Case Sharing | Golden Infrared Thermometer Enhances Testing of 1cm² Microcrystalline Material Heat Dissipation Performance
![]() 05/26 2025
05/26 2025
![]() 691
691
Material science, a cornerstone of modern technology, spearheads advancements across various scientific and technological domains. Materials exhibiting robust heat dissipation, superior thermal conductivity, or resistance to extreme temperatures hold immense potential in electronics, transportation, aerospace, and beyond.

Infrared thermal imagers, non-contact temperature measurement devices, swiftly and precisely identify thermal anomalies by imaging and analyzing surface temperature distributions. In electronics and semiconductor industries, they play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency in power consumption design, material analysis, and research on high-temperature-resistant materials.
01 Project Background
The Xi'an-based research institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, a hub for strategic high-tech innovation and applied basic research, sought to evaluate the heat dissipation performance of 1cm² crystalline materials using an infrared thermal imager. This endeavor demanded high precision in temperature measurement and image quality.
02 User Pain Points
High Demands on Temperature Measurement Accuracy: Continuous temperature monitoring of the small crystalline materials necessitated exceptional image quality and temperature measurement accuracy, ensuring stable and precise data.
Challenges in Capturing Temperature Rise Trends: The testing process involved heating the materials with a laser while capturing data at peak temperatures. This required non-contact temperature detection capable of tracking the entire material's temperature rise.
03 Solution
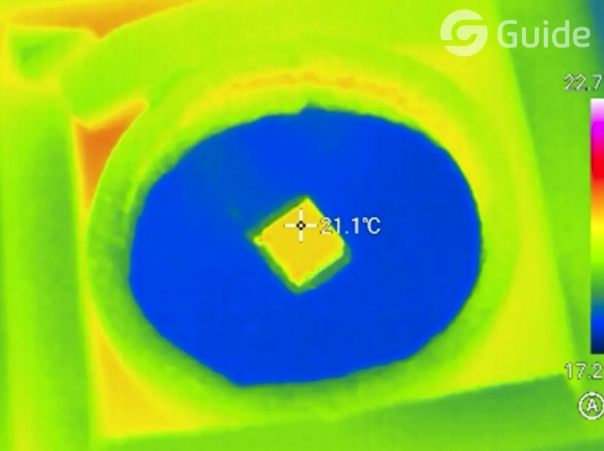
After fixing the crystalline material, it was heated via laser irradiation. The thermal imager monitored temperature changes, with a rectangular analysis area added to track the maximum temperature. Upon reaching peak temperature, a photograph was taken for record. Post-experiment, thermal images were analyzed using "ThermoTools" infrared analysis software.
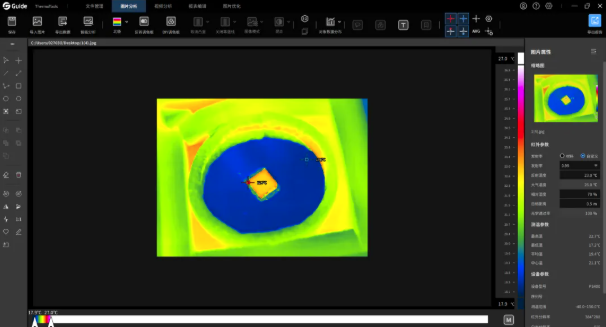
ThermoTools processed images and generated analysis reports.
04 Advantages of Thermal Imaging
Non-contact Temperature Measurement: Infrared thermal imagers visualize temperature distributions clearly, aiding R&D in assessing thermal loads and enhancing heat dissipation designs.
High-precision Measurement and High-resolution Imaging: Detecting subtle temperature changes and producing high-definition images facilitate intuitive research, data recording, and result presentation.
Wide Applicability: Suitable for metals, ceramics, composites, and polymers, they can be used in diverse environments and complex conditions.
Evaluation of Heat Dissipation Solutions: Quickly and intuitively assessing the efficacy of different heat dissipation strategies during material research and design phases.
05 Recommended Product

The Golden PT series flagship infrared thermal imager, the world's first million-pixel portable device for temperature measurement, boasts advanced focusing technology, a wide temperature range, ultra-high accuracy, and modular design with various lenses. It enables R&D personnel to visualize temperature distributions, assess thermal loads, capture minute temperature differences, and enhance heat dissipation performance testing.