also relies heavily on advertising, displaying marketing content based on users' real-time locations and search queries. For instance, paid users are prioritized in restaurant searches. Google's ad display is considered more subtle and non-intrusive. Additionally, Google Maps' commercialization includes API services, data licensing, and partnerships with ride-hailing companies.
Gaode Maps has also faced criticism for being overly ad-driven, though it enjoys certain advantages over Baidu Map.
Gaode has established a foothold in the ride-hailing market by providing aggregated traffic inlets for ride-hailing platforms and deriving revenue from them. Furthermore, Gaode Maps integrates with other Alibaba ecosystems, bridging travel, local life, and tourism scenarios. For instance, it has partnered with Flying Pigs for hotel check-ins navigated by Gaode Maps, enabling the purchase of scenic area tickets and group-buying of food and car maintenance services within the app.
While Gaode Maps' merchant volume and variety may not rival Meituan, it offers merchants a seamless link from exposure to transaction through its platform.
Group purchases can also be completed on Baidu Map, such as for food, but may require jumping to the Meituan app, lengthening the user journey. Each additional step introduces uncertainty into consumer decision-making. Currently, Baidu Map lacks the payment methods and user habits necessary to support the completion of consumption and transactions within its platform.
Moreover, technological competition in the mapping industry has further exacerbated Baidu Map's challenges.
According to the 2024 Intelligent Driving Supplier Installation Volume Rankings by Gasgoo Auto Research Institute, Gaode Maps led the high-precision map market in 2024, capturing over half of the market share, while Baidu Map did not rank among the top five.
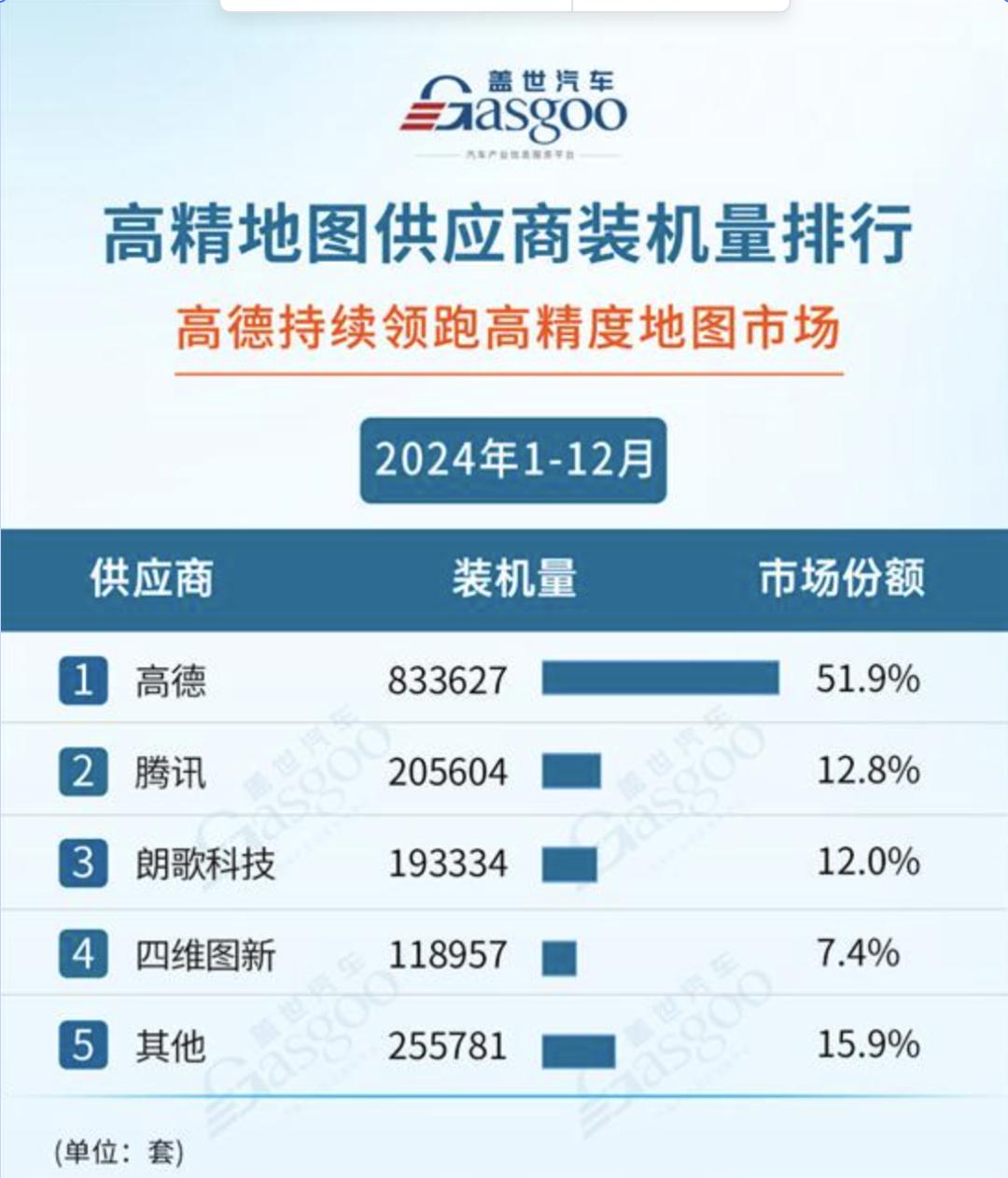
Therefore, compared to the diversified monetization strategies of other maps, Baidu Map relies more heavily on advertising.
II. The Dilemma and Strategies of Aggressive Monetization
Baidu Map's aggressive monetization may be tied to Robin Li's 2025 OKR. According to media reports, at the beginning of the year, Robin Li set the 2025 OKR for the map business as "making CM positive for the map," with CM vaguely referred to as either customer management or margin, intensifying the focus on the map business.
So, why the map business?
As discussed in "The Time Left for Robin Li is More Cruel Than the Financial Report Numbers," Baidu's traditional advertising business has weakened due to the erosion of its search moat.
In the fourth quarter of 2024, Baidu's online marketing revenue declined by 7% year-on-year to 17.9 billion yuan, marking three consecutive quarters of negative growth. Although Baidu's advertising revenue accounted for 55% of its total revenue for the year, the trend of user time shifting to platforms like Douyin and Xiaohongshu has persisted, adversely affecting Baidu's mobile ecosystem's active user numbers and user stickiness.
Affected by these factors, Baidu's stock price has fallen below its net asset value since November 2024, with the current price-to-book ratio around 0.86, indicating a market value that is only 86% of its net asset value. Baidu needs to present an appealing capital narrative beyond advertising.
In its financial reports over the past two years, Baidu has placed significant emphasis on its two major businesses: artificial intelligence and intelligent driving. The future of AI and autonomous driving will be the long-term "story" that Baidu narrates.
Intelligent driving once rescued Baidu. In 2021, intelligent driving drove Baidu's stock price to recover and reach new highs, showcasing its AI capabilities.
At that time, Robin Li outlined three commercialization paths for intelligent driving: providing automotive manufacturers with autonomous driving technology solutions; building cars end-to-end with Baidu's autonomous driving innovations and bringing the most advanced technology to market first; and Robotaxi, offering autonomous driving travel services.
With the collapse of Jiyue towards the end of last year, Baidu could no longer pursue the second path.
In 2022, Baidu Map was transferred to the IDG Business Group (Intelligent Driving Group), which now encompasses autonomous driving travel services (Luobo Kuaipao), automotive intelligence solutions, and Baidu Map.
Luobo Kuaipao represents a growth area, but it may not be sufficient.
Automotive intelligence solutions encompass intelligent driving, intelligent cabins, and intelligent maps. In selling intelligent solutions, Baidu faces competition from other suppliers available to automotive manufacturers.
While Baidu has a head start in intelligent driving, and Baidu Apollo can be considered a pioneer in domestic intelligent driving, the results show that many cars are renowned for being equipped with Huawei's intelligent driving, while few automakers promote Baidu's intelligent driving as their hallmark. Intelligent driving system providers are concentrated among "Dijiahuamo" (Horizon Robotics, DJI Automotive, Huawei, Momenta).
Thus, Baidu Map has emerged as a business that must be vigorously developed.
High-precision maps themselves involve high costs. Creating maps requires Class A surveying and mapping qualifications, collection vehicles equipped with LiDAR, and substantial investments in manpower, material resources, and finances for data collection and production, as well as AI technology for data analysis. The investment is substantial, and the threshold is high.
According to the "2020 White Paper on High-Precision Maps for Intelligent Connected Vehicles" by the China Intelligent and Connected Vehicle Industry Innovation Alliance, using professional surveying and mapping vehicles, the surveying and mapping efficiency for centimeter-level high-precision maps is approximately 100 kilometers of road per vehicle per day, with costs potentially reaching thousands of yuan per kilometer.
Coupled with the trend of "emphasizing perception, downplaying maps" in intelligent driving, Baidu's familiar and proficient method of advertising monetization has become a straightforward, immediate, and effective approach.
From this perspective, Baidu Map's innovation appears more like a shortcut than an innovation.