2025 Third Quarter Self-Driving Financing Roundup: Autonomous Driving's "Golden Pathway" and "Critical Link" Take Shape, with Robotaxi Attracting 5.7 Billion Yuan and Component Sector's "Big Three" Do
![]() 10/17 2025
10/17 2025
![]() 509
509
Introduction
The self-driving sector's "funding spree" continued unabated in the recently concluded third quarter of 2025.
Data from the New Strategy Low-Speed Autonomous Driving Industry Research Institute reveals that over 58 investment and financing deals were sealed globally in just three months, with total disclosed funding exceeding 14.6 billion yuan. Among these, some companies secured a staggering 3.5 billion yuan in a single round, while others dominated 70% of component sector financing with a single hardware product. Meanwhile, industry giants quietly assembled "Robotaxi alliances" through strategic investments.
What's particularly noteworthy is that while the number of financing events remained relatively stable compared to Q3 2024, capital became significantly more concentrated—23 "100-million-yuan-class" financings accounted for 98% of total funding, including four billion-yuan-class mega-deals.
This shift signals that capital is no longer "spreading its bets" but is instead making targeted investments in core sectors.
On one hand, the Robotaxi sector emerged as the top beneficiary with 5.7 billion yuan in funding, while on the other, LiDAR companies secured 70% of component sector financing. The "golden pathway" and "critical link" of autonomous driving have become unmistakably clear.
Today, Unmanned Vehicle Insights (WeChat Official Account: Unmanned Vehicle Insights) analyzes this financing landscape to reveal where capital—with its real money votes—sees the future of autonomous driving.
(Reference: "Three-Year Financing Showdown: China's 'Scenario-Driven' vs. U.S.' 'Tech-Barrier' Approaches in Autonomous Driving")
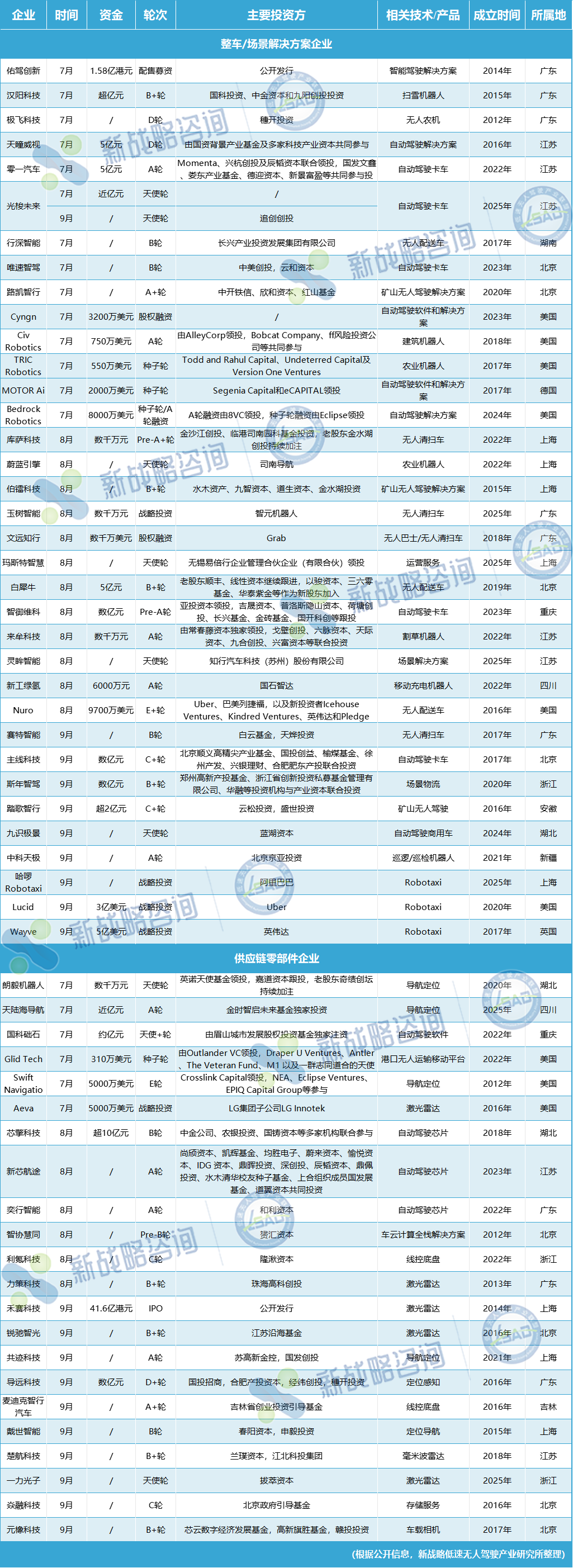
I. Vehicle Sector Showdown: Robotaxi Commands Half the Market as Giants Form Alliances
Vehicle and solution providers stole the spotlight in Q3 financing.
Thirty-six companies secured over 10.561 billion yuan, representing nearly 70% of total funding. The Robotaxi subsector dominated with 5.714 billion yuan, leaving other segments far behind.
This "winner-takes-most" pattern reflects capital's strong confidence in smart mobility's commercialization.
The most striking overseas move came from Uber's "double play."
In Q3, the ride-hailing giant invested 2.84 billion yuan in autonomous tech firm Nuro and EV maker Lucid.
As early as July, Uber had hinted at forming a "Robotaxi alliance," and now with real capital deployed, its acceleration is clear—
Nuro provides the "brain" (autonomous tech), while Lucid supplies the "body" (EV manufacturing), filling Uber's hardware and tech gaps in autonomous driving.
Industry insiders note, "Uber learned from missing the mobile payment boom. This time, it's securing a seat at the Robotaxi table."
Domestically, a "multi-center" financing pattern emerged.
Guangdong, Beijing, Shanghai, and Jiangsu became financing hubs, with 33 companies in these regions securing 5.25 billion yuan.
WeRide's Robotaxi fleet in Guangzhou now numbers hundreds of vehicles, with peak-hour orders in Tianhe District rivaling traditional taxis.
BaiNiu's unmanned delivery vehicles operate routinely in multiple Shanghai communities, and post-Q3 financing, plans to expand to 10 Yangtze River Delta cities were announced.
These visible commercial deployments explain capital's enthusiasm.
Beyond Robotaxi, last-mile logistics and trunk transportation remained hot sectors.
Unmanned delivery vehicles secured 897 million yuan, while autonomous trucks received 800 million yuan, both showing signs of transitioning from pilots to scale.
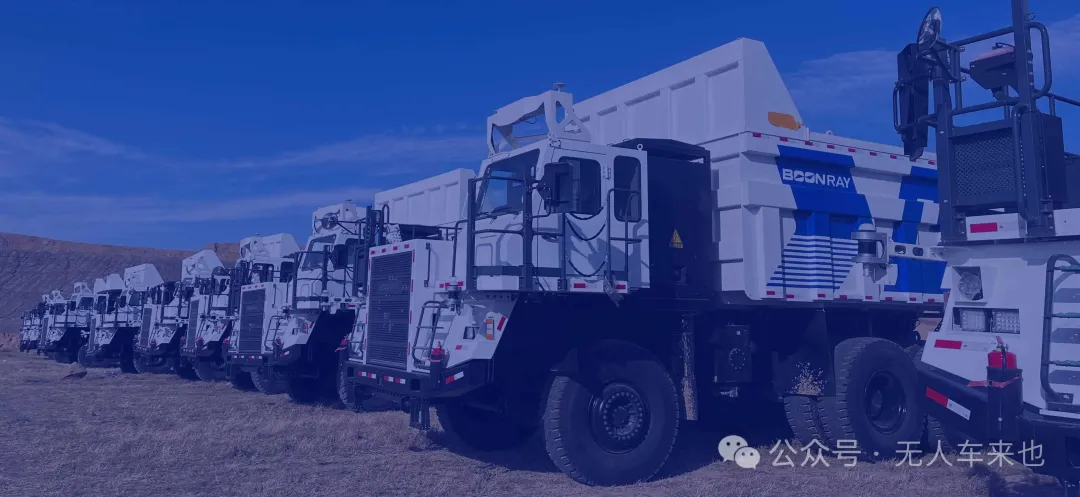
Bermic completed a multi-billion-yuan Series B2 round, with its unmanned heavy trucks achieving 24/7 operation at Jiangsu ports. Drivers now monitor from control centers, boosting efficiency by 30%.
(Reference: "Bermic: Mine Autonomous Driving's Rising Star Secures Multi-Billion Financing for Battery-Swapping Trucks")

Set Intelligence's delivery robots now serve multiple Shenzhen office buildings, handling parcels and catering with each vehicle averaging over 50 daily deliveries.
The commercial "closed loop" in these scenarios is becoming clearer, encouraging sustained capital investment.
Notably, some niche sectors secured funding despite smaller totals, relying on strong certainty.
Unmanned sanitation vehicles, agricultural machinery, and mine automation received limited Q3 financing but feature high technical barriers and clear business models, forming stable investment logics.
For example, mine automation specialist Bermic expanded operations in Shanxi coal mines post-Q3 financing. This "closed scenario + rigid demand" combination has proven highly resilient.
II. Component Sector Undercurrents: LiDAR Captures 70% of Funding as "Big Three" Define Tech Ceilings
If the vehicle sector represents "open competition," the component sector is all about "subtle rivalry."
In Q3, 22 component companies secured 5.756 billion yuan. While total funding lagged behind vehicles, the "highly concentrated, sharply differentiated" pattern stood out—LiDAR alone captured 4.168 billion yuan, accounting for over 70% of component financing. Alongside chips and positioning/navigation, these "three pillars" largely determine autonomous driving's tech ceiling.
LiDAR's funding surge is remarkable.
Five deals secured over 4.1 billion yuan, with Hesai Technology's Hong Kong IPO raising 4.16 billion Hong Kong dollars (≈3.806 billion yuan), making it Q3's component sector "funding king."
(Reference: "Hesai: World's Largest LiDAR IPO Debuts on HKEX with 37B HKD Valuation")

Just years ago, LiDAR was a "10,000-yuan-plus" luxury, but tech breakthroughs have slashed prices to the thousand-yuan range, enabling scale deployments in Robotaxi and sanitation vehicles.
Hesai's latest product improves ranging to 150 meters while cutting costs by 40%, securing orders from multiple domestic automakers immediately after launch.
Capital's LiDAR frenzy stems from "performance gains + cost reductions" creating explosive opportunities.
The autonomous driving chip sector, though seeing fewer deals (just three), secured 1 billion yuan, focusing on "domestic substitution" and "computing power upgrades."
Semidrive Technology's Series B round raised over 1 billion yuan for its 200TOPS chip, perfectly compatible with L4 systems and breaking foreign monopolies.
(Reference: "Semidrive Lights Up Autonomous Driving Chip 'Stellar One' with 1B Yuan Funding")
Another startup's edge computing chip targets low-cost markets, widely used in agricultural machinery. Priced under 2,000 yuan, it makes autonomous tech affordable for SMEs. As the "computing power race" intensifies, domestic chip breakthroughs have begun.
While positioning/navigation and software sectors received modest funding (467 million yuan and 121 million yuan respectively), they form autonomous driving's "invisible foundation."
Ruichi Zhiguang's HD map updates achieve "minute-level" synchronization of construction zones and restrictions on complex urban roads, keeping autonomous vehicles on track.
Gongji Technology's algorithm platform serves over 20 autonomous driving companies, shortening iteration cycles from three months to one.
These "under-the-radar" technologies are critical for safety and efficiency, explaining industrial capital's keen interest.
This "components follow vehicles" pattern actually signals industry maturity.
Robotaxi needs LiDAR for perception accuracy, delivery vehicles require low-cost chips, and trucks depend on high-precision positioning—
Vehicle sector scale demands drive component tech breakthroughs, which in turn accelerate vehicle deployments, forming a perfect industrial loop.
III. New Capital Logic: Money Chases "Certainty," with Both Early and Late Stages Hot
Q3 financing data reveals capital's evolving strategies:
No longer chasing concepts but betting on "commercialization certainty;"
Willing to provide "seed money" for startups while also offering "scale-up funds" for mature firms, creating a "dual-hot" scenario.
Financing round distributions offer clues. Early-stage companies secured nearly 45% of funding, with Series A and B+ rounds driving growth.
Meanwhile, 16 startups received seed or angel investments, accounting for nearly 30%.
This "early and late-stage"布局 (layout) indicates capital aims to capture both mature firms' commercialization dividends and startups' tech breakthroughs.
Wayve's $500 million (≈3.571 billion yuan) strategic investment exemplifies "betting on the future." The British startup focuses on end-to-end autonomous tech and immediately announced a German research center post-Q3 financing, targeting European Robotaxi deployments.
(Reference: "Wayve Partners with Uber for London Autonomous Trials: A 1B Pound Driverless Feast?")
Meanwhile, Hesai's IPO represents "harvesting the present," becoming the first listed LiDAR firm with mature products and orders.
The geographical "Matthew effect" is also pronounced.
Ninety percent of overseas financing went to U.S. companies, while domestically, tech hubs like Guangdong and Beijing dominated.
U.S. firms like Nuro and Lucid gained capital favor with mature ecosystems, while domestic players like Minieye and WeRide leveraged manufacturing bases and application scenarios in the Pearl and Yangtze River Deltas for rapid growth.
This "industrial cluster + capital aggregation" model amplifies leading regions' advantages, turning autonomous driving competition into a "regional ecosystem battle."
Compared to Q3 2024, total financing rose slightly while deal count remained flat, indicating more concentrated capital flows.
Twenty-three billion-yuan-class financings accounted for 40% but contributed 98% of funding, showing capital's shift toward leaders and core sectors.
Firms with tech barriers, commercial scenarios, and closed loops secure more funding;
Those relying on concept hype without products are being abandoned.
One investor bluntly stated, "We used to invest based on PPTs, but now we look at operational data, order volumes, and margins. The autonomous driving 'bubble' is deflating."
The Q3 financing list serves as an industry "barometer":
Robotaxi's rise signals smart mobility's imminence, LiDAR's emergence shows core hardware is no longer a bottleneck, and capital's rational return indicates industry maturation from "hype" to "stability."
In summary, Unmanned Vehicle Insights believes:
The 14.6 billion yuan invested isn't for concepts but for tangible, near-term deployments—whether Robotaxis on streets next year, on-demand delivery robots in neighborhoods, or unmanned trucks operating 24/7 on highways and in ports.
The autonomous driving race has shifted from "tech competition" to "ecosystem competition," with capital as the "fuel."
Which sectors will dominate next quarter?
Share your thoughts in the comments!
Note: This article has been edited for clarity and title optimized.
#UnmannedVehicleInsights #SelfDriving #AutonomousDriving #UnmannedVehicles






