DLSS 4 Rockets Game Frame Rates: In-Depth Review of the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE Graphics Card
![]() 01/31 2025
01/31 2025
![]() 731
731
NVIDIA unveiled the highly anticipated GeForce RTX 50 series graphics cards at CES 2025, with the GeForce RTX 5080 and GeForce RTX 5090 D scheduled for release on January 30. On this date, consumers will be able to purchase NVIDIA's powerful cutting-edge technology. In our initial review of the GeForce RTX 5090D graphics card, we marveled at its impressive capabilities, particularly its dominance in 4K gaming with DLSS 4.
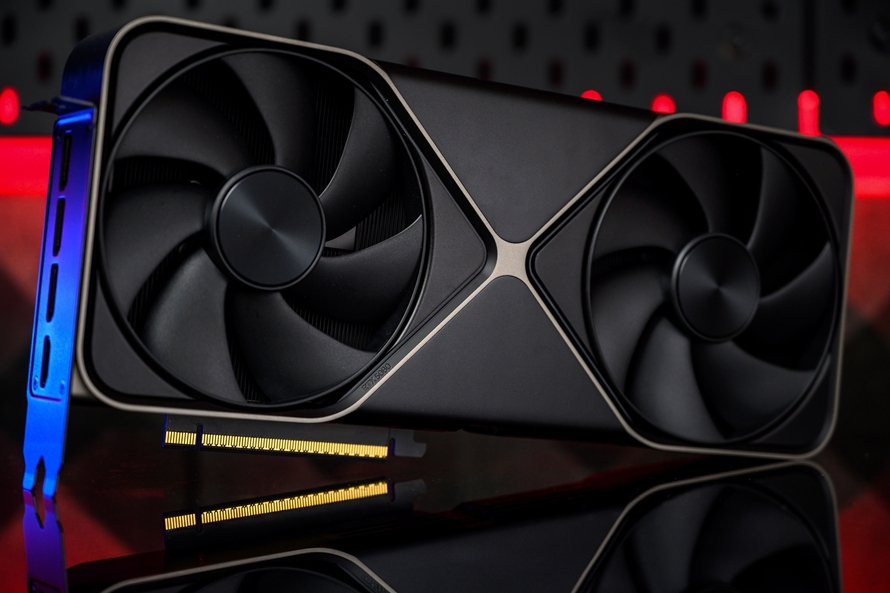

As NVIDIA's next-generation flagship graphics card, the GeForce RTX 5090 D lives up to expectations in terms of performance. Similarly, there is significant interest in the performance of the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 graphics card, especially considering the GeForce RTX 5090 D's price point is not feasible for average consumers. Let's delve into whether the more affordable GeForce RTX 5080 graphics card delivers satisfactory performance.
Architecture Analysis
Today's gamers face a conundrum that is not easily resolved: the pursuit of higher frame rates and superior graphics quality has intensified, yet traditional graphics card performance does not scale linearly. Graphics card transistor density seems to have hit a new bottleneck, and the GPU area cannot expand indefinitely, making further advancements precarious.
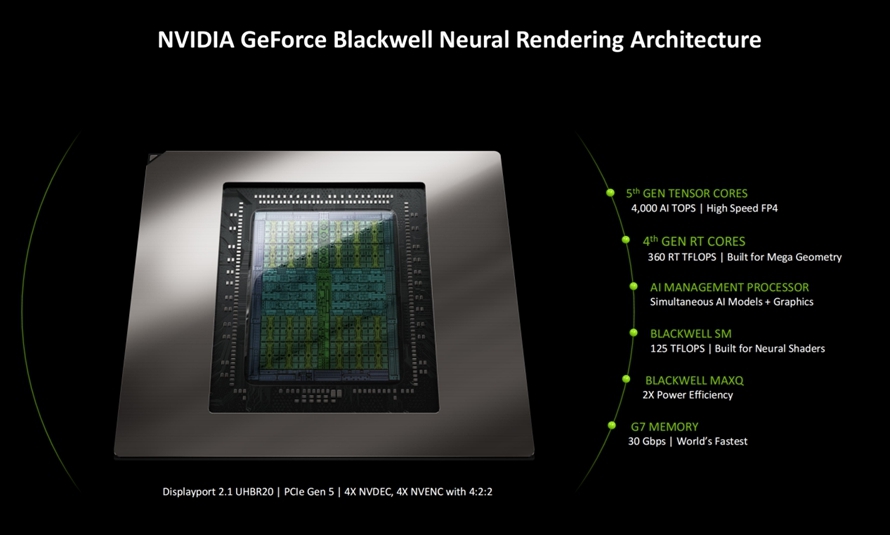
At this juncture, AI steps into the spotlight, transforming underlying rendering methods to enhance game performance. Compared to traditional rasterization computing units, NVIDIA's Blackwell architecture emphasizes strengthening and improving AI computing. This includes the introduction of neural network rendering and enhancements to SM units. Firstly, FP4 computing is introduced, with NVIDIA adding FP4 computing units to the Blackwell architecture GPU and launching the fifth-generation Tensor Core that supports FP4 units, achieving an FP4 precision of 4000 TOPS.
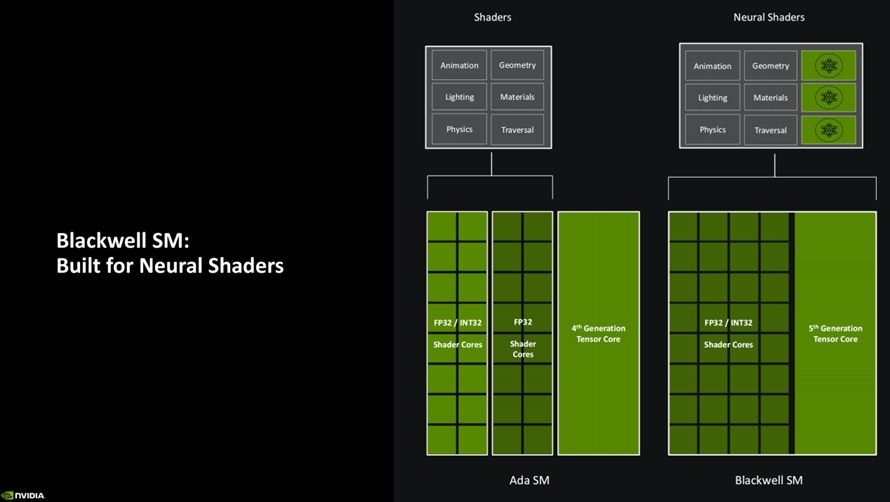
Some may wonder whether FP4 precision can match the simulation of game graphics compared to traditional FP32 single-precision and INT8 precision. In response, NVIDIA states that the booming AI landscape has led to a steady stream of diverse AI algorithms and models. NVIDIA selects and optimizes the AI model most suitable for GPUs and gamers, and FP4 is an ideal algorithmic precision. Hence, NVIDIA decided to incorporate FP4 computing units into the GeForce RTX 50 series graphics cards.
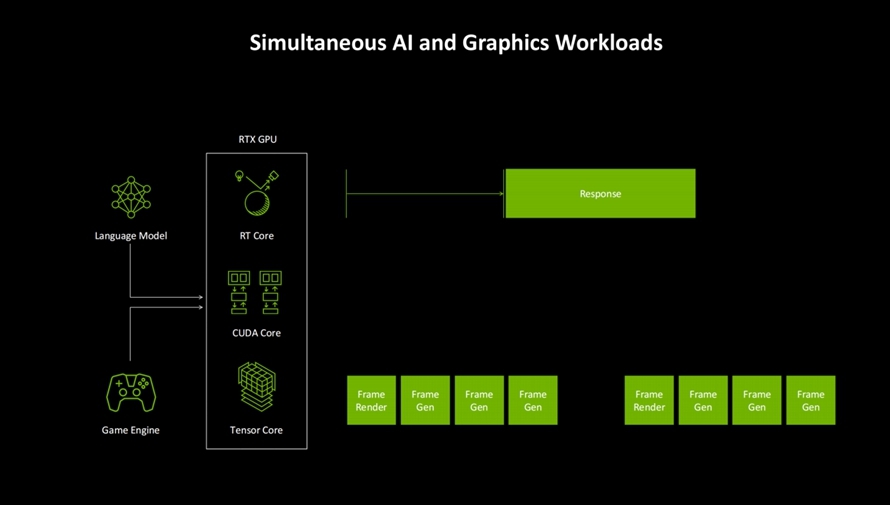
Furthermore, the Blackwell architecture features the fourth-generation RT Core with 360 RT TFLOPS. NVIDIA has also integrated an AI manager into the GPU, effectively managing the growing demand for AI computing power, enabling efficient utilization of these AI capabilities. NVIDIA has reorganized and optimized SM units specifically for neural computing, transitioning from the mixed INT32/FP32 and FP32 design in the Ada architecture to an all-INT32/FP32 shader core configuration, with a peak mixed performance of 125 TFLOPS. This design aims to enhance AI computing efficiency.
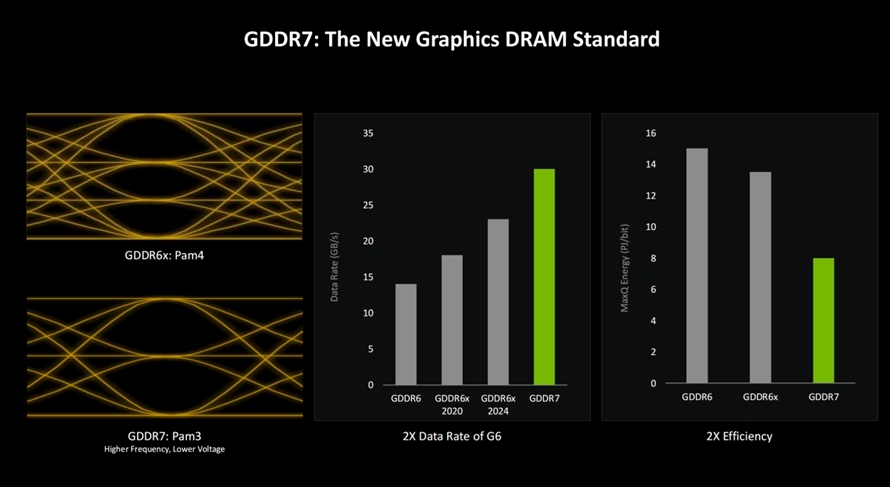
The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 50 series graphics cards also come equipped with brand-new GDDR7 memory, utilizing a novel PAM3 encoding mechanism to provide higher transmission bandwidth, enabling memory frequencies of up to 30Gbps. As technology advances, memory frequencies will continue to increase, potentially exceeding 40Gbps. Such high memory bandwidth accelerates AI computations, and the power consumption of GDDR7 memory is approximately half that of GDDR6.
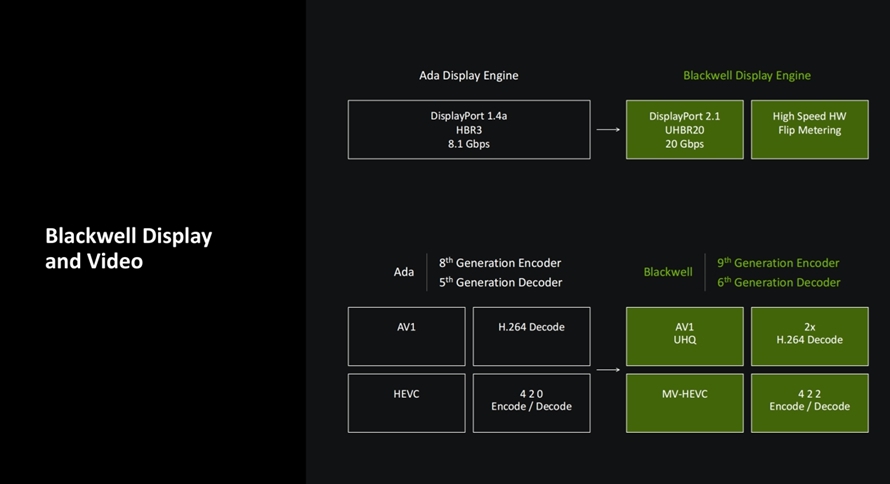
Blackwell also introduces numerous new media encoding features, including DisplayPort 2.1, supporting 4:2:2 H.264 and H.265 codecs, and H265 with MV-HEVC encoding, offering video editors greater freedom. Undoubtedly, the entire Blackwell architecture revolves around AI, leveraging its power to transcend the constraints of Moore's Law and elevate gamers' experiences to new heights.
The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 graphics card boasts 10752 CUDA cores, equipped with fifth-generation Tensor Cores and fourth-generation RT Cores. The GPU has a base clock speed of 2.235GHz and a boost clock speed of 2.52GHz. Additionally, it comes with 16GB of GDDR7 memory.
Graphics Card Appearance
HotTech received the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE graphics card for this review. Due to various reasons, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5090 reference design is not available for sale in China, making the GeForce RTX 5080 FE the highest-end NVIDIA reference graphics card currently available to consumers.
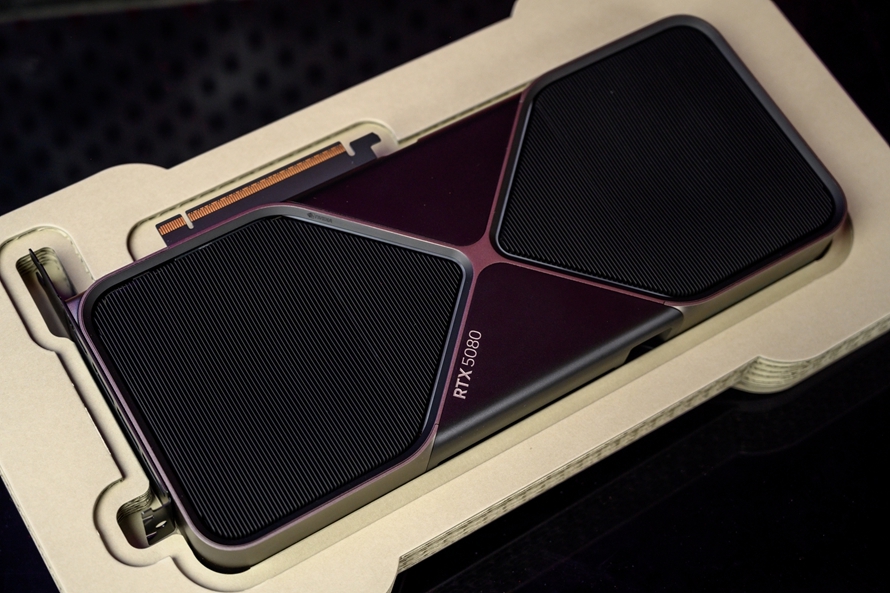
Compared to non-reference graphics cards, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE upholds the exquisite and technologically advanced design of NVIDIA's reference graphics cards. With a champagne-colored theme, it exudes both understated elegance and luxury. Compared to the previous generation of reference graphics cards, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE's most significant change is its slimmer profile, transitioning from a 3.5-slot to a dual-slot design, which is excellent news for users with smaller cases.
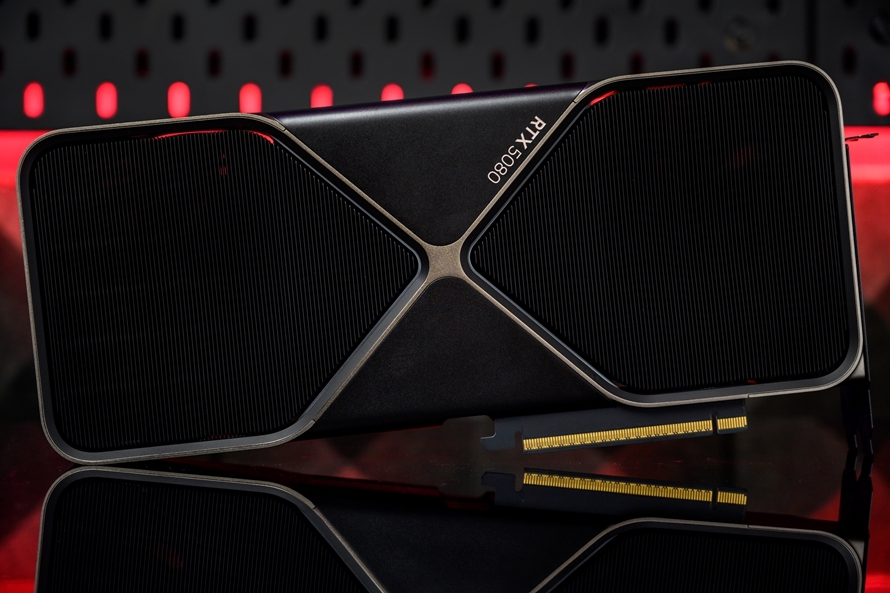

The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE employs a dual-fan design rather than the triple-fan design common in most non-reference graphics cards. NVIDIA states that they have reoptimized the fans and airflow, enabling the dual-fan design to achieve similar cooling performance to triple-fan cooling modules.
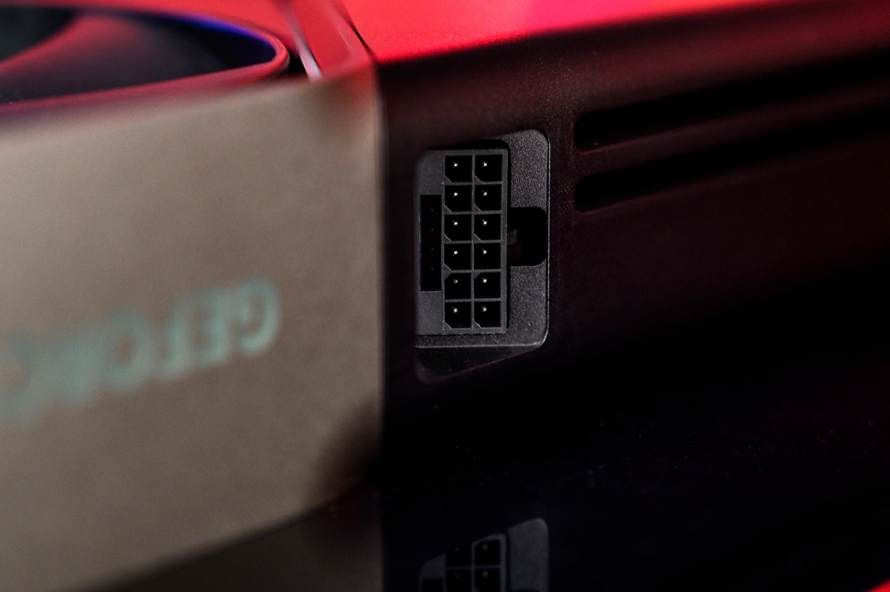

For power delivery, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE uses a diagonal 16Pin power connector. This design ensures a tighter fit between the power cable and graphics card, preventing cable bending and providing a more stable power supply, thus avoiding issues like the RTX 4090 power connector melting. NVIDIA has also adopted the latest 12V-2x6 power supply standard, emphasizing safety.
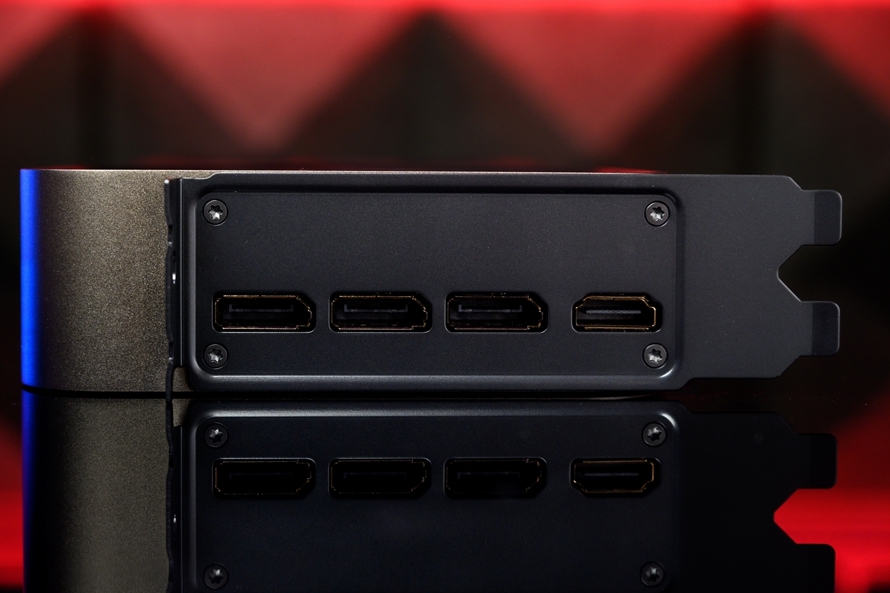

For external connectivity, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE features three DP2.1a and one HDMI 2.1b ports, utilizing the most advanced standards currently available, offering ample bandwidth for gamers and productivity users.

Compared to the bulky GeForce RTX 40 series graphics cards, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE, with its advanced cooling design and increased TDP, maintains a sleek profile, making it more appealing to users.
Configuration Platform
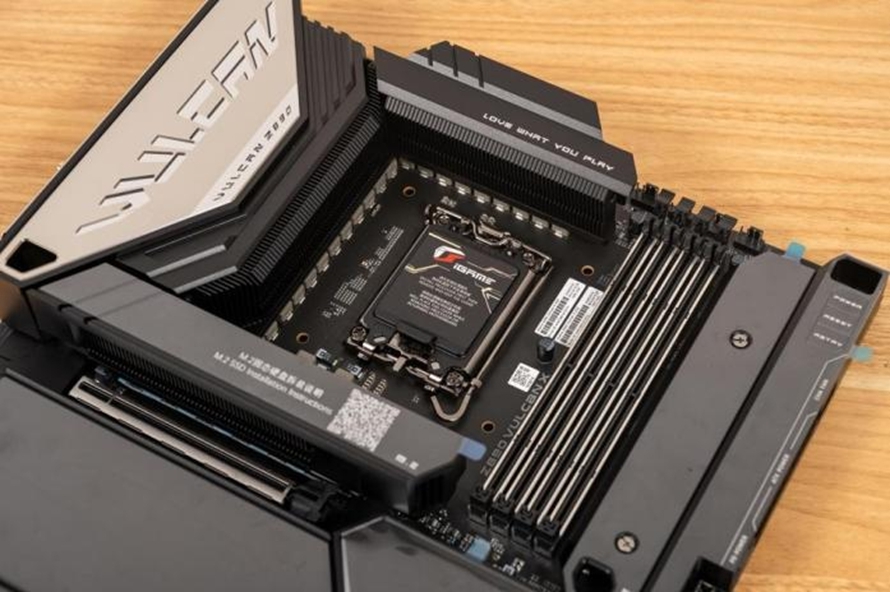
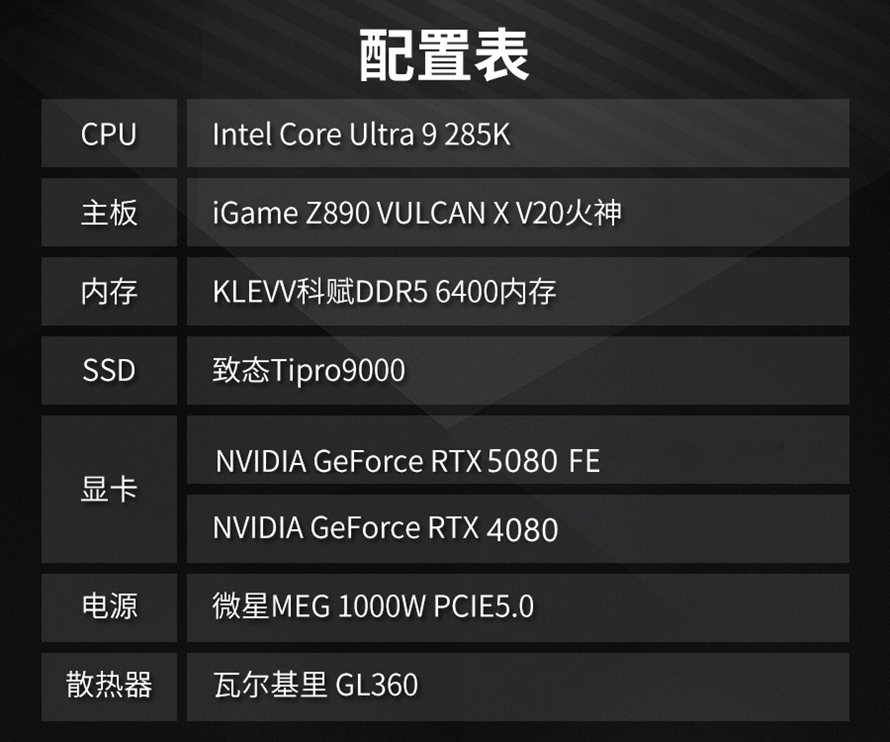

We chose the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K processor paired with the iGame Z890 VULCAN X V20 motherboard. The motherboard features a 20+1+1+1 phase power supply, equipped with advanced components like 105A flagship DrMOS and chip polymer capacitors, providing robust power delivery for the CPU and graphics card. Additionally, it ensures stable chipset cooling with direct-touch heat pipes, multiple aluminum fins, and full-coverage cold plates.

We also selected Crucial's DDR5 memory and Zhitai Tipro9000 PCIe 5.0 SSD, offering maximum read speeds of up to 14GB/s and write speeds of up to 12.5GB/s, delivering impressive performance. Additionally, we chose an ATX 3.1 power supply with an output power of 1000W to provide robust cooling for the entire platform.
Theoretical Performance
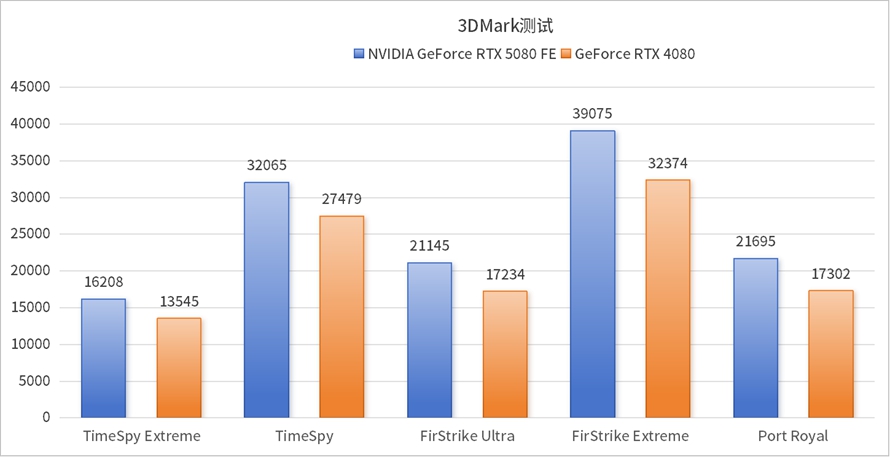
3DMark benchmarks primarily compare traditional raster performance and ray tracing performance. In the 3DMark benchmarks, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE graphics card showed a performance increase of approximately 20%. This increase is primarily attributed to the stacking of computing power and the benefits of GDDR7 memory, which is expected.
Actual Game Testing
DLSS 4
Undoubtedly, with traditional raster performance enhancements waning, AI has emerged as the most significant technological advancement for enhancing the gaming experience, allowing gamers to achieve more with less.
NVIDIA is heavily promoting DLSS 4. As NVIDIA's ace technology, DLSS has evolved continuously over the past six years. In 2025, it incorporated Transformer model support. Compared to traditional CNN models, Transformer models can double the number of AI parameters and quadruple computing performance, providing more stable image quality and richer game graphics details. This technology is available not only for GeForce RTX 50 series graphics cards but also for GeForce RTX 40, GeForce RTX 30, and GeForce RTX 20 series graphics cards.
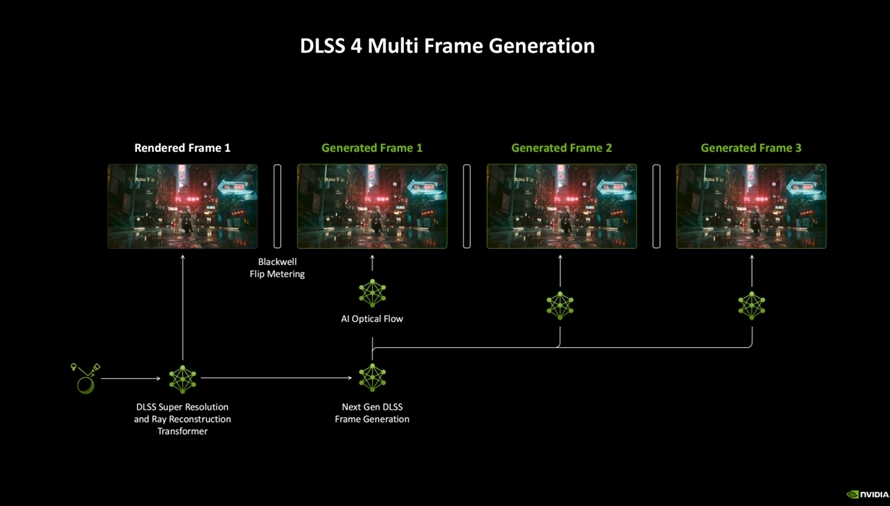
For gamers, the most significant innovation of DLSS 4 lies in multi-frame generation, where AI can generate more pixels and frames. The GeForce RTX 40 series graphics cards used hardware optical flow accelerators, while the GeForce RTX 50 series employs AI models for calculations. With the new model, three generated frames can be produced between each traditionally rendered frame, significantly boosting game performance. In other words, the traditional GPU only needs to handle rendering 1/16 of the pixels in the scene, with AI handling the rest, resulting in a dramatic increase in game frame rates.

GeForce RTX 5080 Graphics Card Image Quality Settings
GeForce RTX 4080 Graphics Card Image Quality Settings
NVIDIA stated that at the time of the graphics card's launch, 75 games and applications will support DLSS 4 technology. Through testing, it was found that there are two methods for implementing DLSS 4. Games like "Cyberpunk 2077", "Hogwarts Legacy", "Alan Wake 2", and "Star Wars Jedi: Survivor" use built-in DLSS 4, while games like "Dragon Age 4" and "Marvel's Midnight Suns" require the NVIDIA app to forcibly enable DLSS 4 technology. Additionally, different games have varying naming conventions for DLSS 4. Based on the descriptions of two built-in games, frame generation can be broadly divided into two parts: DLSS 3 is equivalent to 2x frame generation, while DLSS 4 includes 3x and 4x multi-frame generation.
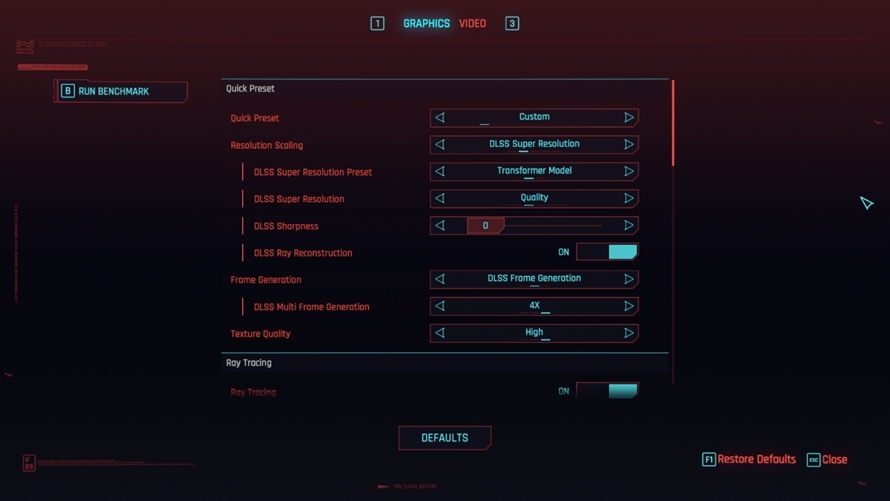
Here, it's worth mentioning "Cyberpunk 2077", which not only provides detailed DLSS settings but also allows for switching between Transformer models and CNN models, making it extremely convenient. It's no wonder this game is hailed by players as a dedicated graphics card benchmarking game.
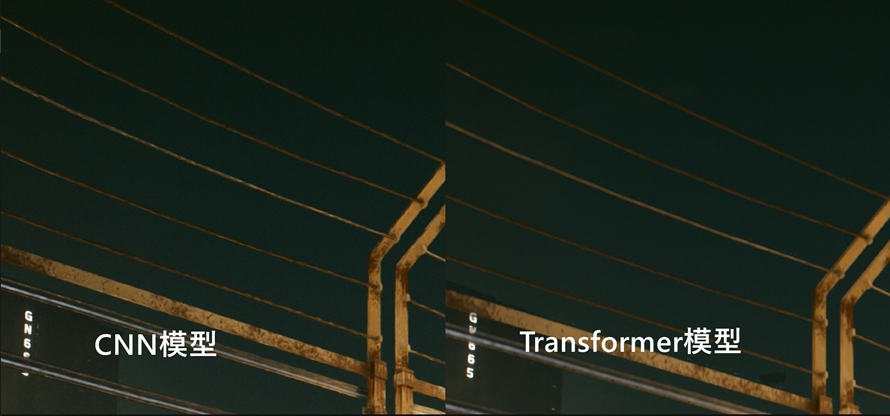

Comparing the CNN model and Transformer model in the same scene, the Transformer model delivers more refined imagery, with more natural object details and smoother transitions compared to the CNN model, resulting in a more stable picture.
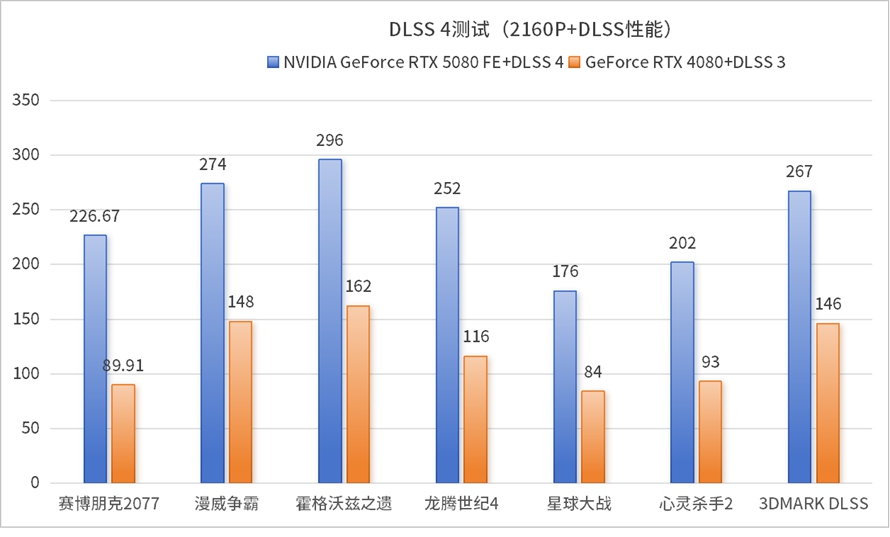
With the help of DLSS 4's multi-frame generation technology, the frame rate of the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE graphics card has been significantly boosted, with an average performance approximately double that of the GeForce RTX 4080 graphics card with DLSS 3 frame generation enabled. In games like "Cyberpunk 2077", the lead even reaches 2.5 times. This is because compared to the GeForce RTX 5090, the GeForce RTX 5080 graphics card is more prone to being graphics-limited, so after the frame rate increase, the bottleneck factors of other configurations become smaller, naturally leading to a larger relative improvement.
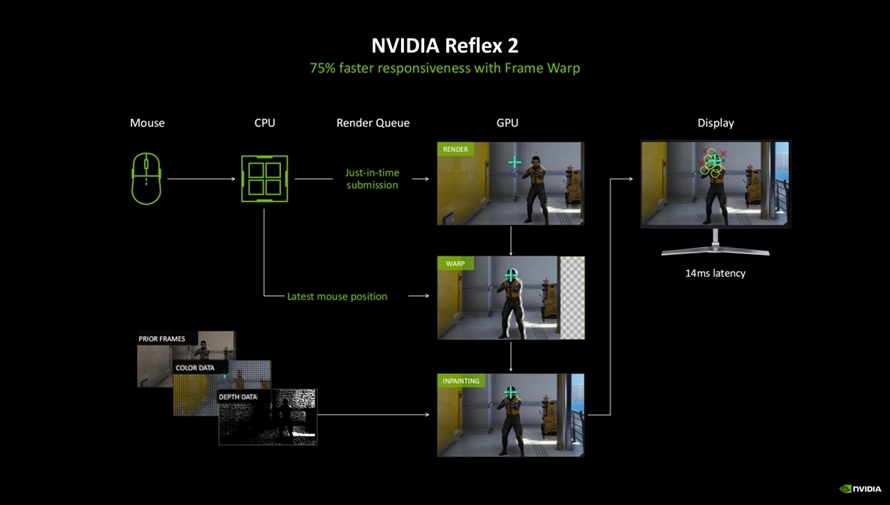
In addition to DLSS 4, to satisfy gamers' pursuit of lower input and output latency, NVIDIA has introduced NVIDIA Reflex 2 technology, which can reduce frame rate latency by up to 75%, providing a smoother gaming experience for esports players. NVIDIA stated that "VALORANT" and "The Finals" will be the first to adopt NVIDIA Reflex 2 technology.
Actual Game Testing
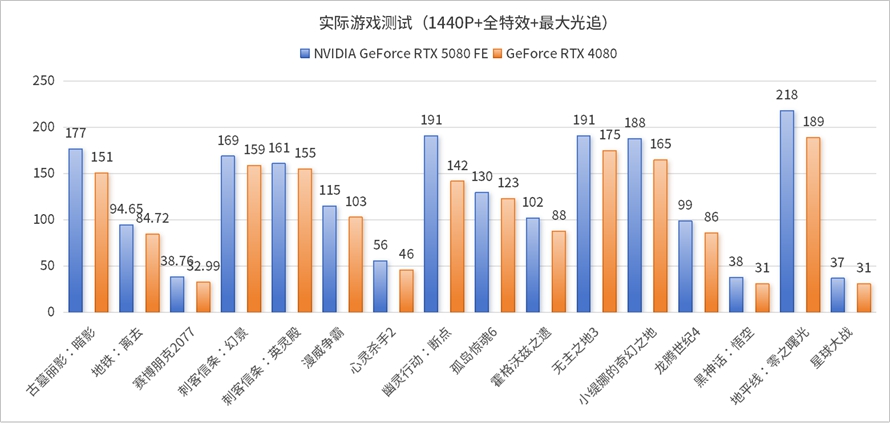
Without DLSS 4, the increase in game frame rates is primarily due to CUDA improvements. Additionally, considering factors like drivers and actual optimizations, the actual performance improvement in traditional games is lower than the theoretical performance improvement in 3DMark, with an increase of approximately 18% at 4K resolution and 15% at 2K resolution.
We conducted a comparative analysis of the temperature and power consumption of the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 FE graphics card versus the GeForce RTX 4080. Given its larger chip area, an increase in power consumption for this new generation of graphics cards was anticipated. Nevertheless, thanks to its sophisticated cooler design, the RTX 5080 maintains temperatures under full load that are remarkably similar to its predecessor, highlighting NVIDIA's commitment to innovative cooling solutions.
Conclusion: DLSS 4 Unleashes Untapped Potential
Throughout testing, the formidable capabilities introduced by DLSS 4 left a profound impression, particularly the multi-frame generation technology that propels game frame rates to unprecedented heights. It's astonishing to witness a graphics card achieve over 200 frames per second at 4K resolution with ray tracing enabled, a feat now made possible by AI. The advent of DLSS 4 technology has significantly bolstered the GeForce RTX 50 series, pushing the boundaries of gaming performance.

As NVIDIA's flagship technology, DLSS has undergone continuous refinement over the years. The company plans to introduce DLSS with enhanced features, further elevating the gaming experience. The integration of Transformer models and neural network shaders introduces a revolutionary programming paradigm for developers, streamlining the process of application and game development. However, during testing, we observed that forcibly enabling DLSS 4 via the NVIDIA APP, as opposed to using the built-in game settings, can be inconvenient and may lead to invalid configurations. Therefore, close collaboration between game developers is crucial for the swift adoption of DLSS 4. Titles like "Cyberpunk 2077" that promptly add DLSS 4 support through updates offer a welcome boon to gamers.

In the current landscape of limited raster performance advancements, the industry has collectively embraced the full potential of AI. DLSS 4, powered by cutting-edge algorithms, enables players to immerse themselves in a gaming experience that harmoniously balances high resolution with high frame rates, pushing frame rates to new heights. As DLSS 4 continues to evolve and AI algorithms are honed, an increasing number of games will integrate DLSS 4 support, heralding a new AI era for the gaming industry.