$400 Billion in Revenue, $130 Billion in Net Profit: Google's Strength Exceeds Many Imaginations
![]() 02/12 2026
02/12 2026
![]() 387
387
Introduction: Google, combining hardware and software, now has the capital to compete with OpenAI and NVIDIA, its strength exceeding many people's imaginations.

Written by Li Ping | Produced by Leishi Business Review
1
Revenue Surpasses $400 Billion
Not long ago, Google's parent company Alphabet (hereinafter referred to as Google) released its Q4 2025 results and full-year 2025 financial report. Data shows that in Q4 2025, Google's total revenue reached $113.828 billion, up 18% year-over-year, with net profit of $34.5 billion, up 30% year-over-year; diluted earnings per share were $2.82, up 31% year-over-year. All three core metrics exceeded Wall Street's consensus expectations.
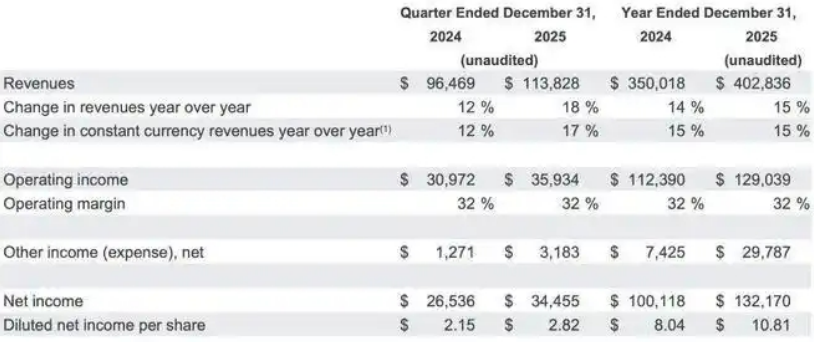
Looking at the full year of 2025, Google's total revenue reached $402.8 billion, up 15% year-over-year, making it the first tech company in history to surpass $400 billion in annual revenue. In terms of net profit, Google's 2025 net profit reached $132.17 billion, up 32% year-over-year, primarily driven by the implementation of AI technology and the rapid expansion of Google Cloud.
In response, Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai stated in the earnings report that Q4 2025 was an "exceptionally strong quarter" for Google, with the company's annual revenue surpassing $400 billion for the first time, and sustained expansion in search, cloud, and subscription businesses. Meanwhile, the Gemini app also achieved significant growth in scale and depth, with monthly active users reaching 750 million. A more critical metric is the leap in user engagement, including usage frequency, session depth, and user retention rates, which have significantly improved across global platforms.
From a revenue composition perspective, Google's main businesses are divided into three parts: Google Services, Google Cloud, and Google's other investments (AI, robotics, autonomous vehicles, healthcare). Among them, Google Services is further divided into advertising business and Google Other (Google Play, hardware, YouTube subscription revenue), while the advertising business mainly consists of search, YouTube, and network alliance advertising, representing Google's most core foundational business.

The financial report shows that in Q4 2025, Google's search advertising business generated $63.073 billion in revenue, up 16.7% year-over-year, exceeding analyst expectations of $61.4 billion, demonstrating robust performance in its core business. In response, Google management stated in a conference call that the prosperity of the search business is mainly driven by vertical sectors, particularly retail, which has boosted advertiser performance.
Google Cloud generated $17.664 billion in revenue, up 48% year-over-year, far exceeding the average growth rate of the cloud computing industry and significantly outperforming competitor Microsoft Azure's performance in the same period. By the end of 2025, Google Cloud's annualized revenue had surpassed $70 billion, with a backlog of orders worth $240 billion, more than doubling year-over-year, driven by surging demand for enterprise AI infrastructure, enterprise AI solutions, and core Google Cloud platform products.
While maintaining high revenue growth, Google Cloud's profitability has also significantly improved. In Q4 2025, Google Cloud's operating profit margin surged to 30.1% from 17.5% the previous year, with operating profit reaching $5.313 billion, up 154% year-over-year. After years of high capital investment, Google Cloud has entered a harvest phase.
In other businesses, YouTube advertising generated $11.4 billion in revenue, up 9% year-over-year, slightly below market expectations of $11.8 billion. Some analysts believe that the high base effect of political advertising from the U.S. elections in the same period of 2024 was a primary reason for YouTube advertising's revenue falling short of expectations this quarter. Other revenues, including YouTube membership subscriptions, Google Play, and Pixel hardware, totaled $13.6 billion, primarily driven by growth in YouTube memberships and Google One services.
Non-core business units (Other Bets), including autonomous driving company Waymo and life sciences division Verily, achieved $370 million in sales revenue, down 8% year-over-year (from $400 million), with a net loss of $3.6 billion, mainly due to Waymo recognizing $2.1 billion in employee equity compensation expenses this quarter. Just days before the Q4 earnings release, Waymo announced the completion of a new $16 billion funding round, with a post-money valuation of $126 billion, making Waymo the world's first Robotaxi super unicorn with a valuation exceeding $100 billion.
2
Doubling of Capital Expenditures Sparks Controversy
Overall, with the help of AI, Google's Q4 performance fully exceeded market expectations. However, due to the company's 2026 capital expenditures (ranging from $175 billion to $185 billion) also significantly exceeding investor expectations, Google's stock price initially fell more than 6% after the earnings release, marking another major divergence between Google's long-termism and Wall Street's short-term performance focus.
Data shows that in Q4 2025, Google's capital expenditures reached $27.9 billion, nearly doubling from $14.3 billion in the same period last year. For the full year of 2025, Google's capital expenditures ultimately reached $91.45 billion, up 77% year-over-year (from $52.5 billion). This calculates to a nearly 100% increase in Google's 2026 capital expenditures.
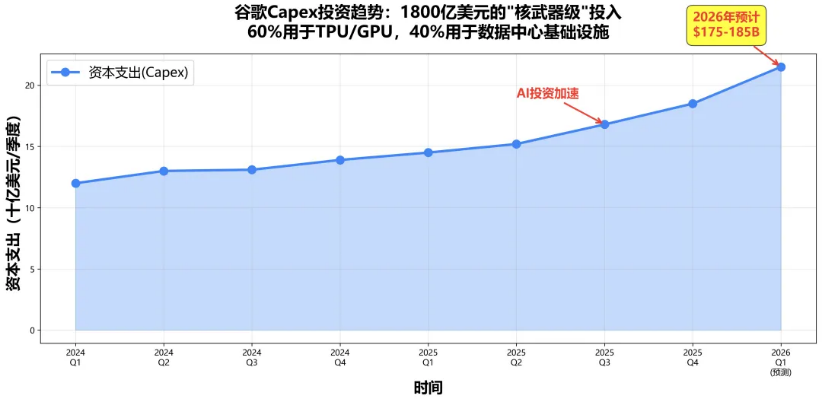
In response, Google CEO Sundar Pichai stated in the earnings conference call that investments in AI and related infrastructure are comprehensively driving revenue and growth. To meet customer demand and seize expanding future opportunities, capital expenditures in 2026 are expected to range between $175 billion and $185 billion, primarily for server and data center infrastructure to support AI development.
In recent years, secondary market investors have repeatedly expressed "dissatisfaction" with Google's high capital expenditures. In the first half of 2024, Google's capital expenditures reached $25 billion, nearly doubling year-over-year. Due to investor concerns over excessive capital spending, Google's stock price experienced a significant decline in Q3 2024, with its total market value evaporating by more than $500 billion.
Q4 2024 financial data showed that Google's capital expenditures in that quarter reached $14 billion, up 30% year-over-year, significantly exceeding previous guidance of around $13 billion. Meanwhile, to address the shortage of high-performance computing chip supplies, Google decided to significantly increase capital expenditures in 2025 for AI infrastructure expansion, with capital expenditures expected to reach $75 billion, about 30% higher than the generally expected $58.8 billion. The day after the earnings release, Google's stock price fell more than 7%, with its market value evaporating by more than $180 billion overnight.
However, in hindsight, investors' concerns over Google's "overinvestment" were clearly overblown. For the full year of 2025, Google's actual capital expenditures ($91.45 billion) significantly exceeded initial expectations ($75 billion), but this did not hinder Google's earnings from exceeding expectations and its stock price from soaring. For the full year of 2025, Google's stock price rose approximately 66%, achieving its best annual performance since the 2009 financial crisis and joining NVIDIA in the $4 trillion market cap club.
In fact, since ChatGPT's debut, discussions about search engines being disrupted have been rampant, with Google being labeled as facing a "midlife crisis." However, fears that Google would become the "next Yahoo" have not materialized.
Instead, with the launch of a series of blockbuster products, including the Gemini 3 large language model, Nano Banana image generation model, Veo3 video generation model, and TPU chips, Google, which advocates long-termism, ultimately regained the high ground in AI technology, and its stock price soared. As Gil Luria, an analyst at research firm DA Davidson, said, "Google Cloud's growth far exceeded expectations, and more importantly, it surpassed Microsoft Azure's growth rate for the first time in several years. This seems to prove that Google's increased capital spending is justified."
3
From Gemini 3 to TPU Chips
On November 19, 2025, Google officially launched its latest Gemini 3 series AI models and simultaneously released the Gemini 3 Pro preview. Gemini 3 is equipped with a 1 million token context window, achieving a milestone breakthrough in the deep fusion processing of images, videos, audio, and code, enabling AI to possess comprehensive capabilities in understanding complex scenarios, cross-modal analysis, and autonomous task execution.
In a test covering multiple subjects such as expert knowledge, logical reasoning, mathematics, and image recognition, Gemini 3 scored significantly higher than the latest models from other companies, including ChatGPT. With its leap in scores, strong multimodal understanding, more diverse UI, and stunning front-end capabilities, Gemini 3 is widely regarded as one of the top-performing AI models currently available and is seen as a critical milestone for Google to regain the high ground in the AI race.
In fact, starting from the previous generation Gemini 2.5, Google's capabilities in "cutting-edge models" have gradually caught up to and even surpassed competitors. With the launch of Gemini 3 Pro, Google now has the strength to compete head-on with OpenAI. Even Silicon Valley heavyweight and Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff publicly stated that Gemini 3 has achieved "crazy" leaps in reasoning, speed, and multimodal capabilities, and after spending just two hours with Gemini 3, he no longer wanted to return to ChatGPT.
At the same time, Google also launched a new AI development platform, Google Antigravity, providing developers with a full-stack toolchain for building autonomous agents. Through this platform, developers can more easily build AI applications with task planning, tool invocation, and multi-step execution capabilities, driving the transformation of AI from an "assistant" to a "partner."
Financial data shows that by the end of 2025, Google Gemini's monthly active users exceeded 750 million, a net increase of 100 million from Q3 2025, narrowing the gap with ChatGPT (810 million monthly active users) to just 60 million. Additionally, in terms of enterprise clients, Gemini successfully helped Google secure Apple as a major client, causing a major shakeup in the industry.

On January 12, 2026, Apple and Google issued a joint statement announcing a multi-year cooperation agreement. According to the agreement, the next generation of Apple's foundational models (Apple Foundation Models) will be built based on Google's Gemini models and cloud technology, and these models will support future Apple intelligent features, including the more personalized Siri to be launched this year.
Stimulated by this blockbuster news, Google's market value surpassed the $4 trillion mark for the first time, becoming the fourth publicly traded company to exceed $4 trillion in market cap, following NVIDIA, Microsoft, and Apple.
Notably, Gemini 3 uses Google's own TPU chips rather than NVIDIA chips that power OpenAI's systems. As a result, Gemini 3's success initially caused "TPU panic" in the secondary market. On November 25, 2025, NVIDIA's stock price plunged more than 7% in early trading, with its total market value evaporating by $115 billion in a single day.
If the release of Gemini 3 marked Google's successful comeback in the large model sector, then the external supply of TPU chips has given Google the capital to challenge NVIDIA.
Google's TPU (Tensor Processing Unit) is an AI-specific chip independently developed by Google, primarily used to accelerate machine learning and AI computing tasks. In 2015, Google's first-generation TPU was introduced under extreme secrecy, primarily designed for internal services such as search and Gemini models, forming a strong internal demand closed loop (closed loop). In October 2023, Google's seventh-generation TPU (TPU v7, codename Ironwood) was officially released, with performance 10 times higher than the sixth-generation TPU and single-chip computing power reaching 1 exaFLOP (FP8 precision). Data shows that TPU v7 offers 1.9 times better inference efficiency than NVIDIA's A100, making it more suitable for the real-time computing needs of Agent-type AI.
Additionally, as the first dedicated inference chip in TPU history, Google's TPU v7 offers a more significant cost advantage. Bernstein Research data shows that under equivalent computing power, TPU's energy consumption cost is 42% lower than NVIDIA's H100, and its hardware procurement price is only 50%-70% of the latter. Therefore, for tech giants like Meta, whose annual computing power expenditures exceed $10 billion, switching to TPUs means saving billions of dollars each year.
In October 2025, AI startup Anthropic announced that it would use up to 1 million Google TPU chips to train its Claude large model, with a total value reaching tens of billions of dollars. In addition to Anthropic, Google TPU's external client list also includes giants such as Apple, Meta, and Cohere. Morgan Stanley's latest research report data shows that Google's TPU production forecast for 2027 has been significantly raised from around 3 million units to around 5 million units, an increase of about 67%, with TPU external sales becoming a promising new business for Google.
Against the backdrop of an increasingly intense AI arms race, Google has built a unique computational power moat through high-intensity R&D investment and an innovative AI technology stack model (AI infrastructure, Models, AI Platform, AI Agents). It maintains strong competitiveness at every level, including TPU chips, AI supercomputer architectures, software, and large models, thereby gaining the capability to 'outcompete OpenAI and challenge NVIDIA.' Clearly, Google, with its integrated hardware and software approach, now has the resources to compete head-to-head with NVIDIA, and its future development warrants further anticipation.