Beijing Jiaotong University & ByteDance's Latest Open-Source ThinkGen: First to Explicitly Utilize Multimodal CoT for Generative Tasks, Achieving SOTA Performance in Multiple Tasks
![]() 12/31 2025
12/31 2025
![]() 411
411
Interpretation: The Future of AI Generation
Key Highlights
First Thinking-Driven Visual Generation Framework: ThinkGen is the first thinking-driven visual generation framework that explicitly utilizes the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning capabilities of MLLMs to handle various generative scenarios. This addresses the limitations of existing methods in terms of generalization and adaptability, as they typically design CoT mechanisms for specific scenarios.
Decoupled Architecture: ThinkGen adopts a decoupled architecture, separating a pre-trained MLLM from a Diffusion Transformer (DiT). The MLLM is responsible for generating customized instructions based on user intent, while the DiT generates high-quality images based on these instructions. This design overcomes the lack of advanced reasoning capabilities in existing frameworks.
Visual Generation Instruction Refinement (VGI-refine) Module: To address the issue of redundant information during CoT reasoning, the VGI-refine module is introduced. This module extracts concise instructional information from the MLLM's reasoning chain and concatenates it with learnable Prepadding States, enabling adaptive adjustment of the MLLM's representation distribution to better align with the DiT's requirements.
Separable GRPO-based Training Paradigm (SepGRPO): A separable reinforcement learning training paradigm called SepGRPO is proposed, alternating reinforcement learning between the MLLM and DiT modules. This flexible design supports joint training on different datasets, facilitating effective CoT reasoning across a wide range of generative scenarios.
Achieving SOTA Performance in Multiple Generative Scenarios: Extensive experiments demonstrate that ThinkGen achieves robust, state-of-the-art performance across multiple generative benchmarks, particularly excelling in reasoning-intensive tasks.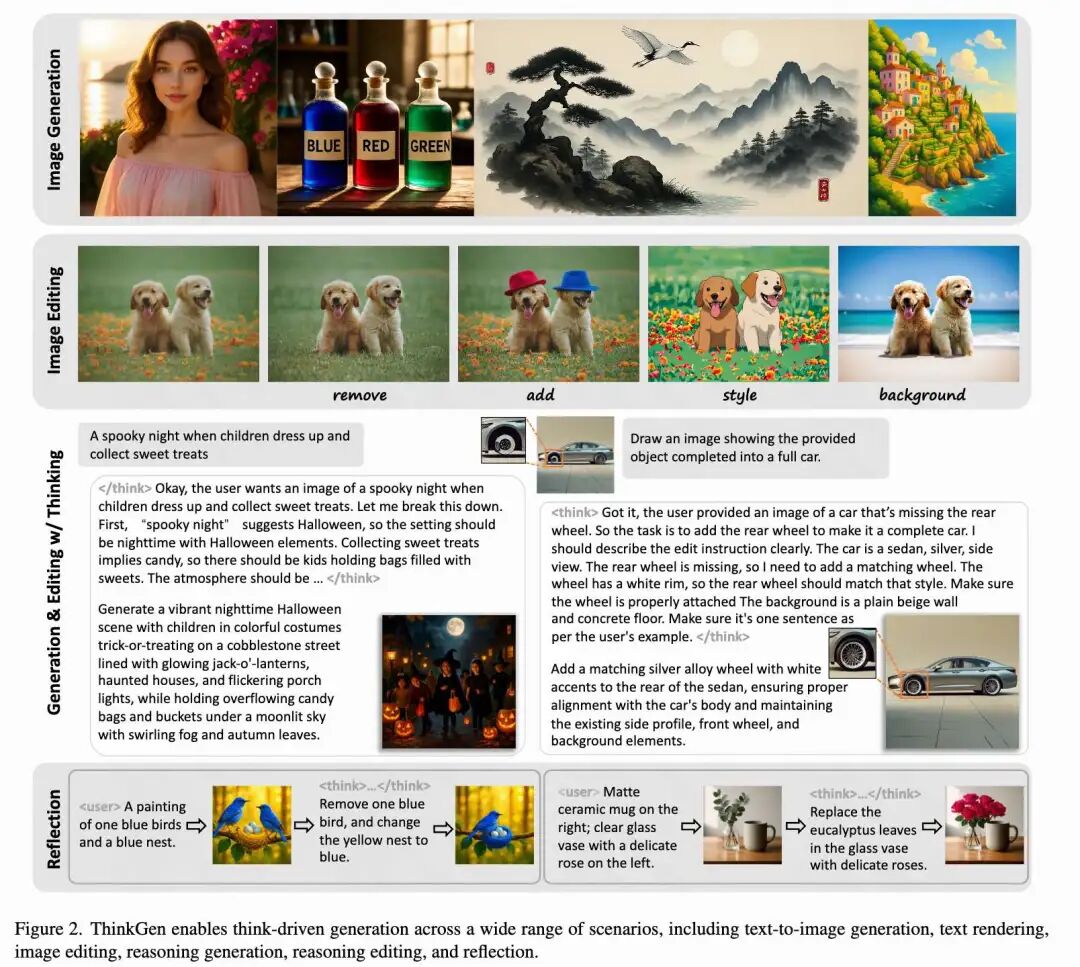
Summary Overview
Problems Addressed
Existing multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated the effectiveness of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning in understanding tasks. However, their extension to generative tasks remains in its infancy.
The CoT mechanisms for generative tasks are often customized for specific scenarios, limiting their generalization and adaptability. This results in performance degradation in broader tasks and typically requires manual intervention to activate CoT reasoning for different generative tasks.
Current frameworks generally lack advanced reasoning capabilities.
Proposed Solution
This paper introduces ThinkGen, a universal and thinking-driven visual generation framework designed to explicitly leverage the CoT reasoning capabilities of MLLMs to solve complex tasks across various generative scenarios.
By decoupling the architectures of MLLM and Diffusion Transformer (DiT), it enables the formulation of high-quality plans before generation.
Applied Technologies
Decoupled Architecture: The framework includes a pre-trained MLLM (for generating customized instructions) and a Diffusion Transformer (DiT) (for generating high-quality images).
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Reasoning: Explicitly leverages the CoT reasoning capabilities of MLLMs to systematically solve complex tasks by generating explicit intermediate steps.
Visual Generation Instruction Refinement (VGI-refine): Introduces the VGI-refine module to filter out redundant information from the MLLM's autoregressive CoT outputs and align them with learnable Prepadding States.
Separable GRPO-based Training Paradigm (SepGRPO): A training strategy that alternates reinforcement learning between the MLLM and DiT modules, aiming to encourage the MLLM to generate instructions aligned with the DiT's preferences and enable the DiT to generate high-quality images based on these instructions.
Achieved Effects
Achieves robust, state-of-the-art performance across multiple generative benchmarks. ThinkGen demonstrates exceptional performance in a wide range of generative scenarios when employing CoT reasoning (as shown in Figure 1 below). Enables effective CoT reasoning across diverse generative scenarios, thereby enhancing generalization capabilities.
Architectural Approach
ThinkGen adopts a decoupled architecture, consisting of a pre-trained MLLM and a Diffusion Transformer (DiT). The MLLM is responsible for generating customized instructions based on user intent, while the DiT generates high-quality images based on these instructions. This decoupled design ensures optimal performance of each component while maintaining system scalability and modularity, as shown in Figure 3 below.
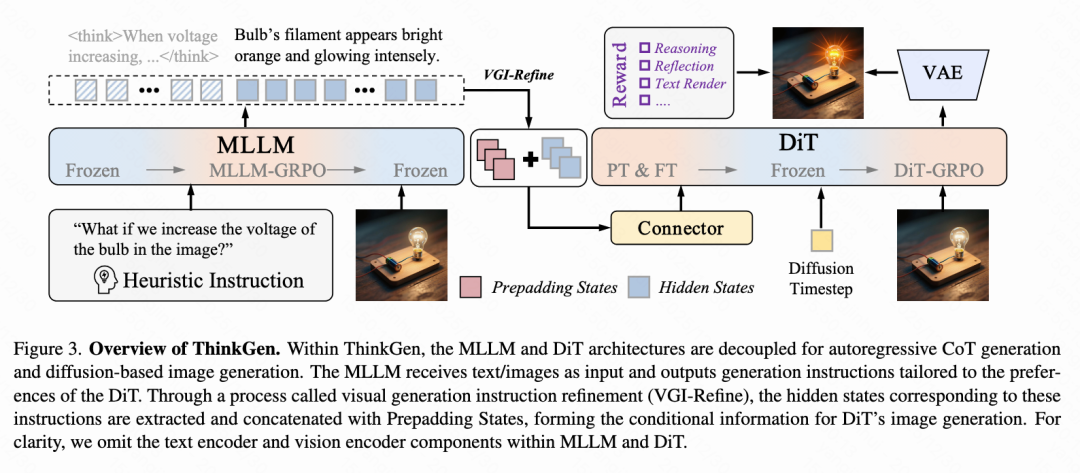
Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)
ThinkGen utilizes MLLMs to process visual and textual inputs and perform CoT reasoning through autoregressive generation. The MLLM is initialized using Qwen3-VL-8B-Think. For image generation tasks, a specialized system prompt ([SYS]) is designed to prompt the MLLM to understand user intent and provide appropriate rewriting instructions. Subsequently, the last two layers of hidden states generated after the
Diffusion Transformer (DiT)
ThinkGen employs a standard DiT architecture, initialized using OmniGen2-DiT-4B. The MLLM's output serves as conditional text input for the DiT. In image editing tasks, additional reference images are processed through a VAE and used as conditional visual inputs. Visual and textual inputs are concatenated with noisy latent features to enable cross-modal joint attention. A simple linear layer is employed as a connector to align features from multiple conditional inputs.
VGI-refine
To address the redundant information present in the MLLM's autoregressive Chain-of-Thought (CoT) outputs, the Visual Generation Instruction Refinement (VGI-refine) module is introduced, comprising two steps. First, instruction tokens following the
Training Strategy
The training of ThinkGen is divided into five distinct stages, as shown in Figure 4 below. Initially, supervised pre-training of the DiT is conducted (Stages 1-3) to ensure high-quality image generation. Subsequently, a separable MLLM and DiT reinforcement learning method called SepGRPO is introduced (Stages 4-5). Through SepGRPO training, the MLLM learns to generate descriptions or editing instructions that best align with the DiT's preferences, while the DiT further optimizes to generate higher-quality images based on these instructions.
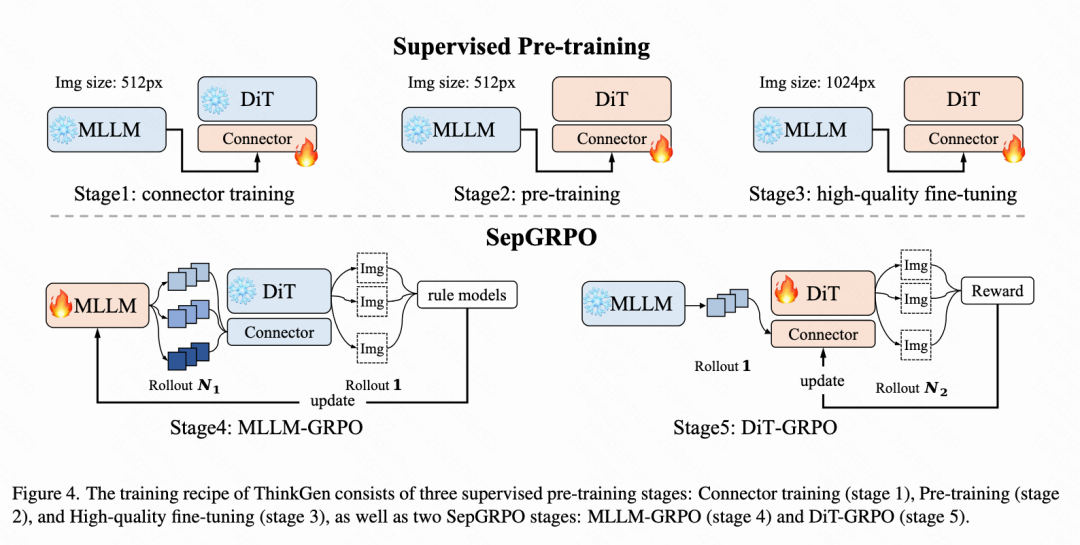
Supervised Pre-training
The supervised pre-training phase (Stages 1-3) aims to align the DiT with the MLLM while improving image generation quality. The Rectified Flow training paradigm is adopted, directly regressing the velocity field by minimizing the Flow Matching objective.

where denotes the target velocity field.
Input Format: During the pre-training phase, to avoid the costly process of rewriting each caption or editing instruction, pseudo-CoT templates are constructed to simulate the MLLM's CoT process. Specifically, the content within is left blank, and the original caption or editing instruction is simply repeated as the answer.
Stage 1 Alignment: In this stage, K learnable pre-filling states are introduced, and the DiT is aligned with the MLLM by training only the linear connector while keeping the MLLM and DiT frozen.
Stage 2 Pre-training: In this stage, all DiT parameters are trainable. The training corpus comprises 60M image samples, including text-to-image, image editing, text rendering, and contextual generation data.
Stage 3 High-Quality Fine-Tuning: During the supervised fine-tuning stage, a 0.7M high-quality subset is constructed to enhance the DiT's instruction-following capabilities and image aesthetics.
SepGRPO
SepGRPO, a reinforcement learning training strategy, aims to encourage the MLLM to generate captions/editing instructions that best align with the DiT's preferences while enabling the DiT to generate higher-quality images based on these instructions. SepGRPO decouples the unfolding processes of text and vision: first, the DiT is fixed, and GRPO is applied to the MLLM through joint multi-task training; then, the MLLM is fixed, and GRPO is applied to the DiT.
Input Format: During policy training, a specialized [SYS] is designed to facilitate cold starts, allowing the MLLM to explore text conditions preferred by the DiT. Specifically, the [SYS], input sample [C], and special
Stage 4 MLLM-GRPO: In this stage, GRPO is applied to the MLLM to encourage the generation of rewritten text aligned with the DiT's preferences. The MLLM is optimized across multiple scenarios to enhance the generalization capabilities of CoT reasoning. Five representative generative scenarios are selected: semantic composition, reasoning generation, text rendering, image editing, and reflection. As shown in Table 1 below, for each scenario, dedicated datasets are collected and curated, and corresponding rule-based models are designed to guide optimization.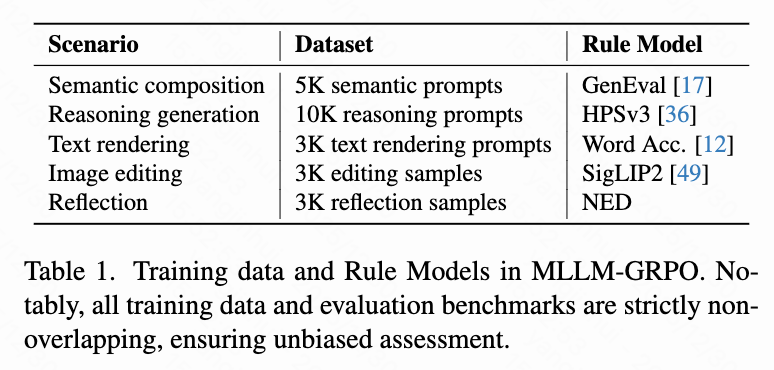
For each input to the MLLM, rollouts are executed from the policy to generate trajectories , and the DiT uses these trajectories to generate corresponding images. The rule-based model is used to compute the reward for each trajectory. Subsequently, the advantage for the -th trajectory is computed in a group-relative manner:
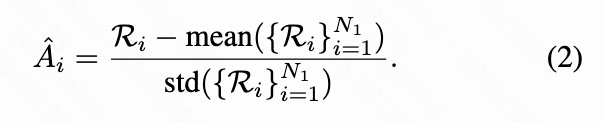
The policy is then updated by optimizing the GRPO objective, which is a clipped surrogate function regularized with KL divergence:
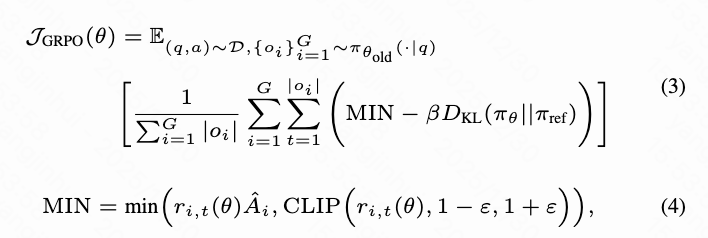
where denotes the probability ratio of the current token output by and . During this process, the DiT and rule-based model jointly serve as the reward model.
Stage 5 DiT-GRPO: In this stage, FlowGRPO is applied to enhance the DiT's instruction-following capabilities. Data from the Simple Scene and Text Rendering scenarios, along with their corresponding reward calculation methods, are utilized. Summary of Experimental Results
ThinkGen has been evaluated across various generative scenarios and compared with existing methods. The results demonstrate significant performance improvements in reasoning generation, reasoning editing, text-to-image generation, and image editing.
Reasoning Generation
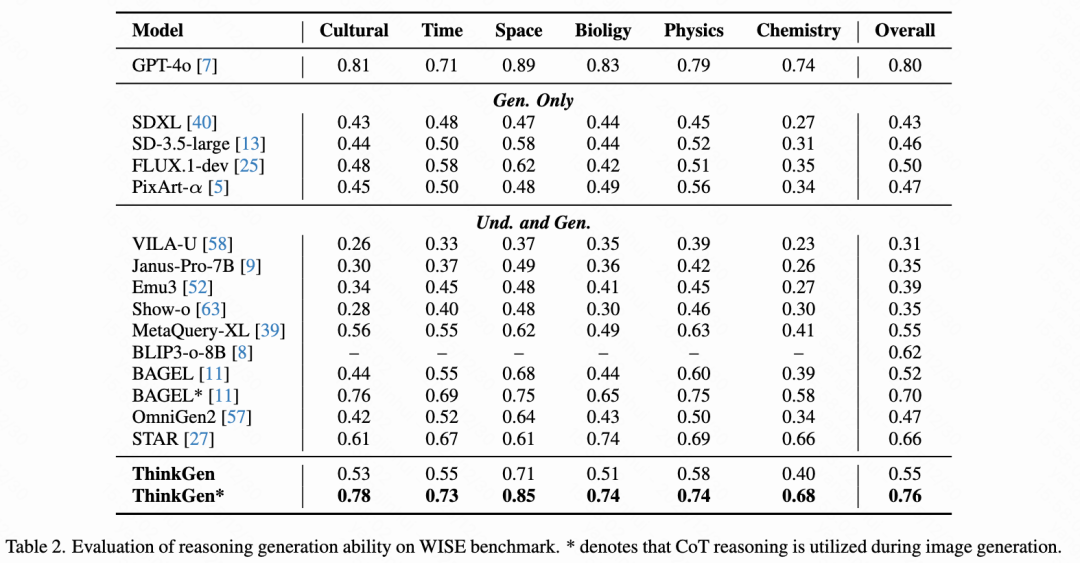
As shown in Table 2 below, on the WISEBench benchmark, ThinkGen exhibits a significant advantage over direct generation methods. By leveraging CoT reasoning, ThinkGen achieves a substantial improvement of +21% (0.55 → 0.76) and establishes a new state-of-the-art performance on WISEBench.
Reasoning Editor
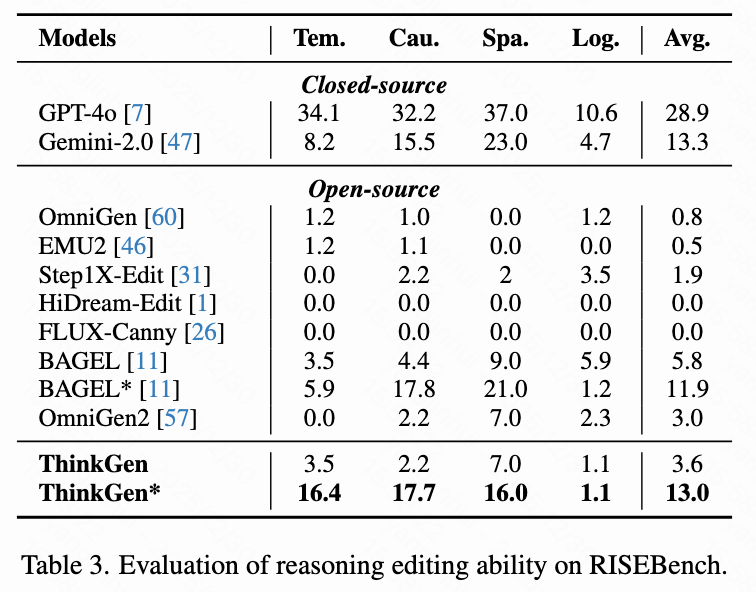
As shown in Table 3 below, on RISEBench, ThinkGen's CoT reasoning ability significantly surpasses that of open-source models (3.6 → 13.0) and achieves results comparable to those of the closed-source model Gemini-2.0.
Text-to-Image Generation
As shown in Table 4 below, ThinkGen consistently demonstrates improvements across all scenarios through CoT reasoning in the GenEval, DPG-Bench, and CVTG benchmarks, achieving the best results among many well-known models. These results indicate that ThinkGen possesses strong instruction-following and text-rendering capabilities.
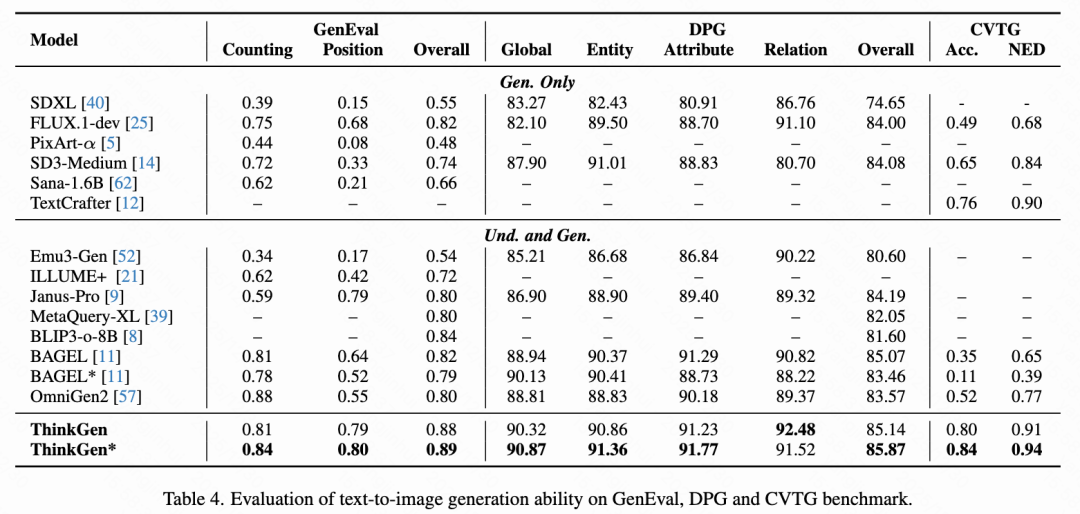
Image Editing
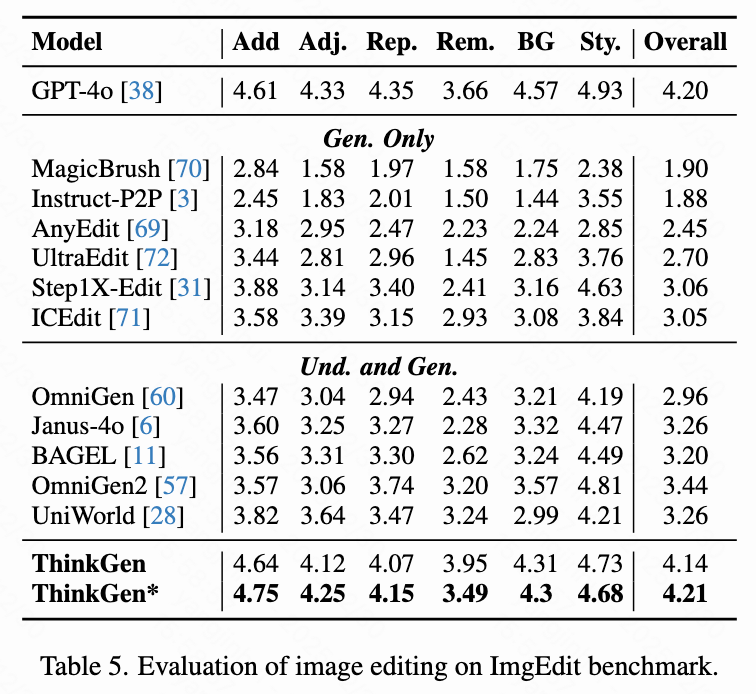
As shown in Table 5 below, on ImgEdit, ThinkGen displays significantly superior metrics compared to a range of open-source models, achieving performance comparable to that of GPT-4o.
Ablation Study
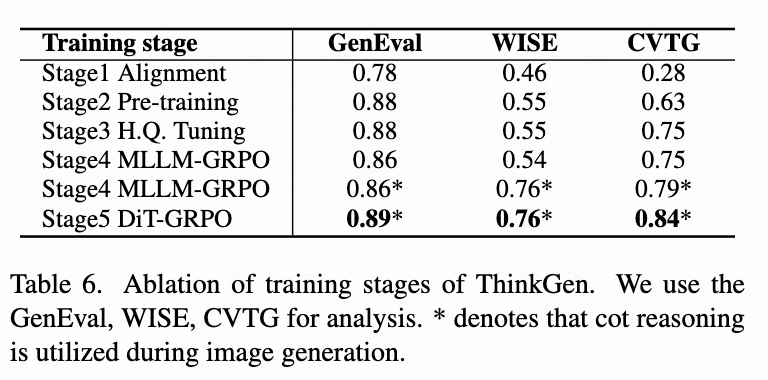
Training Stage Ablation: As shown in Table 6 below, the gradual application of each training stage contributes to the performance of ThinkGen.
Training only the connector (Stage 1) results in poor text-rendering performance (CVTG: 0.28), indicating a lack of sufficient fine-grained alignment between MLLM and DiT. Large-scale pre-training (Stage 2) significantly improves image quality, with GenEval increasing by 10%, WISE by 9%, and CVTG by 35%. High-quality fine-tuning (Stage 3) further enhances image details, with CVTG improving by +12.0%. Applying GRPO to MLLM (Stage 4) slightly affects image generation on GenEval (-0.01) and WISE (-0.01), but combining it with CoT significantly boosts reasoning and generation capabilities (WISE: 0.55 → 0.76). DiT-GRPO (Stage 5) further improves image generation quality, especially in fine-grained text-rendering tasks (CVTG: 0.79 → 0.84).
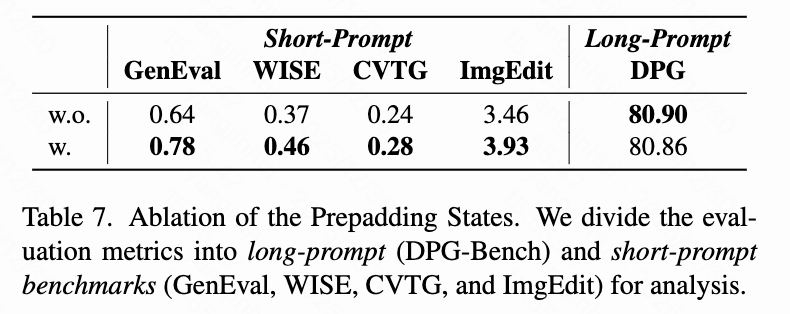
Prepadding States: As shown in Table 7 below, pre-padding states significantly improve performance in short-prompt benchmarks (GenEval: 0.64→0.78, WISEBench: 0.37→0.46, CVTG: 0.24→0.28, ImgEdit: 3.46→3.93).
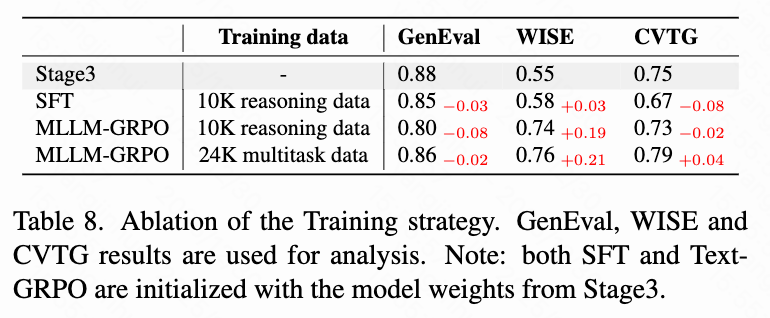
Training Strategy: As shown in Table 8 below, directly applying SFT to DiT with reasoning data does not improve performance in reasoning benchmarks. However, training MLLM using MLLM-GRPO greatly enhances ThinkGen's reasoning ability (WISE: 0.55 → 0.74).
Extraction Strategy in VGI-refine: As shown in Table 13 below, using only the hidden states after the <

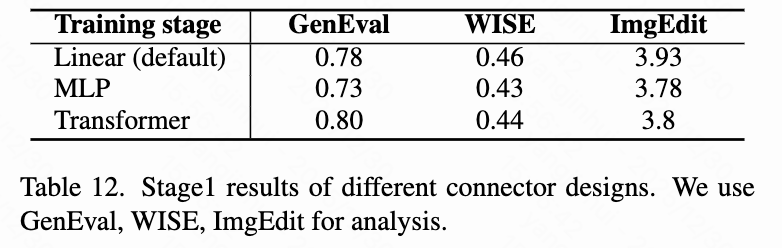
Connector Design: As shown in Table 12 below, the linear layer connector outperforms MLP or Transformer connectors.
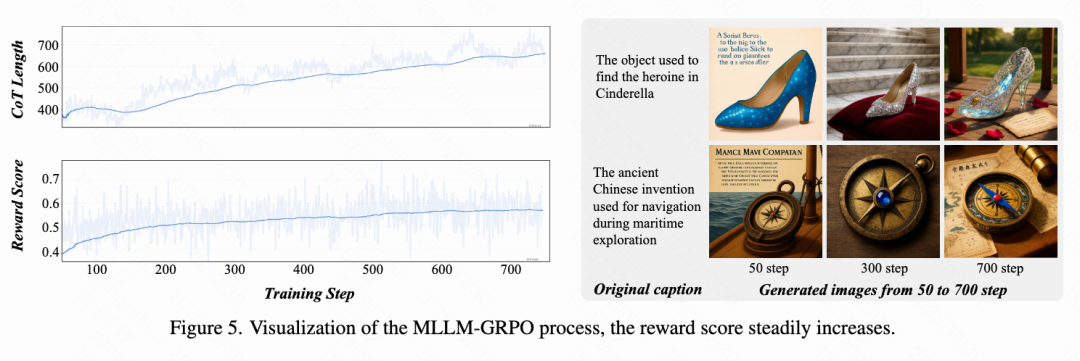
SepGRPO Process Analysis
As shown in Figure 5, by visualizing the intermediate process of SepGRPO, the following key phenomena are observed:
Increased CoT Length: The average CoT length gradually increases, indicating that the model develops more complex reasoning abilities during training.
Unified Reward Growth: As training progresses, multi-task rewards steadily increase, indicating that ThinkGen learns to adaptively think in different scenarios.
Image Quality Improvement: Image visualizations at 50, 300, and 700 steps show a clear trend of improvement in image generation quality, with generated images exhibiting richer details and higher fidelity.
Conclusion
ThinkGen, a novel thinking-driven framework, is capable of automatically applying Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning to diverse generation tasks. Our method adopts a decoupled MLLM-DiT architecture and is trained through SepGRPO, enabling it to formulate high-quality plans before generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ThinkGen achieves significant improvements in reasoning-intensive tasks. This work represents a crucial step toward building smarter, more versatile generative models that seamlessly integrate reasoning and creation.
References
[1] ThinkGen: Generalized Thinking for Visual Generation