Ilya Sutskever —— AI's Most Prominent "Advocate" and Also Its Deepest "Critic"
![]() 12/08 2025
12/08 2025
![]() 615
615
On November 26, 2025, Safe Superintelligence (SSI) founder and former OpenAI chief scientist Ilya Sutskever made a startling forecast during an interview with renowned tech podcast host Dwarkesh Patel: "The era of merely depending on data accumulation and computational power expansion, known as the Scaling Law era (2020 - 2025), has drawn to a close. We are now re-entering a 'research era' that necessitates the exploration of entirely novel algorithms and data formulations."

Ilya Sutskever (left) and Dwarkesh Patel (right)
Moreover, at the 2024 NeurIPS conference, he presented a similar conclusion: pre-training hinges on vast quantities of data, yet there is a ceiling to the amount of internet data available, indicating that the pre-training era is destined to end.

The pre-training era is drawing to a close (PPT from the 2024 NeurIPS conference speech)
The reason this prediction holds significant weight and has ignited widespread contemplation and discussion within the industry is that Ilya Sutskever himself has been a staunch advocate of the 'Scaling Law' for over a decade. He was the very individual who later successfully showcased its potential to the world through the GPT-3 model.
It could even be argued that Ilya Sutskever has transformed the 'Scaling Law' into an industry paradigm, one that many have come to view as gospel. However, it is precisely this strongest proponent of the 'Scaling Law' who is now beginning to acknowledge its limitations and propose new lines of thought.
Yet, this profound insight and prediction do not signify a shift in Ilya Sutskever's stance; rather, they are an inevitable reflection of his unique intellectual attributes. He consistently adheres to a profound 'top-down' belief system to deduce the future trajectory of technology.
The crux of Ilya Sutskever's belief system lies in the pursuit of a correct understanding of the 'essence of intelligence,' rather than blind adherence to any specific technology. His early conviction in the Scaling Law stemmed from his belief that 'scaling up' was the correct path to achieving the essence of intelligence.
As the Scaling Law reached its peak, he observed fundamental contradictions in the models that could not be resolved through mere 'scaling up': a significant gap between exceptional benchmark performance and fragile real-world generalization capabilities. This contradicted his understanding of 'true intelligence.'
At this juncture, Ilya Sutskever's 'top-down' intellectual traits came to the fore. Rather than ignoring these fundamental contradictions to uphold the old path, he re-evaluated the current trajectory based on a higher-level belief ('what constitutes true intelligence'). This prompted him to seek new research paradigms that are closer to the essence of intelligence. Thus, he recently arrived at a new conclusion: the Scaling Law path, which relies solely on scaling up, is reaching its limits, and when combined with mainstream reinforcement learning methods, it not only consumes vast amounts of computational power but also exhibits fundamental flaws in achieving true intelligence generalization.
Ilya Sutskever is widely regarded as a pure scientist with rare 'researcher taste,' possessing both exceptional engineering intuition and profound philosophical thinking. As his mentor, Geoffrey Hinton, has remarked, he possesses 'astonishing raw intuition' and never takes anything at face value, always striving to integrate new information into his own robust worldview framework.
This profound top-tier praise naturally sparks great interest in Ilya Sutskever. Next, we will trace his journey of growth and exploration to gain a deeper understanding of this thinker who consistently stands at the forefront of AI technological waves, gazing even further into the future.
I. Academic Deep Dive (2003 - 2013): Opening the Door to AI and Studying Under the 'Godfather of Deep Learning,' Hinton
Ilya Sutskever was born in December 1986 in Nizhny Novgorod, Russia (formerly Gorky in the Soviet Union). At the age of 5, he immigrated to Israel with his family, and at 16, he moved to Canada, where he commenced his academic journey at the University of Toronto.
He earned a Bachelor of Mathematics (2005), a Master of Computer Science (2007), and a Ph.D. (2013) from the University of Toronto. His academic tenure at the university laid a solid foundation for his future deep dive into the field of AI.
The most transformative moment in this academic career was his encounter with Geoffrey Hinton, the 'Father of Deep Learning.' It is said that in 2003, as a low-year undergraduate student, Ilya Sutskever, driven by his fascination with neural networks, bravely knocked on Hinton's office door. This pure thirst for knowledge and the courage of a young novice moved the academic giant, and the two began a deep collaborative mentor-student relationship.
During his student years, Ilya Sutskever's most iconic achievement was igniting the deep learning revolution with AlexNet.
In 2012, while still pursuing his Ph.D. under the guidance of Professor Geoffrey Hinton, Ilya Sutskever collaborated with his fellow lab mate Alex Krizhevsky, under Hinton's overall supervision, to develop the groundbreaking deep convolutional neural network known as AlexNet.
Alex Krizhevsky was the primary designer and implementer of the network architecture. Ilya Sutskever's core contribution lay in the engineering implementation; he wrote highly optimized GPU code and personally procured and assembled a computing system composed of multiple GTX 580 GPUs, providing the crucial computational power foundation for training the massive AlexNet.
Ultimately, AlexNet won the 2012 ImageNet image recognition competition by a landslide, far surpassing traditional methods. This victory is widely recognized as the starting point of the deep learning revolution, completely reversing the academic skepticism towards neural networks and ushering in a new era of artificial intelligence.
II. Google Era (2013 - 2015): Reshaping the Foundations of NLP and Machine Learning
In late 2012, following the breakthrough success of AlexNet, Professor Geoffrey Hinton, along with his two graduate students Ilya Sutskever and Alex Krizhevsky, co-founded DNNResearch. At its inception, the company had no actual products or production plans; its core assets were the top-tier talents and proprietary technologies of these three deep learning pioneers.
To maximize the company's value, Geoffrey Hinton initiated a small-scale bidding process for his startup. This event quickly attracted the attention of four of the most keenly AI-focused entities at the time: Google, Microsoft, Baidu, and the then-independent star startup DeepMind, which had not yet been acquired by Google.
Ultimately, Google emerged victorious in March 2013, acquiring DNNResearch for approximately $44 million. This move is widely regarded as a classic example of an 'acqui-hire.'
Through this acquisition, Google gained the team's proprietary technologies in the field of deep learning. Meanwhile, Professor Hinton continued to provide guidance to Google as a consultant, while Ilya Sutskever and Alex Krizhevsky joined as full-time employees. Among them, Ilya Sutskever was appointed as a research scientist on the Google Brain team.
During his time at Google Brain, Ilya Sutskever led and deeply participated in two far-reaching projects: one revolutionized the core framework of natural language processing, and the other laid the engineering foundation for the entire AI community.
1) Seq2Seq: A Paradigm Revolution in Sequence Modeling
Before the advent of Seq2Seq, neural networks faced significant challenges in handling tasks like translation because the models required fixed-length inputs and outputs. In 2014, Ilya Sutskever collaborated with Oriol Vinyals and Quoc Viet Le to develop the Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) learning algorithm.
The core innovation of this algorithm lies in its encoder-decoder architecture: the encoder neural network compresses an input sequence of arbitrary length into a fixed-dimensional context vector (a semantic summary); the decoder then uses this vector as its initial state and, combined with the content generated at each step, autoregressively generates the target sequence word by word. This marked the first achievement of end-to-end variable-length sequence conversion.
Seq2Seq broke free from the traditional method's limitation of 'fixed-length input/output' and transmitted the semantic information of the input sequence through 'hidden states,' providing a core framework for subsequent neural models to handle complex sequence tasks.
2) TensorFlow: Laying the Engineering Paradigm for Deep Learning
TensorFlow is an open-source machine learning framework launched by the Google Brain team in 2015. The introduction of TensorFlow transformed powerful machine learning capabilities into accessible tools. It enabled researchers and engineers worldwide to more easily build, train, and deploy complex models, including Seq2Seq, greatly accelerating the democratization and industrialization of AI technology.
As a research scientist at Google Brain, Ilya Sutskever was an early deep participant and significant contributor to the project. For instance, in Google's 2016 core system paper on TensorFlow, 'TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems,' Ilya Sutskever was one of the core authors.
III. OpenAI Era (2015 - 2024): The 'True Brain' Behind OpenAI
1) Co-founding OpenAI and Serving as Chief Scientist
In late 2015, Ilya Sutskever made a decision that stunned the industry: he left his high-paying position at Google to co-found OpenAI with Elon Musk, Sam Altman, Greg Brockman, and others, serving as the chief scientist.
Ilya Sutskever's decision to leave Google and co-found OpenAI was driven by a clear set of beliefs. He aimed to establish a platform where 'technology is not monopolized,' with the fundamental goal of ensuring that powerful artificial intelligence develops in a safe and responsible manner, ultimately benefiting all of humanity.
Thus, from its inception, OpenAI established its fundamental nature as a 'non-profit organization,' precisely reflecting Sutskever's philosophy in an institutionalized form: prioritizing responsibility to humanity as a whole over commercial interests.
However, this unwavering commitment to AI safety and the public good inevitably created tension with the development path represented by Sam Altman, which focused more on technological iteration and market applications. This became the underlying source of their eventual public disagreements.
2) Leading the Development of GPT-1/2/3 and DALL-E Series Models
As a co-founder and chief scientist of OpenAI, Ilya Sutskever was the highest technical leader and core architectural decision-maker driving the GPT series from concept to reality. Under his leadership, OpenAI completed a series of iconic model iterations:
GPT-1 (2018): This was the foundational work of the GPT series and even of generative pre-trained language models as a whole. It pioneered the two-stage paradigm of 'unsupervised pre-training + supervised task fine-tuning': first, pre-training on massive amounts of unlabeled text by predicting the next word to grasp general language patterns; then, fine-tuning with a small amount of labeled data for different downstream tasks (such as text classification, question answering, etc.). This paradigm enabled a single model to achieve breakthrough progress in multiple natural language understanding tasks, laying the core methodological foundation for subsequent developments.
GPT-2 (2019): As a breakthrough iteration of GPT-1, its parameter count increased to 1.5 billion, and it was trained on an even larger WebText dataset. It was the first to demonstrate through large-scale experiments that a language model trained solely by 'predicting the next word' could perform various tasks, such as translation and question answering, in a zero-shot setting without fine-tuning. This established the new paradigm of 'language models as universal task solvers,' laying the foundation for subsequent research on scaling up.
GPT-3 (2020): This marked a milestone in the history of large language models. It achieved a qualitative leap in both scale and performance: boasting 175 billion parameters and trained on up to 45TB of data. The success of GPT-3 established the core path of the Scaling Law, directly giving rise to the emergence of 'prompt engineering' and sparking profound contemplation within the industry about the boundaries of AI capabilities and their societal impacts.
DALL-E 1 (2021): This was an AI-driven image generation model. It was not a derivative of GPT but rather based on the same core idea of Transformers, with key architectural innovations. It uniformly represented text and images as discrete tokens and used a single autoregressive Transformer model for joint modeling and generation, proving for the first time that neural networks could generate complex and creative images directly from textual descriptions.
ChatGPT (2022): This was a conversational AI system launched by OpenAI. Its core technology involved specialized optimization of the GPT-3.5 model to achieve 'alignment' with human intentions and values. The key to its breakthrough lay in introducing the 'Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback' training paradigm. This paradigm was not a simple 'fine-tuning' but a systematic engineering effort consisting of three steps: 1) supervised fine-tuning using human-written dialogues; 2) training a reward model that simulates human preferences; 3) using the proximal policy optimization algorithm, guided by the reward model, to optimize the language model on a large scale.
GPT-4 (2023): Released by OpenAI, GPT-4 represents the fourth-generation large-scale multimodal pre-training model, marking a significant leap at the paradigm level in the reasoning capabilities of large models and cross-modal interactions. It is the inaugural model in the GPT series to support dual input of both text and images, while delivering precise text outputs. This model boasts deep cross-modal reasoning capabilities, enabling it to analyze chart data, identify logical inconsistencies in images, and comprehend the satirical essence and visual humor present in comics. Additionally, GPT-4 has achieved notable breakthroughs in professional academic benchmarks (e.g., ranking within the top 10% of simulated bar exams), long-text processing (supporting up to 25,000-word inputs), and multilingual comprehension.
3. Leading the 'Superintelligence Alignment' Initiative
In July 2023, OpenAI unveiled the formation of the 'Superintelligence Alignment' team, jointly led by Ilya Sutskever and Jan Leike. The project embarked on an exceptionally ambitious objective: to tackle the core technical challenge of ensuring that superintelligent AI systems, surpassing human intelligence, remain aligned with human intentions within a four-year timeframe (by 2027).
The team posits that current AI alignment techniques, which rely heavily on human feedback (such as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback, or RLHF), are insufficient for supervising superintelligence. To overcome this limitation, the team proposed a pivotal technical approach: initially train an 'automated alignment researcher at the human level,' and subsequently leverage this AI researcher, augmented by substantial computational resources, to address more complex superintelligence alignment challenges. OpenAI pledged to allocate 20% of its total computational resources to this endeavor.
In Ilya Sutskever's philosophy, prioritizing the mitigation of AI's potential risks outweighs the pursuit of rapid development. He expresses concerns that AI capabilities could escalate beyond control, posing unpredictable and catastrophic risks. This safety-first mindset has generated inherent tension with internal pressures for swift product iteration and commercialization.
The establishment of the project itself was a proactive measure in response to the industrial reality that 'long-term safety research may be sidelined under the pressures of capital-driven motives.' Ultimately, this ideological clash erupted into a public boardroom crisis in November 2023.
4. The Ousting of CEO Sam Altman
In November 2023, OpenAI found itself embroiled in a governance crisis that sent shockwaves through the tech industry, centered around a fundamental disagreement between Chief Scientist Ilya Sutskever and CEO Sam Altman regarding the pathways for AI development.
Representing certain board members, Ilya Sutskever maintained that OpenAI must stay true to its non-profit roots, prioritizing the prevention of potential risks associated with Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and ensuring that 'AGI benefits all of humanity' as its primary mission, while rigorously preventing commercial interests from undermining its core objectives. Conversely, Sam Altman's faction contended that the company's immediate priority was to expedite productization, secure substantial funding, and continue investing in research and development to ensure survival and maintain technological leadership amidst fierce competition.
The conflict reached its zenith in early November 2023, triggered by a series of specific incidents. Ilya Sutskever secretly collaborated with then-CTO Mira Murati to compile a multi-page PDF memorandum, detailing evidence of Sam Altman's 'consistent lack of candor' with the board across various domains (including product safety approval processes, internal fund allocations, etc.). This memorandum was disseminated via 'self-destructing' emails to three independent directors.
With the backing of the independent directors, the board took swift action on November 17, 2023 (the date of the public announcement), voting to remove Sam Altman as CEO and dismiss co-founder Greg Brockman as board chairman on the grounds of 'lack of candor in communication.' This decision was made by Ilya Sutskever and three independent directors (totaling four votes), with Sam Altman and Greg Brockman casting dissenting votes (totaling two votes).
Sam Altman's removal sparked a company-wide upheaval. Over 95% (more than 700) of OpenAI's employees signed a joint letter, threatening to defect to Microsoft unless the board reinstated Sam Altman. Major investors, led by Microsoft, also exerted tremendous pressure.
Confronted with the imminent collapse of the company, Mira Murati and the entire executive team swiftly aligned themselves with Sam Altman. Under intense pressure, Ilya Sutskever publicly expressed on social media on November 20 that he 'deeply regretted participating in the board's actions' and signed the employee petition.
After days of intense negotiations, Sam Altman successfully returned on November 21, 2023, on the condition of a complete board restructuring. All original directors, except Adam D'Angelo (including other independent directors and Ilya Sutskever), resigned from the board.
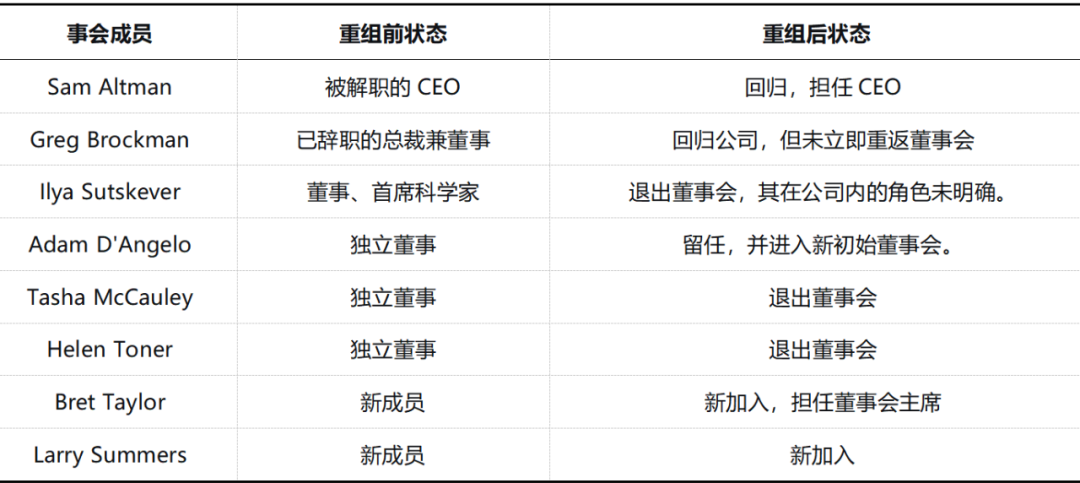
Board Restructuring Post-Sam Altman's Return
Upon his return, Sam Altman consolidated his authority by forming a new board dominated by business leaders and accelerated the company's commercialization efforts. While Ilya Sutskever retained his title of 'Chief Scientist,' he was effectively sidelined and officially departed from OpenAI in May 2024.
IV. SSI Era (2024–Present): A Steadfast Advocate for AI Safety
Following his departure from OpenAI, Ilya Sutskever co-founded Safe Superintelligence Inc (SSI) in June 2024, alongside Daniel Gross (a former Apple AI executive and Y-Combinator partner) and Daniel Levy (a former member of OpenAI's technical team).
The company's mission is singular and unwavering: to directly develop safe superintelligence, explicitly stating that it will not be swayed by product cycles or short-term commercial pressures.
In its nascent stages, SSI adopted a highly focused elite model, comprising a team of approximately 10 employees, with offices in Palo Alto, California, and Tel Aviv, Israel.
Roughly three months after its inception, SSI announced in early September 2024 that it had secured $1 billion in cash financing, valuing the company at over $5 billion. Investors included top-tier venture capital firms such as Sequoia Capital, a16z, DST Global, SV Angel, and NFDG. By April 2025, following the acquisition of an additional $2 billion in funding, SSI's valuation skyrocketed to $32 billion.
However, in late June 2025, co-founder and CEO Daniel Gross was recruited by Meta and departed from SSI. Ilya Sutskever promptly announced that he would personally assume the CEO role, stating that SSI had rejected Meta's acquisition offer and would remain steadfast in its original mission.