Qualcomm: 'Storage Shortage' Worsens—Are Smartphone Stocks on the Brink?
![]() 02/09 2026
02/09 2026
![]() 530
530
On the morning of February 5, 2026, Beijing time, following the close of the U.S. stock market, Qualcomm (QCOM.O) released its financial report for the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (as of December 2025). The key highlights are as follows:
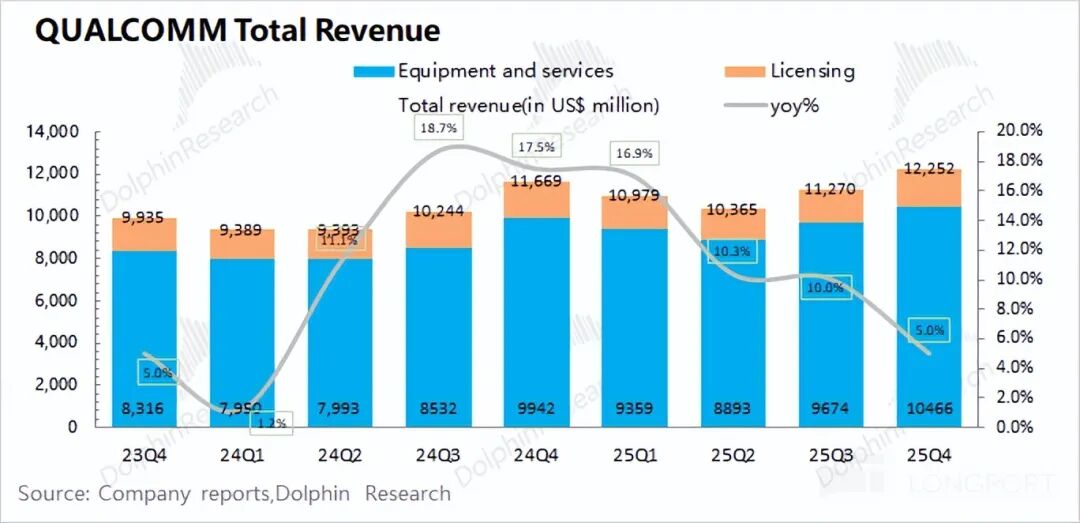
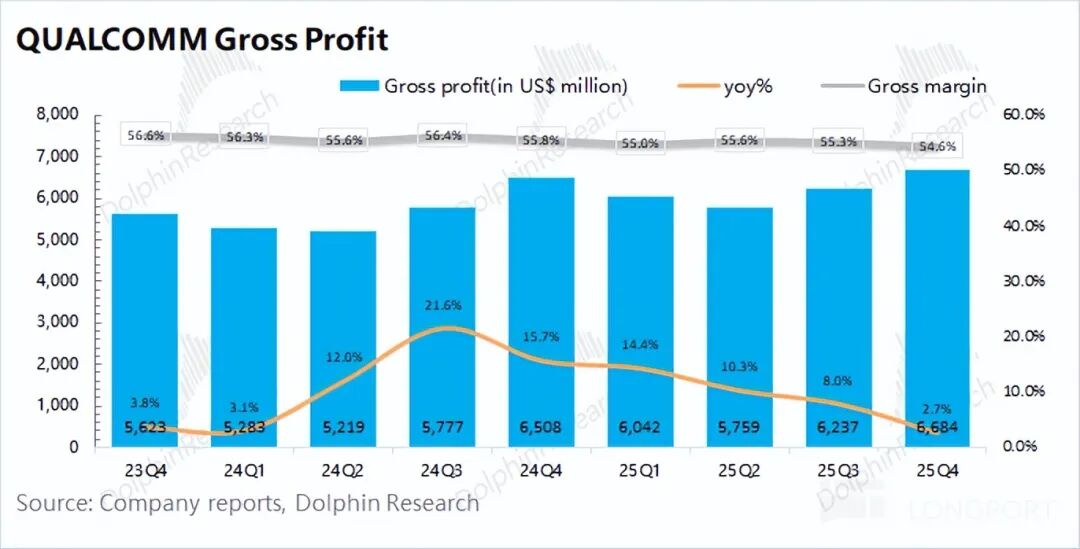
1. Core Financial Data: Qualcomm reported quarterly revenue of $12.25 billion, up 5% year-over-year, aligning with market expectations of $12.2 billion. However, the company's growth rate slowed significantly this quarter, primarily due to the sluggish downstream smartphone market. The gross margin stood at 54.6%, down 1.2 percentage points year-over-year and below market expectations of 55.2%. The storage shortage dragged down the gross margin of Qualcomm's hardware business (QCT).
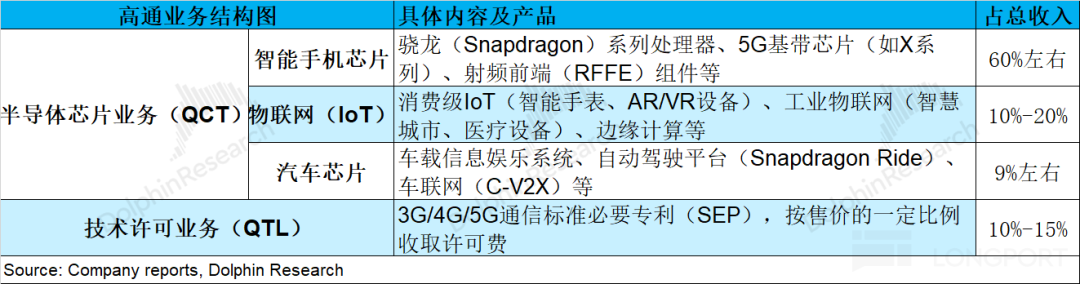
2. Business Segment Performance: Qualcomm's operations are mainly divided into two segments: semiconductor chip business (QCT) and technology licensing business (QTL), with the semiconductor chip business being the primary revenue contributor, accounting for nearly 90%.
Within the semiconductor chip business: ① Smartphone business revenue reached $7.8 billion this quarter, up 3.3% year-over-year. Growth in this segment slowed significantly, mainly due to two factors: firstly, overall smartphone market shipments experienced only low single-digit growth; secondly, the company's flagship product launch was brought forward to the previous quarter, leading to some demand being pulled forward.
② Automotive business revenue was $1.1 billion, up 14.6% year-over-year, driven by increased shipments of Snapdragon Digital Cockpits. ③ IoT business revenue stood at $1.69 billion, up 9% year-over-year, driven by demand for consumer, network, and industrial products. However, compared to previous growth rates exceeding 20% year-over-year, IoT revenue growth slowed significantly due to tightened government subsidies in the Chinese market.
3. Operating Expenses: The company's operating expenses rose to approximately $3.32 billion, with R&D expenses increasing to about $2.45 billion and sales expenses for the quarter at $870 million.
Due to the decline in gross margin and the increase in operating expenses, Qualcomm's core operating profit for the quarter was $3.37 billion, down 5% year-over-year.
4. Next Quarter Guidance: Qualcomm expects revenue for the second quarter of fiscal year 2026 to range between $10.2 billion and $11 billion, falling short of market expectations of $11.2 billion. The company also anticipates Non-GAAP earnings per share for the next quarter to be between $2.45 and $2.65, below market expectations of $2.9.
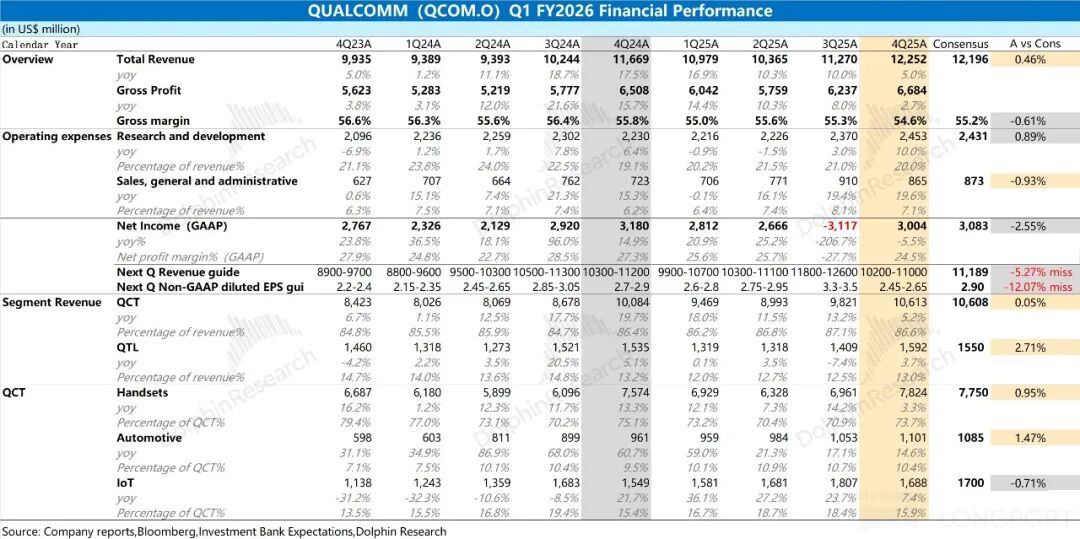
Dolphin Research's Overall Assessment: Storage Shortage Continues to Weigh on Core Business
Qualcomm's revenue for the quarter met market expectations, but the decline in gross margin was primarily influenced by factors such as storage shortages and price increases, which dragged down the gross margin of the company's hardware business (QCT).
The impact of storage shortages and tightened government subsidies this quarter had already been factored in by the market, so the performance of the company's various businesses generally met expectations. However, what disappointed the market the most was the guidance for the next quarter.
For the next quarter, Qualcomm expects revenue to be between $10.2 billion and $11 billion, below market expectations of $11.2 billion. Non-GAAP earnings per share are expected to range between $2.45 and $2.65, also falling short of market expectations of $2.9. This suggests that the company may face declines in both revenue and gross margin in the next quarter.
The primary contributor to the company's performance decline is the smartphone business. Qualcomm expects next quarter's smartphone business revenue to be around $6 billion, marking a double-digit year-over-year decline. The company attributes this to insufficient DRAM supply. Although the market had already lowered its expectations for the company, it did not anticipate the storage issue to have such a significant impact.
Beyond the Financial Report: Market Focus on Qualcomm
a) Traditional Sector: Core Business Faces Ongoing Pressure
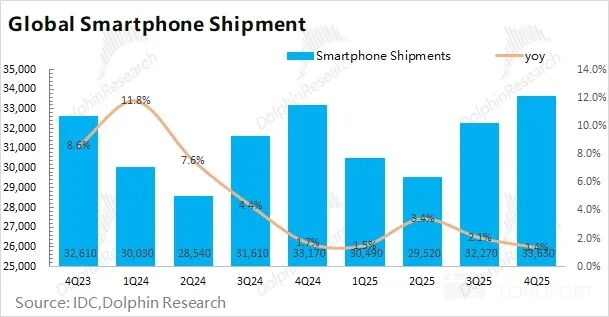
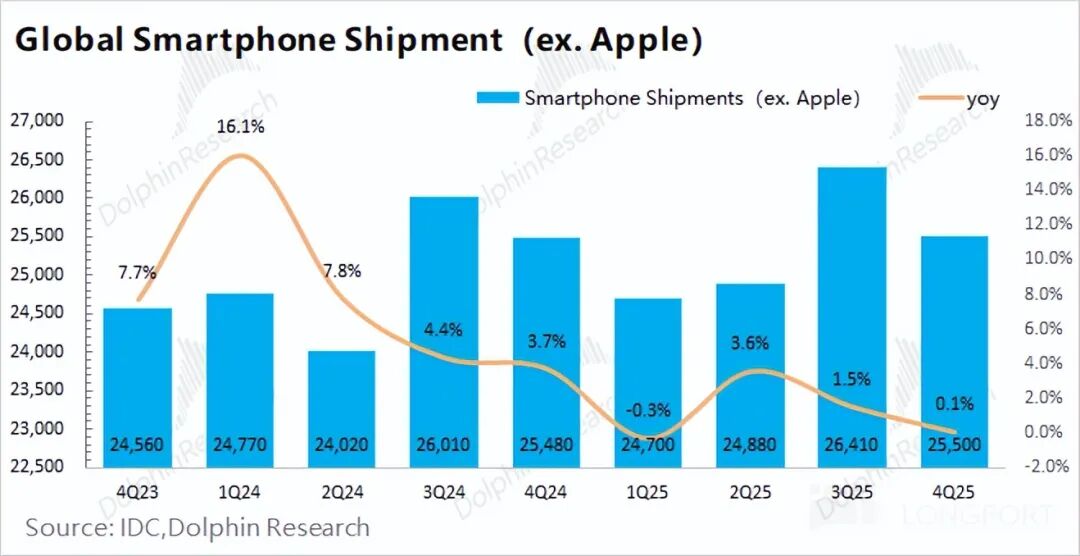
The smartphone business is the largest segment of Qualcomm's operations, accounting for more than half of its revenue. However, the overall smartphone market has been tepid, with global smartphone shipments reaching 363 million units this quarter, up just 1.4% year-over-year.
The smartphone market is dominated by two major camps—Apple and Android. Looking at the detailed breakdown, Apple's smartphone shipments increased by 5.7% year-over-year this quarter, while the Android camp saw no year-over-year growth in shipments, which also affected Qualcomm's smartphone business performance this quarter.
The recent pressure on smartphones, IoT, and other categories is mainly due to storage shortages and tightened government subsidies. From the company's guidance this time, the storage shortage issue appears to be more severe than anticipated.
Qualcomm expects next quarter's smartphone business revenue to be around $6 billion, down about 13% year-over-year. This means the storage issue has not only "eroded" gross margins but has escalated into a "shortage" situation, directly affecting smartphone shipments (storage shortage → inventory/shipment disruptions → revenue decline). The escalation of the "storage shortage issue" will continue to suppress the company's core business.
b) AI Sector: AI PCs and Data Centers as Potential Growth Markets
Qualcomm's strategic布局 (strategic deployment) in the AI sector has not yet had a significant impact on the company's performance in the short term but mainly provides growth prospects.
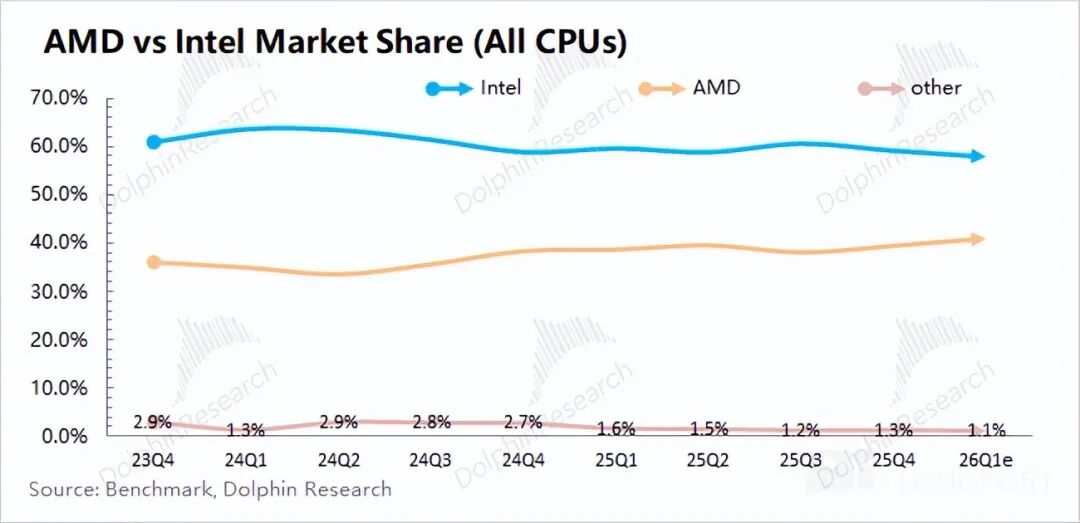
① AI PCs (competing with Intel): Qualcomm released its second-generation PC platform—Snapdragon X2 series (including Elite Extreme, Elite, and Plus). The Hexagon NPU computing power reached 80 TOPS (up from 45 TOPS in the previous generation), supporting local operation of 13B parameter LLMs.
With the maturity of the Windows on Arm architecture, Qualcomm has established partnerships with industry giants like Microsoft, Dell, and Lenovo, breaking the x86 monopoly and entering the mainstream price range. Although Qualcomm has now entered the PC market, its current market share is still low and poses little threat to Intel and AMD.
② AI Data Centers (competing with NVIDIA): Qualcomm announced in late October 2025 that it would launch two new AI chips—AI200 (mass production in 2026) and AI250 (mass production in 2027), marking the company's strategic shift into the data center market.
From current information: 1) The AI200 is a rack-level solution focused on "high memory capacity + low total cost of ownership (TCO)," specifically optimized for inference scenarios of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal models. 2) The AI250 adopts a near-memory computing architecture, with core advantages of "over 10x effective memory bandwidth improvement + lower power consumption," focusing on inference scenarios with extremely high memory bandwidth requirements.

Qualcomm has announced that Humain, an AI startup in Saudi Arabia, has become the company's first customer, planning to deploy 200 megawatts of computing power based on the AI200 chip starting in 2026 (Dolphin Research estimates this could bring $3 billion in revenue opportunities).
The value analysis section has been published in the Changqiao App under the 'Dynamic - Depth (Investment Research)' article with the same title.
Overall, with the storage issue escalating from "price increases" to "shortages," Qualcomm's core business performance is unlikely to improve. Previously, the market only considered that "storage price increases" would suppress some terminal demand, expecting the company's smartphone business to face pressure in 2026 but not to see a double-digit decline, and had already lowered the company's target price.
At this stage, only breakthroughs in the AI PC or data center sectors can bring some confidence to the market. From the guidance provided by management this time, the company is facing greater pressure than "expected." The storage issue not only affects gross margins through price increases but also impacts product inventory/shipments due to "shortages."
With persistent storage shortages, the company's core business is unlikely to improve, and market expectations for the company's performance and valuation will be adjusted downward again.
The following is a detailed analysis:
I. Overall Performance: Significantly Slowed Growth
1.1 Revenue
Qualcomm achieved revenue of $12.25 billion in the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (Q4 2025), up 5% year-over-year, meeting market expectations of $12.2 billion.
Although all of the company's businesses saw growth this quarter, the growth rate of QCT (semiconductor chip business) slowed significantly, mainly due to factors such as "storage shortages and tightened government subsidies."
1.2 Gross Profit
Qualcomm achieved a gross profit of $6.68 billion in the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (Q4 2025), up 2.7% year-over-year.
The company's gross margin for the quarter was 54.6%, down 1.2 percentage points year-over-year and below market expectations of 55.2%, mainly due to the impact of storage price increases, which dragged down the gross margin of the hardware business (QCT business) this quarter.
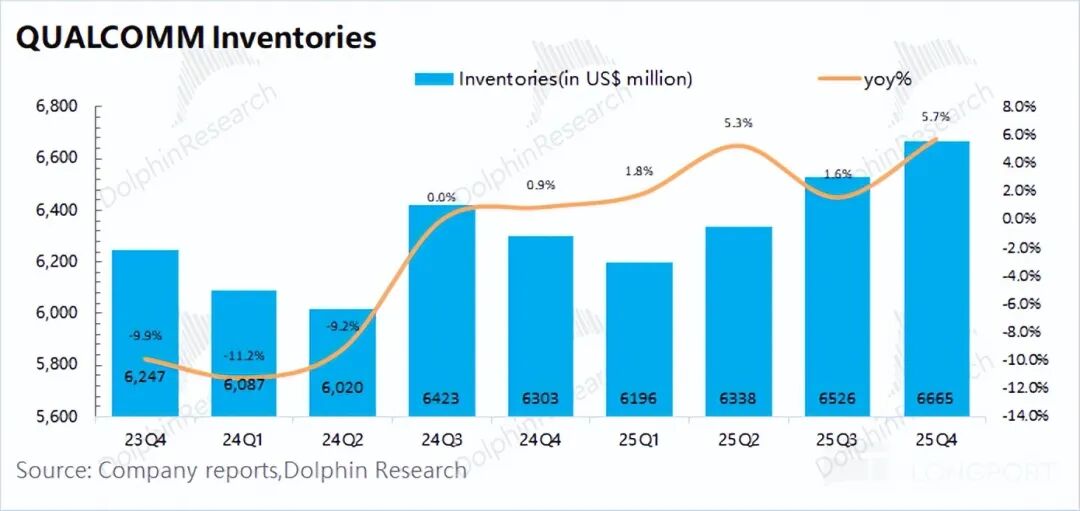
Qualcomm's inventory was $6.67 billion in the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (Q4 2025), up 6% year-over-year.
Considering the company's guidance, Dolphin Research believes that current demand for smartphones and other products is relatively weak, and the company's motivation to stock up is not strong. Given the storage shortage, the company's current inventory is structural, with storage categories being relatively scarce.
1.3 Operating Expenses and Profit
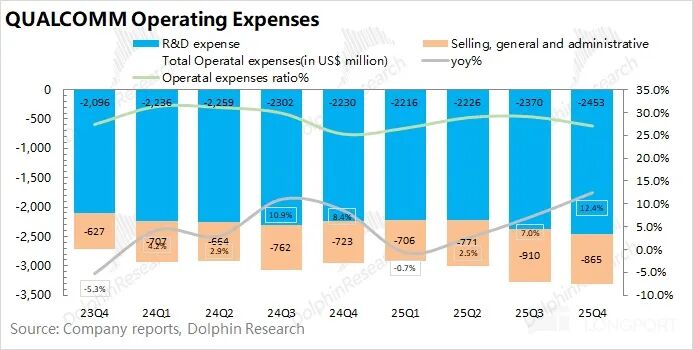
Qualcomm's operating expenses were $3.32 billion in the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (Q4 2025), up 12.4% year-over-year.
Among them: ① This quarter's R&D expenses were $2.45 billion, up 10% year-over-year, remaining the company's largest investment. ② This quarter's sales and administrative expenses were $865 million, up 19.6% year-over-year.
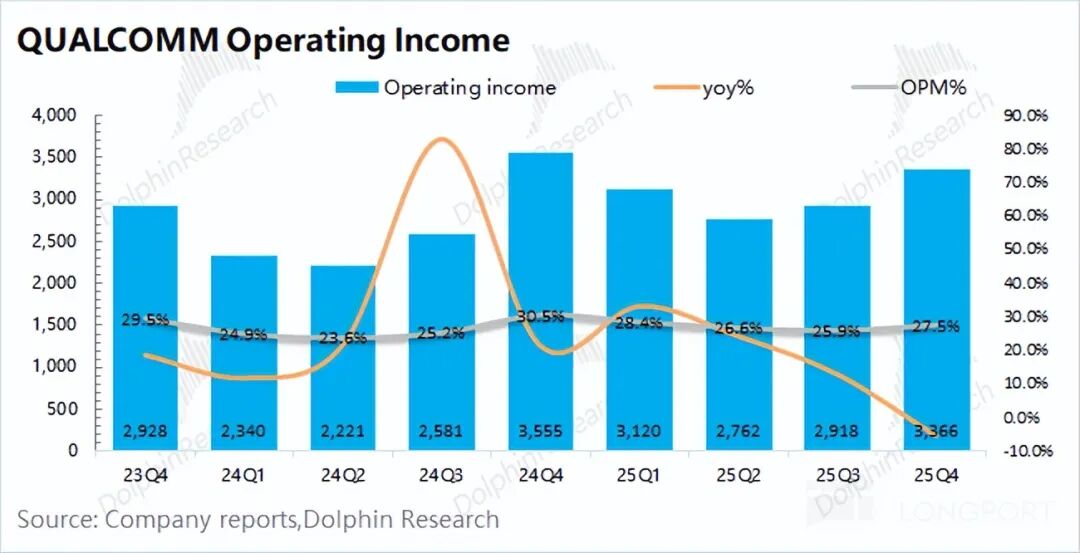
Since the company's profit is affected by tax adjustments, core operating profit is more valuable. Qualcomm's core operating profit for the quarter was $3.37 billion, down 5% year-over-year, with a core operating profit margin of 27.5%. The decline in profit this quarter was mainly due to the decline in gross margin and the increase in expenses.
II. Business Segment Breakdown: Storage Shortage Leads to Double-Digit Decline in Smartphones
From Qualcomm's business segment breakdown, QCT (CDMA business) remained the company's largest revenue source this quarter, accounting for 87%, mainly including revenue from semiconductor chips. The remaining revenue mainly came from the QTL (technology licensing) business, accounting for about 13%.
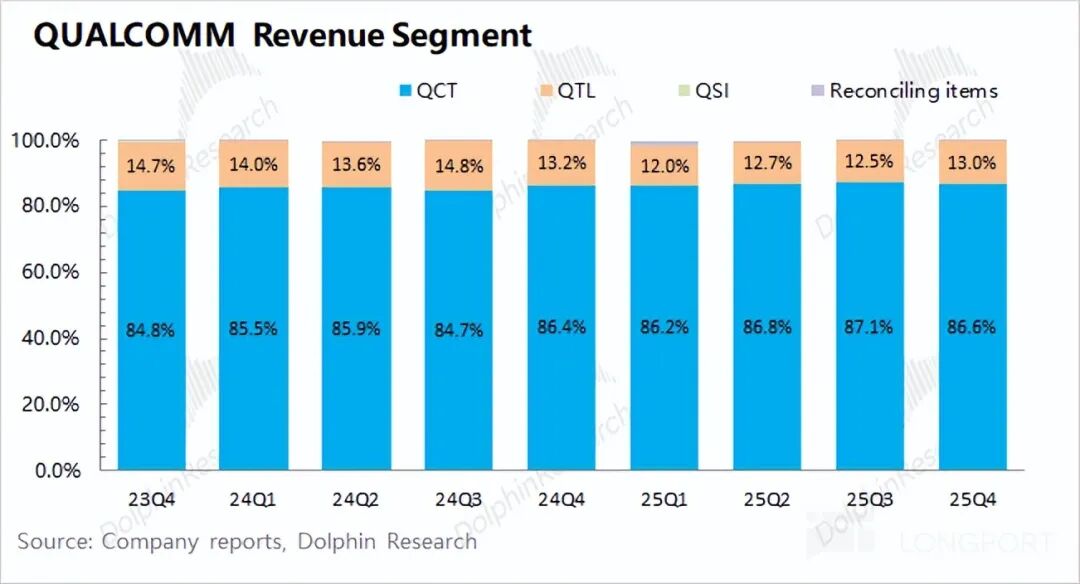
The QCT business is the most important part of the company. Looking at the specific breakdown:
2.1 Smartphone Business
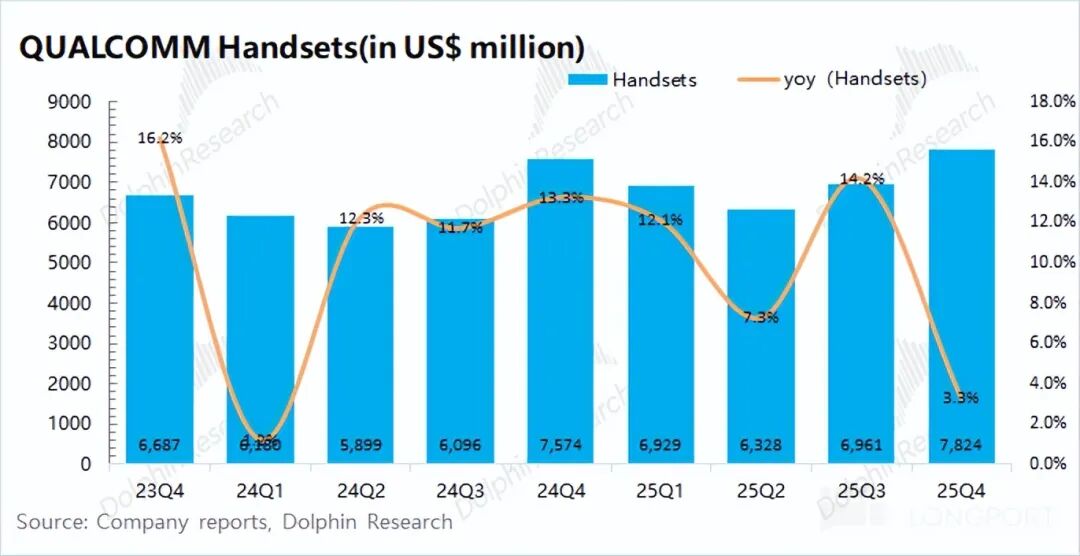
Qualcomm's smartphone business achieved revenue of $7.82 billion in the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (Q4 2025), up 3.3% year-over-year, meeting expectations of $7.75 billion.
For the slowdown in the company's smartphone business growth this quarter, Dolphin Research believes there are two main reasons: ① The company brought forward the release of its flagship product, the Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen5, to the previous quarter. ② The overall industry performance of the smartphone market was sluggish.
Combining industry data, under the influence of Apple's new phone strategy of "more features at the same price," smartphone shipments (excluding Apple) in the fourth quarter of 2025 were 255 million units, basically flat year-over-year, indicating a rather sluggish Android market.
Compared to this quarter's performance, the company has provided a revenue guidance of USD 6 billion for its mobile business next quarter, indicating a double-digit decline.
In response, the company cited "memory shortages" as the reason. Previously, the market expected that rising memory prices would increase costs and
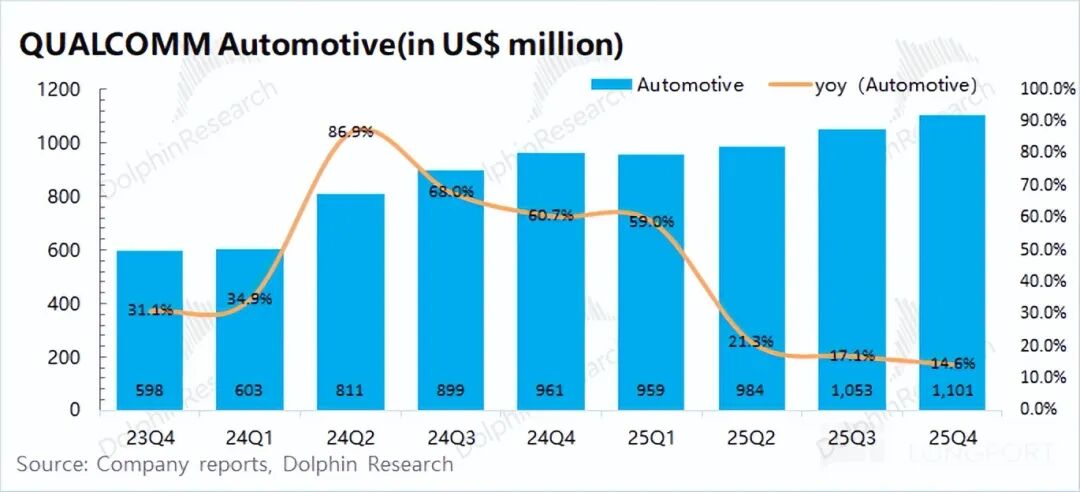
In the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (equivalent to the fourth quarter of 2025), Qualcomm's automotive business generated revenue of USD 1.1 billion, marking a 14.6% year-on-year increase and aligning with market expectations of USD 1.08 billion. This growth was primarily propelled by a surge in shipments of the Snapdragon Digital Chassis.
Qualcomm has forged long-term partnerships with the Volkswagen Group, while leading automakers such as Toyota and Hyundai are set to adopt its solutions. Looking ahead, the company anticipates that its automotive business will experience a year-on-year growth exceeding 35% in the next quarter, although it will still constitute only approximately 10% of the company's total revenue.
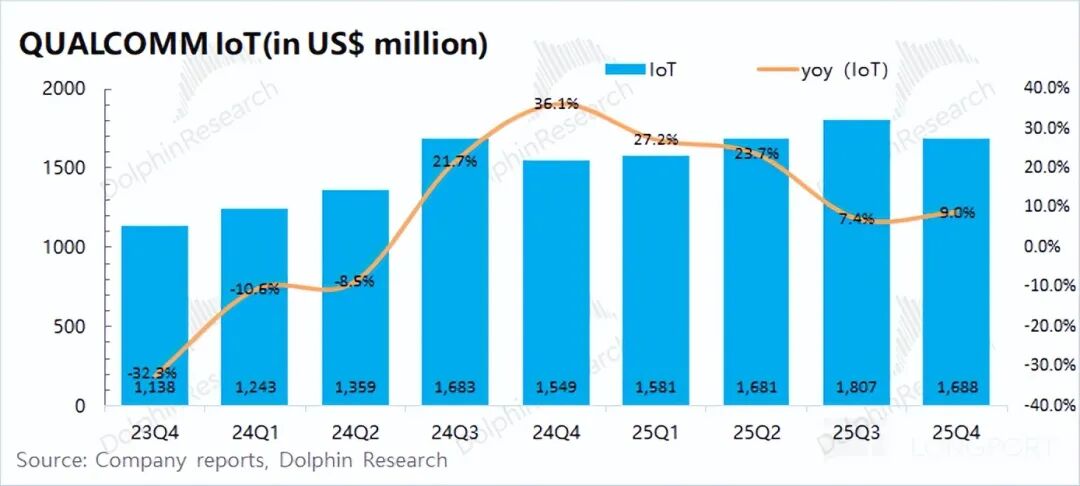
2.3 IoT Business
In the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (i.e., the fourth quarter of 2025), Qualcomm's IoT business raked in revenue of USD 1.69 billion, reflecting a 9% year-on-year increase and meeting market expectations of USD 1.7 billion. Following a period of double-digit growth, the IoT business's growth rate has now decelerated to single digits.
Qualcomm's IoT business mainly encompasses consumer electronics, edge networking, and industrial products. During this quarter, the growth of the IoT business was spurred by increases in consumer, networking, and industrial products.
In addition to its conventional products, the market is also keeping a close eye on the company's AI PC and data center businesses:
① AI PC Business: Currently classified under the IoT business segment, mainly due to its relatively modest scale. The company rolled out the Snapdragon X2 product in the latter half of last year, elevating AI computing power to 80 TOPS (a significant increase from 45 TOPS in the previous generation).
The company harbors hopes that AI PCs will emerge as a new growth engine. However, its current market share in the PC segment remains limited, posing challenges in competing with Intel and AMD.
② Data Center Business: The company previously announced its foray into the data center market. Dolphin Research posits that subsequent related revenues may either be incorporated into the IoT segment or disclosed separately.
Mass production and shipments have yet to commence. The company's announced customer, Humain, plans to deploy 200 megawatts of computing power based on the AI200 chip, potentially unlocking revenue opportunities worth approximately USD 3 billion for the company.
- END -
// Reprint Authorization
This article is an original work by Dolphin Research. Any reproduction requires prior authorization.
// Disclaimer and General Disclosure
This report is crafted for general comprehensive data purposes, intended for broad reading and data reference by users of Dolphin Research and its affiliated institutions. It does not take into account the specific investment objectives, product preferences, risk tolerance, financial situation, or unique needs of any individual recipient. Investors are strongly advised to consult with independent professional advisors before making investment decisions based on this report. Any individual making investment decisions using or referring to the content or information in this report assumes full responsibility for all associated risks. Dolphin Research shall not be held liable for any direct or indirect responsibilities or losses arising from the utilization of the data contained in this report. The information and data in this report are sourced from publicly available materials and are provided solely for reference. Dolphin Research endeavors to ensure, but does not guarantee, the reliability, accuracy, or completeness of the information and data.
The information or opinions presented in this report shall not, under any jurisdiction, be construed or deemed as an offer to sell securities or an invitation to buy or sell securities. They shall also not constitute recommendations, solicitations, or advice regarding securities or related financial instruments. The information, tools, and materials in this report are not intended for distribution to or use by individuals or residents of jurisdictions where such distribution, publication, provision, or use would violate applicable laws or regulations or subject Dolphin Research and/or its affiliates or associated companies to registration or licensing requirements in such jurisdictions.
This report reflects only the personal views, insights, and analytical methods of the relevant contributors and does not represent the official stance of Dolphin Research and/or its affiliated institutions.
This report is produced by Dolphin Research, and all copyrights are retained by Dolphin Research. No institution or individual may, without the prior written consent of Dolphin Research, (i) produce, copy, reproduce, duplicate, forward, or create any form of copies or reproductions in any manner, and/or (ii) directly or indirectly redistribute or transfer them to other unauthorized persons. Dolphin Research reserves all related rights.