5G Private Networks Usher in Rapid Growth, Yet Cloud Vendors Quietly Exit the Stage
![]() 08/26 2025
08/26 2025
![]() 463
463
According to the latest report titled "5G Private Network Market: 2025-2030" by market research firm SNS Telecom & IT, investments in 5G private networks by vertical industries are anticipated to surge at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 41% from 2025 to 2028, surpassing $5 billion by the end of 2028. This anticipated business milestone, representing an annual market space of $5 billion, marks a decade-long journey since the commercial launch of the world's first 5G network in 2018, which has been far from smooth. Notably, this year has witnessed significant changes in the supplier structure of 5G private networks, with some major players exiting the field amidst various factors. However, amidst the wave of digital transformation, 5G private networks continue to hold significant value. As the market undergoes consolidation, suppliers are expected to become more focused, and economies of scale will gradually emerge.
Despite a relatively low base, 5G private network revenue has embarked on a trajectory of rapid growth.
In China, 5G industry applications have achieved substantial progress after six years of development, with 5G private networks commencing rapid expansion. China Mobile's financial reports reveal its 5G private network revenue. The 2024 annual report indicated a revenue of 8.7 billion yuan, marking a 61% year-on-year increase. The 2025 interim report further showed a revenue of 6.1 billion yuan, up 57.8% year-on-year. Similarly, China Unicom's 2025 interim report noted a 60% year-on-year increase in 5G private network revenue, although the total revenue figure was not disclosed. China Telecom's financial report, however, did not reveal 5G private network revenue or growth data.
While 5G private networks have experienced rapid growth over the past two years, they have yet to become a significant revenue driver. For instance, in the first half of 2025, China Mobile's 5G private network revenue accounted for 5.16% of its government and enterprise market revenue and 1.12% of its total business revenue. China Telecom and China Unicom did not disclose total revenue data, but it is reasonable to assume that their share of government and enterprise revenue, as well as overall revenue, is not substantial. Nonetheless, fueled by a growth rate exceeding 50%, 5G private networks have emerged as a highlight, and if this momentum is sustained, they are poised to become a critical revenue growth point in the near future.
Public data indicates that as of June this year, China had over 18,500 "5G+Industrial Internet" construction projects and 58,000 5G virtual private networks, comprehensively covering key application scenarios such as industry, ports, healthcare, and energy. Currently, domestic 5G private networks primarily provide services through virtual private networks, and under the early demonstration effect, other sectors are expected to continue replicating and expanding these initiatives.
Internet giants are quietly exiting the scene, accelerating the shuffle in the 5G private network market.
In the years preceding the commercialization of 5G, 5G private networks were viewed as a pivotal business model in the 5G era, attracting a diverse array of vendors. Telecom operators, communication equipment vendors, IT vendors, internet giants, manufacturing giants, and Open RAN enterprises all harbored high hopes for this market. As previously mentioned, while the current private network market space is limited compared to the public network market, the presence of numerous players suggests a future process of survival of the fittest. It appears that this market shuffle has already commenced, with internet giants beginning to exit quietly.
Previously, the three global cloud vendors—AWS (owned by Amazon), Azure (owned by Microsoft), and Google Cloud—entered the 5G private network market with considerable fanfare, but the current landscape has shifted.
In May this year, AWS confirmed the cessation of its 5G private network service launched in 2021. The company cited spectrum resource limitations and third-party hardware dependencies as hindrances to service development, noting that customers were turning to alternative solutions better suited to their needs. However, AWS retains its "AWS Private Wireless" plan launched in 2023 and continues to offer enterprise private network services through operator partners such as Deutsche Telekom, KDDI, and Orange.
Upon its launch, AWS was optimistic about its 5G private network product. AWS Private 5G was designed as a new managed service enabling enterprises to effortlessly build their own 5G private networks. It is an end-to-end 5G private network solution encompassing network planning, integration, deployment, management, and expansion. A key feature of this solution is pre-integration, which combines the small base station radio units, servers, core network, and access network software required for the 5G private network in advance. Customers do not need to spend time configuring, and network deployment is achieved once the equipment is powered on. The entire process involves more self-deployment by customers and self-configuration through the AWS cloud platform, akin to a DIY deployment model. AWS announced that AWS Private 5G allows enterprises to procure, deploy, and expand 5G private networks in just days, rather than months, significantly lowering the threshold for 5G private network deployment.
Similarly, Microsoft Azure issued an announcement earlier this year stating that its core 5G private network service would be discontinued on September 30, 2025. To prevent service disruptions, customers were urged to migrate to Microsoft's partner solutions, such as Nokia's and Ericsson's 5G private network services, or choose other dedicated network solutions by the specified date.
While Google has not publicly announced its future stance on 5G private network services, it appears that the giant is not actively promoting these services across various platforms.
In the author's opinion, in addition to the spectrum resource limitations and third-party hardware dependencies cited by AWS, the overall market evolution has also led internet giants to abandon the 5G private network field. The primary reasons include: First, the scale of the 5G private network market has fallen short of expectations. These internet giants launched 5G private network services several years ago, but after years of development, the market scale remains limited, failing to generate revenue within a few years. For instance, last year, Azure's cloud business laid off employees, with the operator team being particularly hard hit, directly impacting the provision of 5G services. Second, AI has emerged as the core focus, significantly diverting resources from 5G-related initiatives. Currently, large models are the hottest trend in the technology sector, with vendors investing more heavily, making previously developed 5G businesses appear relatively unremarkable.
Predictions by various research institutions regarding 5G private networks need to be adjusted.
A few years ago, with the entry of public cloud vendors, 5G private networks were perceived to have vast market potential. Based on the development of cellular private wireless networks, many reputable global market research institutions were optimistic about the prospects of cellular private wireless networks and issued various research reports predicting their rapid growth.
For example, market research firm Berg Insight released a report stating that as of 2021, there were over 1,000 private LTE/5G networks globally, and this number is projected to reach over 13,500 by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 57%. Among these, 5G private networks are expected to dominate, approaching 10,000, while LTE private networks will number less than 4,000.
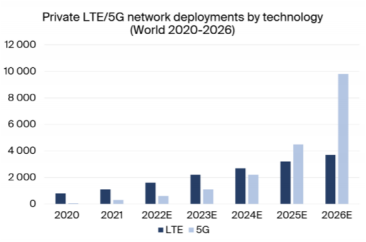
IDC research predicts that global private LTE/5G infrastructure revenue will reach $8.3 billion by 2026, a significant increase from $1.7 billion in 2021. During the forecast period from 2022 to 2026, it is anticipated to achieve a compound annual growth rate of 35.7%.
A previously released report by ABI Research indicated that global 5G private network spending will surpass 5G public network spending by 2036, a prediction that appears even more aggressive. According to ABI Research's forecast, cellular private wireless network capital expenditures are expected to exceed $200 billion by 2026.
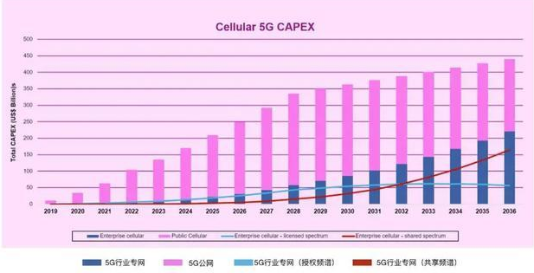
Certainly, the development of 5G private networks is a dynamic process, and 5G's enablement of various industries is a "marathon" that cannot be accomplished overnight. Predictions in this field must be continually updated based on market advancements.
5G private networks remain significant.
The SNS Telecom & IT research report highlights that as end-user organizations intensify their digitalization and automation efforts, some 5G private network deployments have entered a stage of practical use, with increasingly apparent benefits. Notably, 5G private networks have already yielded substantial results in several areas: productivity improvements of 20%-90% in specific manufacturing, quality control, and internal logistics processes; 55% savings in labor costs for warehousing facilities; up to 40% reduction in operating expenses for multimodal railway hubs; 20% and 30% reductions in work-related injuries and harmful gas emissions in refineries, respectively; and 50% reduction in manpower requirements for underground mining operations.
Regarding private network spectrum, SNS Telecom & IT notes that spectrum opening policies, particularly for mid-band 5G NR frequencies such as n40 (2.3 GHz), n38 (2.6 GHz), n48 (3.5 GHz), n78 (3.3-3.8 GHz), n77 (3.8-4.2 GHz), and n79 (4.6-4.9 GHz), as well as shared and local spectrum licensing frameworks, are crucial in accelerating the adoption of 5G private networks. Telecommunications regulators in various countries/regions, including the United States, Canada, Germany, the United Kingdom, Ireland, France, Spain, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Poland, Slovenia, Lithuania, Moldova, Bahrain, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Australia, and Brazil, have issued or are progressing towards granting access to shared and locally licensed spectrum.
At the end of last year, during the Industrial and Information Technology Conference held in China, the conference proposed "advancing the construction of industrial 5G independent private networks" as a key work deployment for 2025, signaling the release of spectrum for 5G private networks. SNS Telecom & IT mentions that telecom operators continue to occupy a pivotal position in the 5G private network market due to their extensive holdings of licensed spectrum, infrastructure assets, and cellular network expertise. As they increasingly focus on vertical B2B opportunities in the 5G era, mobile operators are actively participating in diverse projects, ranging from local 5G infrastructure to sliced hybrid public-private networks that integrate dedicated public mobile network resource slices for wide-area coverage. In addition to operators, wireless communication equipment vendors such as Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei, and ZTE are also significant suppliers of 5G private networks. Furthermore, industrial giants like Siemens have ventured into this field, directly providing private network services to users.
Looking ahead, the survival of the fittest in the 5G private network domain is expected to continue advancing. With the evolution of 5G-Advanced, the implementation of spectrum policies, and the growing demand for industry digitization, the value of 5G private networks will be further demonstrated. While corporate investment in AI may to some extent divert funds from 5G private networks, in the long run, 5G private networks and AI hold the advantage of synergistic operation, as emphasized by a collaboration between Verizon and NVIDIA: "We are leveraging the advantages of dedicated 5G networks and dedicated edge nodes, combined with NVIDIA's AI computing capabilities, to enable real-time AI applications that require security, ultra-low latency, and high bandwidth, which are notable features of these dedicated 5G networks."