What is AI giant Nvidia doing in the automotive industry?
![]() 10/28 2024
10/28 2024
![]() 692
692
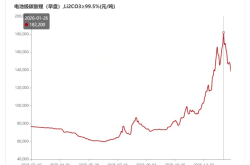
Nvidia, which has made great strides in AI, is often heard in the automotive industry for its various intelligent driving chips. At the same time, we also see that Nvidia's financial report highlights a separate sector for the automotive industry, but its revenue contribution to Nvidia is small and has shown a declining trend in recent years.
So, what is AI giant Nvidia doing in the automotive industry? What percentage of the automotive industry accounts for in its overall revenue?

Therefore, this article will explore Nvidia's strategic and product layout in the automotive industry.
SoC chip platform Drive in intelligent domain control is Nvidia's computing platform for developing intelligent driving. Nvidia Drive made its debut at CES 2015 and has undergone multiple generations of technological iterations. The first-generation Drive CX and Drive PX were based on the Maxwell microarchitecture and focused on smart cockpit and ADAS applications. As early as 2015, they already had 256 to 512 CUDA cores, supporting parallel computing operations.
The second-generation Drive PX2, designed specifically for ADAS intelligent driving functions, was launched in January 2016. Drive PX2 is based on the Pascal GPU architecture and contains up to 12 64-bit Arm CPUs. Tesla's Hardware 2.0 uses Drive PX. Drive PX Xavier, released in January 2017, adopts the Volta microarchitecture, and the initial domestic navigation assistance, such as XPeng's NGP, is based on this platform.
Drive PX Pegasus, released in September 2017, is based on the Turing architecture and is Nvidia's first automotive platform to support AI capabilities, offering a performance boost of approximately 10 times that of Drive PX2. By October 2017, over 200 partners were developing hardware or software products on the Drive platform. Drive AGX Orin, a motherboard series launched in December 2019 and announced in May 2020 to adopt the Ampere architecture, is suitable for ADAS and L3-L4 vehicles. Orin boasts up to 2048 CUDA cores, capable of handling parallel computing for complex AI models, features 17 billion transistors, and complies with the ISO 26262 ASIL-D standard for high security, making it the platform of choice for high-end intelligent applications in China.
Drive Thor: In April 2021, Nvidia announced Drive Atlan based on the Ada Lovelace architecture, but in September 2022, it canceled this product and introduced Drive Thor. At GTC 2024, Nvidia announced that Drive Thor will adopt the Blackwell GPU architecture and Arm Neoverse V3, with the CPU featuring up to 64 cores and set to be released in February 2024. Thor is poised to become the mainstream chip mass-applied in the market starting next year. 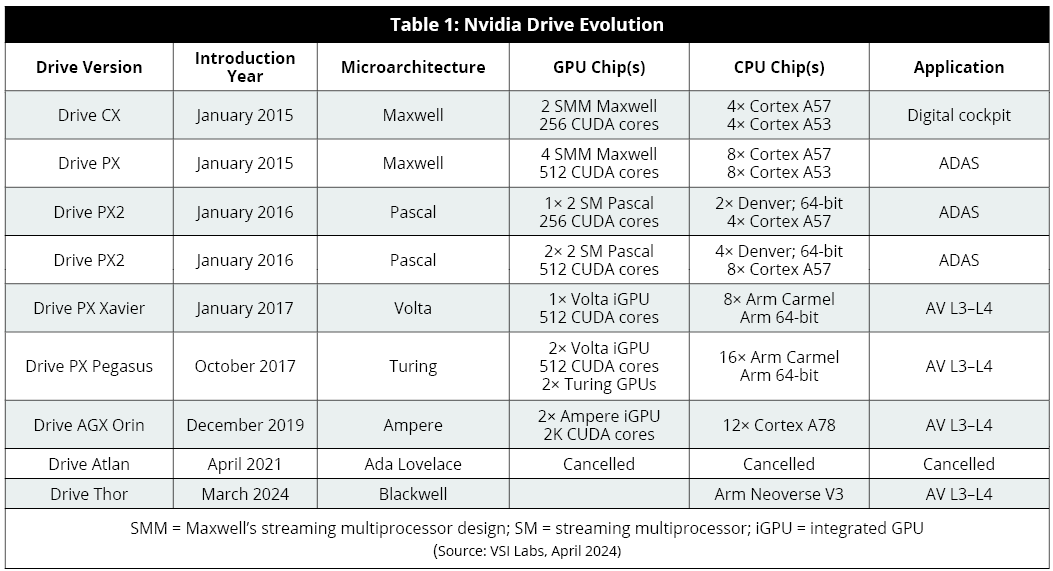
The latest Drive Thor is based on the Blackwell GPU architecture. Compared to Drive Orin, it boasts 12 times more transistors and Nvidia claims a performance boost of over 60 times. Blackwell utilizes 4-bit floating-point (FP4) computation, which is more efficient than the 16-bit floating-point (FP16) computation used in Orin. FP4 and FP8 computations facilitate accelerated training of large language models (LLMs) while reducing power consumption.
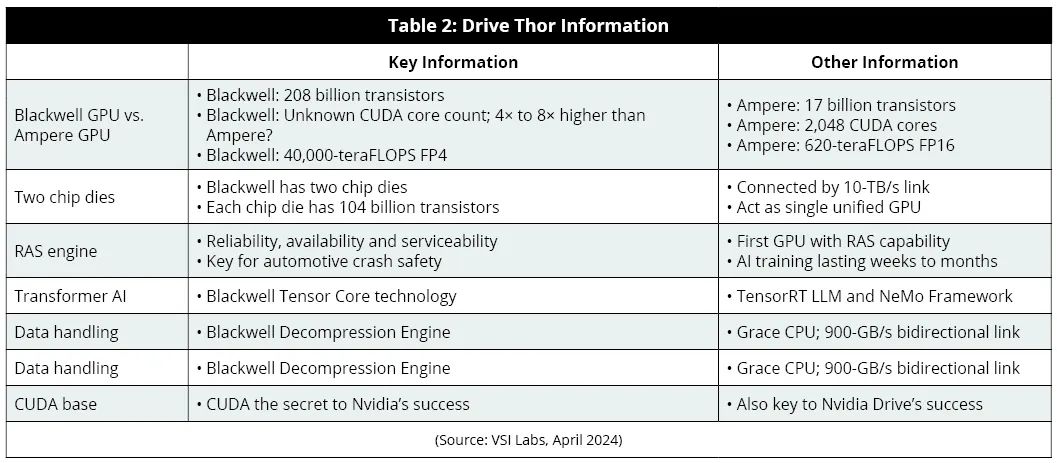
The Blackwell product employs two lithography-constrained chips, interconnected through a 10 TB/s inter-chip link to form a unified GPU. Passenger vehicles equipped with Drive Thor are expected to hit the market starting in 2025, with rumors pointing to BYD's Aoyang series. Blackwell also enhances device reliability through a dedicated reliability, availability, and serviceability (RAS) engine. The RAS AI-driven predictive management system monitors thousands of data points in hardware and software to predict potential safety hazards and provide in-depth diagnostic data for identifying and addressing problem areas. By precisely locating the source of failures, the RAS engine shortens maintenance cycles and prevents potential safety risks that could lead to collisions, injuries, and fatalities.
By learning patterns from vast amounts of textual data, the Transformer AI model can understand and generate human-like text. Blackwell and Drive Thor harness transformer technology to tackle autonomous driving and other automotive challenges. Furthermore, Blackwell's decompression engine accesses the vast memory of Nvidia Grace CPUs via high-speed links, offering 900 GB/s of bidirectional bandwidth, effectively accelerating tasks such as AI and database queries. CUDA is the cornerstone of Nvidia's GPU applications.
The CUDA platform optimizes GPU core utilization for AI models, enabling parallel task execution. Currently, it is estimated that over a hundred automotive industry customers, including major OEMs like BYD, GAC Motor, ZEEKR, and NIO, as well as foreign brands like Mercedes-Benz, Hyundai, and Jaguar Land Rover, are projected to use Nvidia Drive Thor. Nvidia Drive's clientele also includes trucking and L4 Robotaxi mobility companies like 2getthere, AutoX, Didi, Navya, and numerous autonomous driving startups.
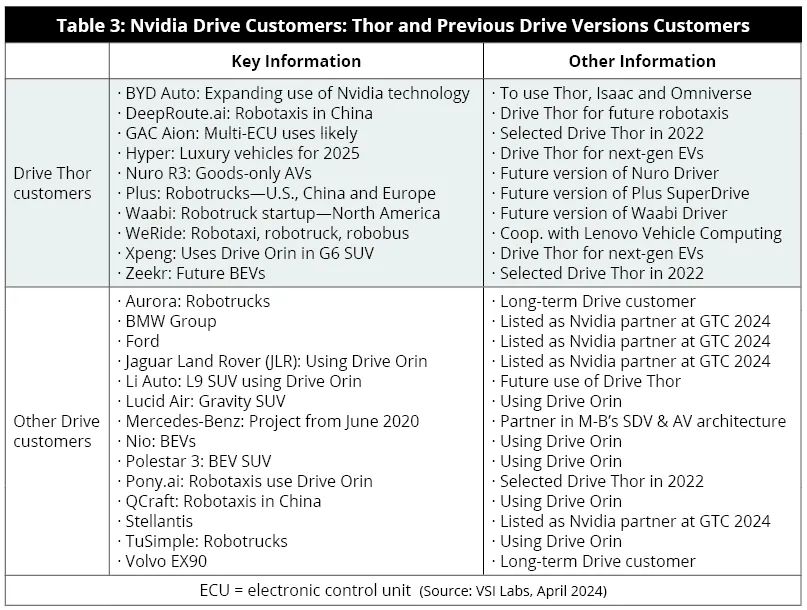
In fact, Nvidia's Thor has already been integrated into vehicles, albeit not the familiar passenger cars but rather the recently launched WeRide's robotaxi, whose domain controller hails from Lenovo Group. In the automotive sector, Nvidia's Inference Microservices (NIM) is a CUDA-based software packaging and delivery method that enhances GPU-centric software usability. NIM services offer developers more opportunities to customize AI software development across a wide range of GPUs.

Leveraging Nvidia's accelerated computing libraries and generative AI models, NIM services benefit from standard NIM APIs and CUDA's vast user base. NIM is particularly suited for business-driven AI applications and will find future use in software-defined vehicles (SDVs), autonomous driving, and infotainment. Comprising a set of optimized cloud-native microservices, NIM can be deployed across cloud platforms, data centers, and GPU-accelerated workstations, thereby expanding the resource pool for AI developers.
Omniverse in the Automotive IndustryNvidia Omniverse is an API, SDK, and service platform that allows developers to integrate OpenUSD with RTX rendering technology into existing software tools to build AI systems. At GTC 2024, Omniverse Cloud introduced five new APIs to help developers directly integrate core Omniverse technologies into existing digital twin designs.
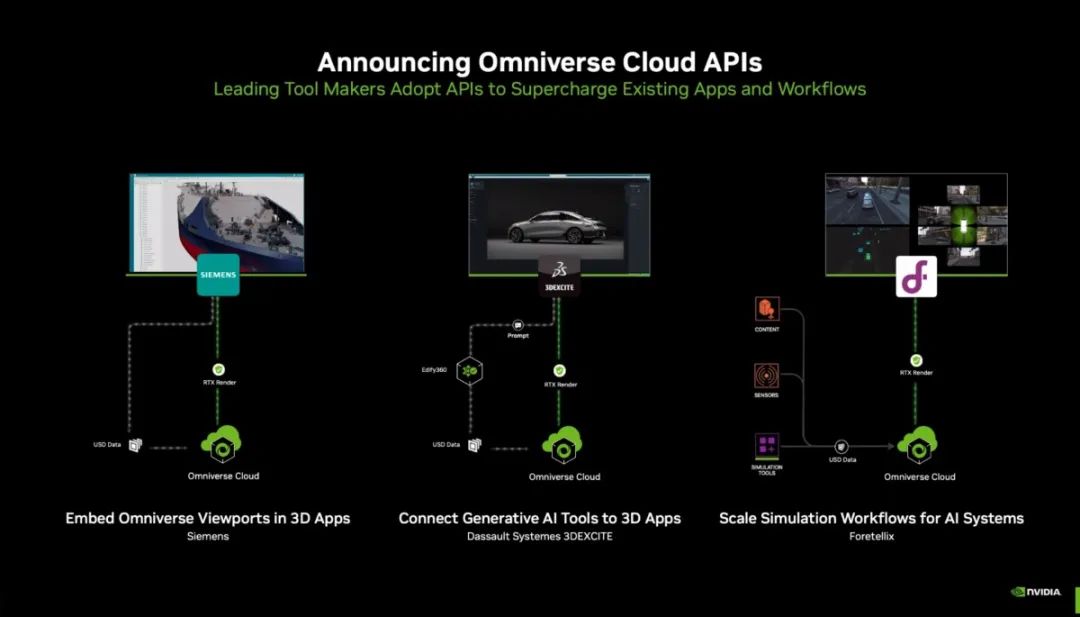
Omniverse's market share in the automotive industry is poised to further increase, particularly in digital twin applications for autonomous driving and software-defined vehicles.SummaryNvidia divides its product line into four major segments:Data Center, encompassing DGX/HGX/MGX/IGX software and systems, GPU | CPU | DPU | NetworkingNVIDIA AI software, the company's core business accounting for 78% of its 2024 revenueGaming, primarily GeForce GPUs for PC gaming and GeForce NOW cloud gaming, contributing 17% of 2024 revenueProfessional Graphics, including NVIDIA RTX GPUs for enterprise applications and Omniverse software, accounting for 3% of 2024 revenueAutomotive Applications, encompassing DRIVE Hyperion sensor architecture with AGX compute, DRIVE AV & IX full-stack software for ADAS, AV, and AI cockpit, and other intelligent vehicle cockpit and intelligent driving hardware and software services, contributing 2% of 2024 revenue

At first glance, the automotive business accounts for a small percentage of Nvidia's overall revenue, yet the company has singled it out. Firstly, AI applications are widespread, permeating all industries, with the automotive sector being just a small part. However, the automotive industry is vast, and the aforementioned classification primarily focuses on end-user applications. For instance, automotive data centers encompass significant business opportunities from intelligent R&D to sales, which are currently hotly contested by various cloud service providers in China.
Moreover, the automotive sector is the primary scenario for the implementation of intelligent AI robots, pioneering the classification of robots. Nvidia projects that its future autonomous driving and robotics business could reach $300 billion.
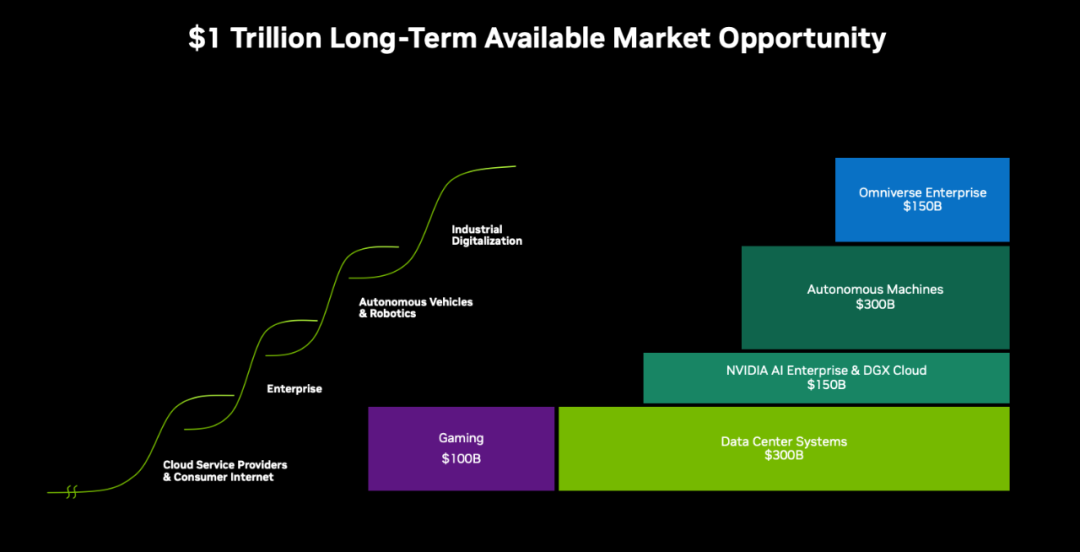
Therefore, AI giant Nvidia's layout in the automotive industry resembles that of Huawei in the telecommunications industry, with a comprehensive AI industry layout ranging from devices to terminals and from hardware to software. Exploring smart vehicles is inseparable from AI and giants like Nvidia that specialize in AI.
Unauthorized reproduction and excerpts are strictly prohibited - Reference Materials:
Company Overview - Nvidia pdf
NVIDIA Investor Presentation October 2024