Is the Emerging Market a Lifesaver or a Mirage? Unveiling AliExpress's Breakout Battle
![]() 04/27 2025
04/27 2025
![]() 601
601
AliExpress, a cross-border e-commerce platform under the Alibaba Group, emerged in 2010 amidst the booming global e-commerce landscape. Fueled by the increasing popularity of the internet, the demand for cross-border shopping skyrocketed, and AliExpress capitalized on this trend, swiftly capturing global attention. With the mission of "making it easy to do business anywhere," it aimed to dismantle national borders and build a bridge between Chinese merchants and global consumers.
During its golden era, AliExpress achieved remarkable success. In the European market, it once reigned as the largest e-commerce platform. According to the evaluation by the third-party institution European Cross-border Commerce, AliExpress stood out among the "Top 10 European Cross-border E-commerce Platforms" with its excellent service and consumer reputation, surpassing e-commerce giants like Amazon and eBay from the United States.
AliExpress undoubtedly shone as a star in the global cross-border e-commerce sector. Its success not only opened up vast overseas markets for Chinese merchants but also provided global consumers with convenient and diverse shopping experiences, serving as a successful model for Chinese e-commerce going global.
However, AliExpress, which once flourished, now finds itself grappling with the dilemma of sluggish growth.
Rapid Decline: The Sobering Reality of a Fallen Giant
AliExpress, once a beacon of success, now faces severe challenges and has slipped from its peak.
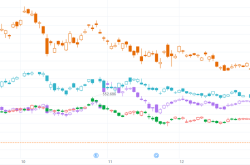
In terms of traffic, AliExpress's performance has been on the decline. According to relevant data statistics, AliExpress's monthly active user growth rate has gradually slowed down over the past few years, with periods of negative growth. In its once dominant markets, such as Europe and Latin America, AliExpress's traffic share has been continuously eroded by competitors. In Europe, with the rise of local e-commerce platforms and the deepening presence of international giants like Amazon, AliExpress's traffic share has gradually declined from its previous highs and now ranks outside the top three in some countries' market traffic.
From the perspective of market share, AliExpress's situation is equally grim. According to a report released by the International Post Corporation (IPC), AliExpress's market share dropped from 16% to 10% in 2024. Temu surpassed AliExpress at an astonishing speed, successfully becoming the world's second-largest cross-border e-commerce platform, with its market share soaring from 7% in 2023 to 21%. SHEIN also maintained a stable market share, ranking fourth with 9%. AliExpress's market share was primarily squeezed due to shortcomings in logistics timeliness and user experience. Despite its rich variety of goods, it has been outpaced by Temu and SHEIN in delivery speed and after-sales service.
Merchant complaints have also surfaced. Many merchants reflect that the platform's traffic allocation mechanism is unfair, making it challenging for new merchants to obtain sufficient exposure opportunities, while top merchants enjoy increasing advantages, leaving small and medium-sized merchants with limited survival space. Some merchants point out that the platform's commissions and various fees have been rising continuously, compressing their profit margins and significantly increasing operating costs. Frequent adjustments to platform rules also leave merchants feeling uncertain, as each change requires substantial time and effort to adapt, increasing the difficulty and uncertainty of operations.
From Peak to Decline: An In-depth Analysis
(1) External Competition's Strong Impact
In the fiercely competitive global e-commerce market, AliExpress faces stiff challenges from multiple competitors. Amazon, as a global e-commerce giant, attracts a vast number of consumers seeking high-quality shopping experiences with its strong brand influence, sophisticated logistics system (such as Amazon Prime's fast delivery service), and diverse product offerings. Its extensive logistics network and advanced warehousing management system worldwide enable rapid delivery, an advantage AliExpress struggles to match.
eBay, as an established cross-border e-commerce platform, boasts a deep user base and stable customer sources in European and American markets. Characterized by auctions and second-hand transactions, eBay has accumulated a large number of loyal users accustomed to trading personalized items. AliExpress finds it challenging to gain a share in this segmented market.
Moreover, the sudden rise of Temu has put tremendous pressure on AliExpress. Temu focuses on an extreme low-price strategy, directly cooperating with factories through innovative business models to eliminate intermediate links and sell goods to consumers at extremely low prices. In price-sensitive markets, Temu's strategy has attracted a large number of cost-conscious consumers, quickly seizing market share. For instance, Temu's prices for clothing and household items are often 20% - 30% lower than those on AliExpress, putting AliExpress at a disadvantage in price competition.
(2) Operational Dilemmas Within the Platform
AliExpress is also plagued by numerous internal operational issues, severely impeding its development. Logistics has always been a significant pain point for AliExpress. Cross-border logistics involves complex processes across multiple countries and regions, including customs and transportation, leading to prolonged logistics times and high costs. According to merchant feedback, the shipping time for some goods from China to Europe can be as long as 15 - 20 days, deterring many consumers who prioritize timeliness. Additionally, the logistics information tracking system is insufficient, often leaving consumers unable to accurately track their shipments, increasing shopping uncertainty.
The issue of fake goods also haunts AliExpress. As an open platform with a large number of merchants, management is challenging. Although the platform has implemented measures to combat fake goods, eradication remains difficult. Consumers have repeatedly purchased poor-quality goods, eroding their trust in AliExpress and affecting their willingness to purchase.
The quality of service provided by merchants on the platform is also inconsistent, with some merchants offering inadequate after-sales service and frequent issues such as difficult returns. This results in a poor shopping experience for consumers, creating a negative impression of the platform and reducing shopping behavior on AliExpress.
The frequent changes in AliExpress's platform rules also leave merchants confused. From product listing review standards to store rating systems, each rule change requires merchants to invest substantial time and effort to adapt, increasing operating costs and difficulties. Some small and medium-sized merchants even struggle to survive on the platform as a result.
(3) The Negative Impact of the Global Economic Environment
Changes in the global economic situation also significantly impact AliExpress. In recent years, global economic growth has slowed down, with some regions even experiencing recession, leading to decreased consumer purchasing power and more cautious spending on non-essential items. Under such circumstances, sales on the AliExpress platform have been significantly affected, especially for mid-to-high-end products, which have seen steep declines.
Currency fluctuations also bring uncertainties to AliExpress's cross-border transactions. When the domestic currency appreciates, the price of imported goods relatively decreases, prompting consumers to turn to other platforms offering more advantageous prices. Conversely, when the domestic currency depreciates, AliExpress merchants' costs increase, compressing their profit margins. To maintain profits, merchants must raise commodity prices, reducing product competitiveness and leading to decreased sales.
The Path to Breakthrough: AliExpress's Self-Rescue Actions
Faced with numerous challenges, AliExpress has not remained idle but has actively taken a series of self-rescue actions, aiming to regain its former glory.
(1) Strategic Adjustment and Mode Innovation
AliExpress has made bold adjustments to its business model, implementing a dual-track driving model of "Trusteeship + POP." Under this model, the status of POP (merchant self-operation mode) has been significantly elevated. The platform provides clear operational directions for different categories of goods based on their characteristics. For non-standard products driven by new arrivals and high product richness, such as clothing and sports equipment, merchants are encouraged to operate independently in the POP mode, with flexible shipping options and more benefits, including new product incubation, key country traffic, penalty exemption quotas, supply chain discounts, and other comprehensive support.
For standard products and lightweight items, the platform recommends spot warehouse shipping, focusing on warehousing + low prices, and enhancing product price competitiveness through marketing channels such as "N yuan for N items" and "Super Explosion Day." This dual-track driving model leverages the advantages of both the POP mode's high product richness and the trusteeship mode's competitiveness in logistics and pricing, infusing new vitality into the platform's development.
(2) Strengthening Platform Governance
In terms of platform governance, AliExpress has intensified efforts to combat fake goods. Through a combination of advanced algorithms and manual reviews, strict quality control is exercised over goods. Once fake goods are discovered, the platform takes severe measures, including removing the goods from shelves, penalizing sellers, deducting deposits, and even canceling their sales qualifications. For serious cases of counterfeit sales, the matter is referred to judicial authorities.
To improve service quality, AliExpress has strengthened supervision over merchants' after-sales service, established a comprehensive complaint handling mechanism, and urged merchants to promptly address consumers' after-sales issues, thereby enhancing consumer satisfaction. The platform has also optimized its rules to make them fairer and more transparent, reducing the impact of rule changes on merchants and creating a stable operating environment.
(3) Expanding into Emerging Markets
AliExpress has actively expanded into emerging markets such as Africa and the Middle East. In Africa, AliExpress has continuously improved localized services, supporting multiple local currency payments, including M-Pesa in Kenya and Opay, Verve bank cards, and other mobile payment methods in Nigeria, further expanding local currency payments to countries like Egypt and Algeria. To enhance logistics timeliness, AliExpress has increased its logistics investment in Africa, with orders in countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and Morocco now delivered within 10 days. It has also set up national exhibition halls in countries like Ethiopia, facilitating offline product selection and ordering for wholesale customers.
In the Middle East market, AliExpress has optimized the platform's product categories based on local consumer needs and shopping habits, adding products that meet local cultural and lifestyle requirements. By collaborating with local logistics partners, it has improved the efficiency and reliability of logistics delivery. The expansion into emerging markets has brought new user groups and market share to AliExpress, becoming a crucial growth point for its future development.
Future Outlook: A Phoenix Rising or a Gloomy Exit?
From its former glory to the current predicament and then to active self-rescue, AliExpress's journey has been fraught with challenges and opportunities. In the future, whether AliExpress can rise from the ashes and once again become a leader in global cross-border e-commerce, or fade away amidst fierce market competition, is a question of concern for many merchants, consumers, and industry observers.
On the positive side, AliExpress's self-rescue actions have yielded some results. Strategic adjustments and mode innovation have infused new vitality into the platform. The dual-track driving model of "Trusteeship + POP" is expected to leverage the strengths of both models to meet the needs of diverse consumers and merchants. Strengthening platform governance, combating fake goods, and improving service quality will help reshape the platform's image and bolster consumer trust. Expanding into emerging markets such as Africa and the Middle East has opened up new growth avenues for AliExpress. These regions hold immense potential in the e-commerce market, and with AliExpress's continuous improvement in localized services, rapid growth is anticipated.
However, AliExpress also faces many uncertainties. External competition remains fierce, with competitors like Amazon, eBay, and Temu unlikely to easily relinquish market share. They possess strong advantages in brand influence, user base, and logistics systems. The instability of the global economic environment, such as economic recession and currency fluctuations, may also negatively impact AliExpress's business. Internal issues, including improving logistics timeliness and stabilizing merchant service quality, still need to be continually addressed.
In summary, AliExpress's future is fraught with variables. But regardless of the outcome, its journey has provided valuable lessons for the cross-border e-commerce industry. It also underscores the importance of paying close attention to the industry's development trends, expecting more excellent cross-border e-commerce platforms to emerge in the ever-changing market environment, creating greater value for global consumers and merchants.